论文总字数:27273字
摘 要
为了缓解城市交通拥堵,改善城市居民出行环境,发展公共交通成为了现代交通领域的主题。现代有轨电车作为一种现代化的轨道交通,具有运量较大、成本适中、绿色环保等特点,在运输能力和性价比方面与普通公交相比有很大优势,适合在中型城市建设,也可以与地铁衔接,作为大容量交通的延伸部分。但由于有轨电车一般采取半独立路权,且运行路径固定,不适应传统的信号控制方法,在交叉口处受社会车辆的干扰较为严重,现实当中有轨电车的运行状况并不理想。
本文借鉴公交优先和分段绿波模型的控制方法,结合有轨电车的运行特征、布线特点和站台设置的特点,在保证有轨电车优先通行及其绿波带宽的同时考虑其他车辆的利益,尽量减小对其他车辆的干扰,从而建立了有轨电车优先通行的干线协调控制模型。由于在有轨电车优先通行策略方面需要知道有轨电车到达交叉口的时间,本文建立了基于BP神经网络模型的有轨电车行程时间预测模型,将靠站时间等不确定因素考虑进去,求解得到有轨电车在交叉口间路段上的行程时间。考虑到现实中与有轨电车运行方式、运输能力较为接近的BRT运行状况较好,本文以常州BRT1号线作为仿真分析的底板,并在仿真时将其转换成运量相当的有轨电车。在调查方案设计过程中,本文将调查数据分为交叉口数据和BRT公交数据两类,分别采用不同的方法进行实地调查,完成调查后对数据进行整理,得到相应的表格和图示。多情景仿真分析对比了原始信号配时方案、传统绿波模型和有轨电车优先通行的干线协调控制模型的效果,分别对有轨电车和社会车辆的运行效果进行了评价。综上所述,本次研究建立了有轨电车优先通行的干线协调控制模型,基于实地调查的数据进行仿真分析,使模型的效果得到验证,具有一定的参考价值。
关键词:有轨电车优先通行,分段绿波模型,行程时间预测,BP神经网络预测模型,多情景仿真分析
Scenario Simulation of Trams Priority at Intersections
Abstract
To relieve urban traffic congestion and improve the urban residents travel environment, development of public transport has become the theme of modern transportation. As a member of up to date rail transits, modern tram has characteristics of large capacity, moderate cost and environmental protecting, and is advanced in transportation capability and cost performance compared with ordinary buses, which means it is suitable to be built in medium-sized city or links to subway as the supplement of mass rapid transit. However, the semi-detached road right and fixed routes of the tram makes it unsuitable to the traditional methods of signal control, and gets significant disruption at the intersections. The operation of the tram in reality fails to reach the ideal.
This paper takes transit priority strategy and segmented green wave model for reference, builds up the tram priority and arterial coordination control model, considering characteristics of operating, route and stops of the tram, and ensures the trams priority and the green wave bandwidth as well as the benefits of other vehicles, minimizing disturbance to the other vehicles. As the arrival time at intersections of tram is needed for tram priority strategy, this paper builds up the tram travel time prediction model on the basis of BP neural network model, taking uncertain factors such as dwell time into account to make out the travel time of tram running between the intersections. Considering that the mode of operation and transportation capability of BRT is similar to tram and its operation condition is better, this paper takes BRT1 line in Changzhou as the template of the simulation analysis, and converts it into tram which is of the same capability during the simulation. In the process of survey design, this paper classifies the survey data into two groups, which refer to data of intersections and data of BRT, using different methods to on-the-spot investigation, and manages the data after the survey to get the corresponding form and graphic. Scenario simulation analysis compares the effect of tram priority and arterial coordination control model with the original signal scheme and traditional green wave, evaluating the performance of tram and social vehicles respectively. To sum up, the tram priority and arterial coordination control model is built in this study, and the effect of this model is verified by the simulation based on survey data, which makes it valuable reference.
