论文总字数:52100字
摘 要
随着桥梁跨度的增加,悬索桥凭借其强大的跨越能力和优越的经济性成为极具竞争力的桥型选择方案;与此同时,桥梁结构表现出轻质、柔性、低阻尼等特点,对风荷载尤为敏感,易于产生各类风致振动现象,从而对桥梁运营期内的安全、可靠以及耐久性能造成影响,引起了国内外各界的广泛关注。模态参数是进行结构动力特性分析的重要指标,可以为结构损伤识别以及有限元模型修正提供依据,对维持桥梁结构的安全运营和保障国家人民财产安全具有重要的现实意义。
本文利用润扬悬索桥结构健康监测系统(SHMS)在“韦帕”台风期间采集的振动响应数据,对主梁模态参数进行识别,主要从以下几个方面开展了研究工作:
- 系统介绍了峰值法(PP)和Hilbert-Huang变换(HHT)的理论基础以及应用于土木工程结构模态参数识别的具体过程。
- 以“韦帕”台风期间润扬悬索桥SHMS采集的主梁振动响应为研究对象,基于Matlab软件,采用平均正则化功率谱(ANPSD)对主梁全长7个截面振动响应信息进行整合处理,在ANPSD功率谱分析的基础上,采用峰值拾取法进行主梁自振频率识别,并采用基于线性插值的半功率带宽法进行阻尼比的识别。将峰值法模态参数识别结果与有限元分析结果进行对比,验证峰值法的有效性。
- 开展了基于HHT的台风期间润扬悬索桥模态参数识别。在经验模态分解(EMD)以及Hilbert变换(HT)的基础上引入Butterworth滤波器与随机减量技术(RDT)对主梁跨中截面进行模态参数估计,得到各阶模态的瞬时频率,并采用最小二乘法对幅值、相位曲线进行线性拟合,识别得到主梁的自振频率和阻尼比,本文分析结果可以为大跨度桥梁的动力特性分析以及损伤评估提供参考。
- 对比分析了峰值法和HHT法的模态参数识别结果,两种方法在特征频率识别方面得到了几乎一致的结果,但阻尼比的识别结果仍然存在差异。对于具有分离模态、低阻尼的结构,峰值法和HHT法识别结果均有效,而对于具有密集模态的结构,因为频率分量之间的重叠,特别是受到高水平噪声的影响时,受限于傅里叶变换的频率分辨率,峰值法可能不能有效地识别出结构的模态参数。
关键词:结构健康监测系统(SHMS);峰值法;HHT;模态参数;台风
Abstract
With the increase of span length of bridges, the suspension bridge has become a highly competitive option owing to its large spanning ability and great economy. However, the increase of bridge span leads to characters like light weight, flexibility, low damping ratio and so on. Particularly, suspension bridge is susceptible to wind load, and can produce kinds of wind-induced vibrations. As a result, problems concerning safety, reliability and durability have received more attention. Modal parameters are important indexes that indicate dynamic characters of structures. The accurate identification of modal parameters is key to the modification of finite element model and damage detection. And it is of much importance to structural analysis and engineering projects.
With the response date of vibration recorded by SHMS of Runyang Suspesnion Bridge (RSB) during Typhoon Wipha, this paper conducted the modal parameter identification of the girder of RSB. The research contents mainly include the following several aspects:
- The theoretical basis of Peak Picking (PP) method and Hilbert-Huang Transform (HHT) method as well as the detailed processes of modal parameter identification using the two methods were introduced systematically.
- Taking the vibration response of the girder recorded by SHMS during Typhoon Wipha as the analysis object, this paper utilized the Averaged Normalized Power Spectral Density (ANPSD) to integrate the vibration data of seven sections along the whole girder. Based on the analysis result of ANPSD, modal frequencies of the girder were identified using PP method. Corresponding modal damping ratios were also identified with half-power bandwidth method with the modification of linear interpolation. By comparing the result of PP method with that of finite element analysis, the validity of modal identification with PP method was confirmed.
- Taking Typhoon Wipha as an example, the modal identification of RSB based on HHT was conducted. On the basis of Empirical Mode Decomposition (EMD) and Hilbert Transform (HT), Butterworth filter and Random Decrement Technique (RDT) were introduced to conduct the modal identification of mid-span section of the girder. And instant frequencies corresponding to kinds of modes were obtained. Least Square method was utilized for the linear fitting of amplitude curves and phase curves. And modal frequencies as well as modal damping ratios of the girder were identified. The analysis result of this paper can serve as reference for the dynamic character analysis as well as damage detection of large-span bridge structures.
- A comparative analysis of results of PP and HHT was conducted. Results showed that the two methods reached an agreement on the identification of natural frenquencies but there was still difference among the identification of damping ratios. it was also demonstrated that for the system with well-separated modes and low damping ratio, both PP and HHT were capable of identifying the modal parameters with higher frequency. But for the very closely spaced modes, the HHT method seemed to be more effective than PP method.
Key words: Structural Health Monitoring System (SHMS); Peak Picking (PP) method; Hilbert-Huang Transform (HHT) method; Modal parameters; Typhoon
目录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 引言 1
1.2 桥梁健康监测概述 2
1.2.1 桥梁健康监测概念的提出 2
1.2.2 桥梁SHMS的组成 3
1.2.3 桥梁SHMS监测的内容 4
1.2.4 桥梁SHMS应用情况 4
1.3 模态参数识别方法 5
1.3.1 人工激励法 6
1.3.2 环境激励法 7
1.4 环境激励模态参数识别方法 8
1.4.1 频域识别法 8
1.4.1.1 峰值法 8
1.4.1.2 频域分解法 8
1.4.2 时域识别法 9
1.4.2.1 随机子空间法 9
1.4.2.2 自然激励法 10
1.4.3 时频域识别法 11
1.4.3.1 HHT法 11
1.4.3.2 小波变换法 11
1.5 本文主要研究内容 12
第二章 基于峰值法和HHT的模态参数识别基本原理 14
2.1 引言 14
2.2 峰值法 14
2.2.1 理论基础 14
2.2.1.1 拉普拉斯变换和傅里叶变换 14
2.2.1.2 传递函数与频响函数 15
2.2.2 模态参数识别 16
2.3 HHT 19
2.3.1 理论基础 20
2.3.1.1 瞬时频率 20
2.3.1.2 固有模态函数 21
2.3.2 模态参数识别 21
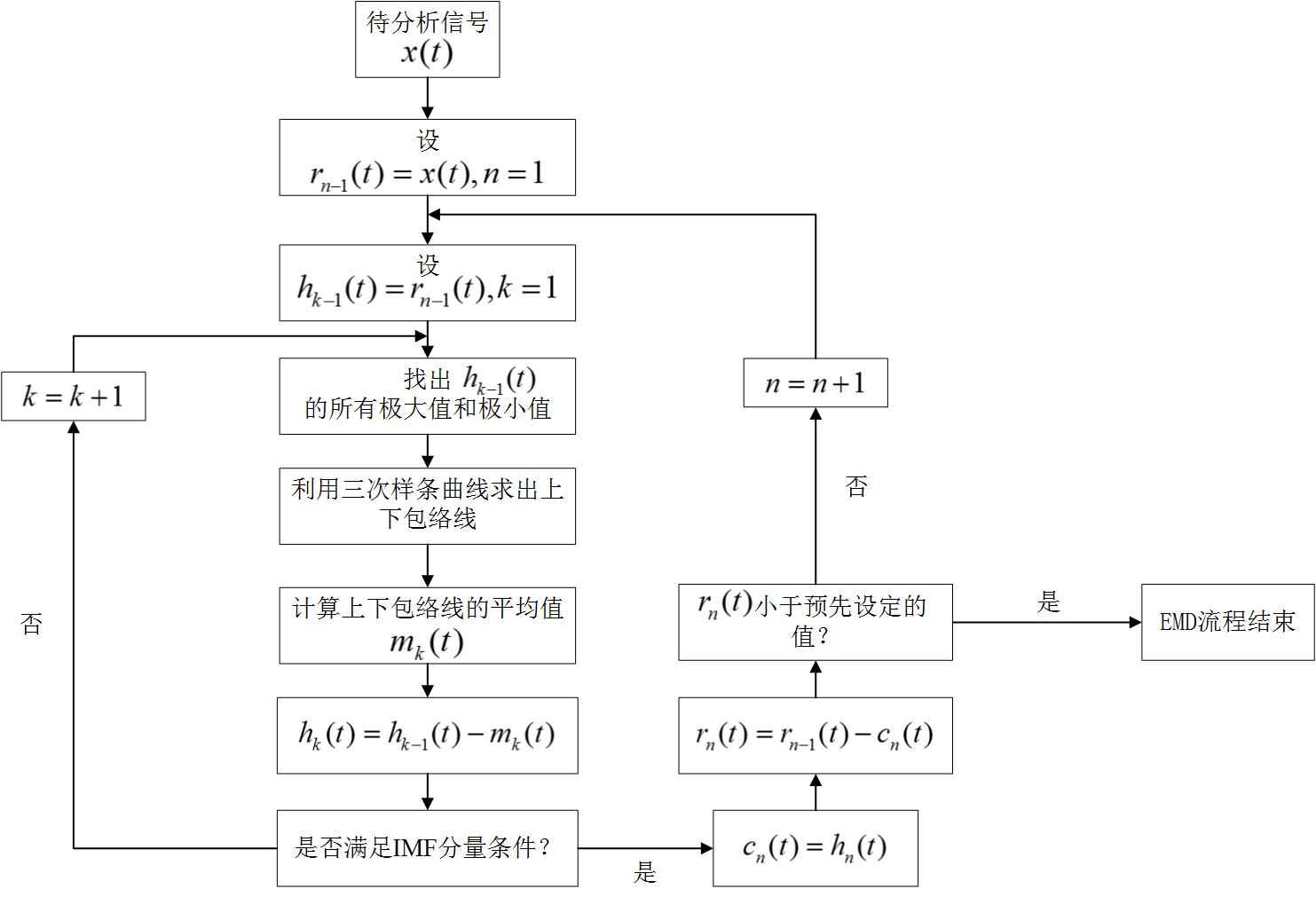
2.3.2.1 经验模态分解 21
2.3.2.2 随机减量技术 23
2.3.2.3 基于HHT的模态参数识别及Hilbert谱分析 24
2.3.3 HHT存在的问题 26
2.3.3.1 包络问题 26
2.3.3.2 收敛问题 26
2.3.3.3 停止准则 27
2.3.3.4 模态混叠 27
2.3.3.5 边端问题 27
2.4 峰值法和HHT的比较 28
2.5 本章小结 28
第三章 基于峰值法的台风期间润扬悬索桥主梁模态参数识别 30
3.1 引言 30
3.2 润扬悬索桥SHMS 30
3.2.1 润扬悬索桥慨况 30
3.2.2 润扬悬索桥SHMS组成 31
3.3 “韦帕”台风数据资料 32
3.4 振动信号功率谱估计方法比较 33
3.4.1 功率谱估计方法 33
3.4.1.1 相关函数法 34
3.4.1.2 周期图法 34
3.4.1.3 Welch法 34
3.4.2 功率谱估计结果 34
3.4.3 功率谱估计方法对比分析 37
3.5 主梁振动信号功率谱估计 37
3.6 主梁振动信号平均正则化功率谱 40
3.7 主梁振动信号相干系数及相位曲线 41
3.8 主梁模态参数识别结果 45
3.9 本章小结 47
第四章 基于HHT的台风期间润扬悬索桥主梁模态参数识别 48
4.1 引言 48
4.2 润扬悬索桥主梁竖向模态参数识别 49
4.2.1 EMD及各阶IMF功率谱分析 49
4.2.2 随机减量计算 51
4.2.3 模态参数识别 52
4.3 润扬悬索桥主梁横向及扭转模态参数识别 55
4.3.1 主梁横向模态参数识别 55
4.3.2 主梁扭转模态参数识别 58
4.4 润扬悬索桥主梁模态参数识别结果分析 61
4.5 基于峰值法和HHT法模态参数识别结果比较 61
4.6 本章小结 63
第五章 结论与展望 65
5.1 主要研究工作与结论 65
5.2 展望 67
参考文献 68
致 谢 72
第一章 绪论
引言
进入21世纪以后,我国交通设施建设快速发展,桥梁建设也迎来了一个新的高峰。不仅跨越长江、黄河的大跨度桥梁工程如雨后春笋般出现,一些特大跨度的跨海湾、海峡大桥也开始修建并投入使用。随着桥梁跨度的增加,悬索桥和斜拉桥成为极具竞争力的选择方案,目前国内已经建成的千米级桥梁,悬索桥的代表有舟山西堠门大桥(主跨1650m,2009年)、润扬长江公路大桥南汊桥(主跨1490m,2005年)、江阴长江公路大桥(主跨1385m,1999年)、香港青马大桥(主跨1377m,1997年);斜拉桥的代表有苏通大桥(主跨1088m,2008年)、昂船洲大桥(主跨1018m,2008年)。
但是,随着桥梁跨径的增加,其建造复杂性增加,再加上大跨径桥梁通常位于情况复杂的江河或海峡环境,长期受到复杂风环境的影响,一些桥梁甚至直接受到台风的正面袭击。在桥梁的长期使用过程中,复杂的荷载作用、疲劳损伤累积、环境腐蚀等综合作用,对桥梁的正常运营形成了不容忽视的安全隐患。如果安全隐患没有被及时发现并得到妥善处理,轻则导致桥梁正常使用寿命减少,重则导致桥梁突然破坏甚至倒塌等灾难性事故,造成巨大的经济损失和人员伤亡。例如,1940年美国Tacoma悬索桥发生颤振风毁;2007年,位于美国明尼苏达州的I-35W密西西比河大桥因为疲劳损伤在交通高峰期间坍塌,造成重大人员伤亡[1]。
悬索桥因其强大的跨越能力备受设计和工程技术人员青睐。但是,随着悬索桥跨度的增大,其柔性增加,对车辆动荷载、风荷载等非常敏感,容易产生结构振动,而结构振动对悬索桥的正常运营、寿命等都有非常大的影响,因此我们有必要对这些桥梁进行动力特性研究,全面掌握他们的运营条件、安全性、耐久性,及时进行养护维修。而结构的振动模态参数是表征其动力特性的重要指标,模态参数的准确、迅速识别不仅是结构动力特性分析的关键环节,也可以为结构的损伤检测奠定基础[2]。现有的模态参数识别方法一般包括人工激励法与环境激励法两种。人工激励法通过对结构施加人为激励来获得结构响应,结合外界激励与结构响应进行识别;环境激励法主要利用天然激励或者非刻意人类行为激励,例如,风荷载对桥梁的激励、行驶中的车辆对桥梁的激励等,仅利用结构响应即可进行模态参数识别。相对于人工激励方法而言,环境激励法是一种天然的激励方式,具有不影响结构的正常使用、节省测试时间、无需施加人工激励、不损伤结构等优点[3],特别对于大跨度桥梁,环境激励法的优势更加明显。但需要注意的是,对于目前大跨结构的模态识别也存在尚未完全解决的问题,例如,在受环境因素影响较大的运行模态试验中,模态参数识别的定阶、虚假模态的剔除和密集模态的识别等[4]。
桥梁健康监测系统(SHMS)可以实时地对桥梁在外界荷载作用下的静动力响应信息进行测试记录,记录内容包括结构的应变、位移、加速度、吊杆/斜拉索拉力、主缆拉力等参数[5]。SHMS记录的数据为基于环境激励的模态参数识别提供了基础。
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:52100字
相关图片展示:



该课题毕业论文、开题报告、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找;