Key words: trams priority; segmented green wave model; travel time prediction; BP neural net prediction model; scenario simulation analysis
目录
摘要 i
Abstract ii
第一章 绪论 - 1 -
1.1研究背景 - 1 -
1.2国内外研究现状 - 1 -
1.2.1国外研究现状 - 1 -
1.2.2国内研究现状 - 2 -
1.3本研究内容、目的及方法 - 2 -
1.3.1研究内容 - 2 -
1.3.2研究目的及方法 - 2 -
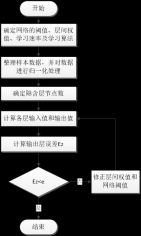
1.4技术路线 - 3 -
第二章 有轨电车相关技术及干线信号协调控制方法 - 4 -
2.1有轨电车相关技术、特点 - 4 -
2.2有轨电车线路布设形式对交通流的影响及优先通行原理 - 5 -
2.2.1有轨电车布线形式对交通流的影响 - 5 -
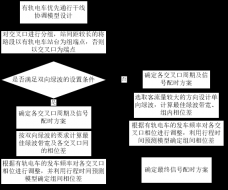
2.2.2有轨电车优先通行原理 - 6 -
2.3干线信号协调控制参数 - 6 -
2.4分段式绿波设计 - 7 -
2.5相位差及最佳绿波带宽的计算 - 8 -
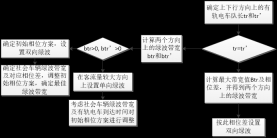
2.6有轨电车优先通行的干线协调控制模型 - 10 -
2.7本章小结 - 11 -
第三章 有轨电车行程时间预测模型 - 12 -
3.1公交行程时间预测常用方法 - 12 -
3.2基于BP神经网络的有轨电车行程时间预测 - 12 -
3.2.1有轨电车运行及道路参数 - 12 -
3.2.2BP神经网络预测模型设计 - 13 -
3.2.3预测及结果分析 - 14 -
3.3本章小结 - 16 -
第四章 基于有轨电车优先通行的数据调查 - 17 -
4.1数据调查基础 - 17 -
4.2调查方案设计 - 17 -
4.3数据调查结果 - 17 -
4.4本章小结 - 19 -
第五章 有轨电车优先通行的多情景仿真与结果分析 - 20 -
5.1有轨电车优先通行信号控制方法效果对比 - 20 -
5.2仿真结果评价 - 22 -
5.2.1有轨电车评价 - 23 -
5.2.2社会车辆评价 - 25 -
5.3本章小结 - 26 -
第六章 结论 - 27 -
6.1研究结论与创新 - 27 -
6.2研究展望 - 27 -
致谢 - 28 -
参考文献 - 29 -
- 绪 论
1.1研究背景
由于小汽车保有量的迅速增涨,道路交通压力日益增大,城市交通拥堵现象日渐加剧,发展公共交通以缓解交通拥堵问题已成为一个重要课题。现代有轨电车具有投资相对地铁和轻轨较小、建设周期短、运输能力较普通公交高等优势,是发展公共交通的不错选择。然而在目前,有轨电车的推行还十分困难。交叉口是其运行的瓶颈,由于转弯减速、停车延误等因素的影响,其服务水平达不到理想的高度。而对道路资源的占用又加剧了其与小汽车的矛盾与竞争。因此,制定针对有轨电车的干线信号协调控制策略,保障其在交叉口的优先通行权,降低其行车延误的同时处理好与其他交通方式的关系,对于发展有轨电车这一公共交通运输方式有重要的现实意义。此外,通过探究不同客流等级下有轨电车运行的干线效益,对于有轨电车的规划建设也具有参考价值。
1.2国内外研究现状
有轨电车诞生于19世纪的欧洲,在初期得到了不错的发展,在城市公共交通中占有较大比例。但随着后来小汽车和公共汽车等的普及,有轨电车建设困难、不利于城市发展的弊端逐渐显露出来,有轨电车也随之被打入冷宫。直到20世纪末,由于汽车行业的过度发展,城市面临交通拥堵、空气污染、用地紧张等伴随而来的问题,发展轨道交通成为了解决城市交通问题和城市发展的新课题。地铁造价昂贵且运营成本高,不适用于中小型城市。因此,节能、环保、成本低的现代化有轨电车成为了很多城市考虑建设的公共交通运输方式。
1.2.1国外研究现状
20世纪90年代末,现代有轨电车在欧洲国家得到尝试性的应用,并取得了不错的效果,多个国家因此相继投入有轨电车的建设。截止目前,全世界已有超过50个国家开始运营现代有轨电车。
由于有轨电车的运营受道路条件的影响,而交叉口处的影响尤其明显,其运营质量受到了一定的限制。通过借鉴公交信号优先控制的方法,一些国家对交叉口信号配时进行了研究的调整[1],以保障有轨电车的通畅运行。德国采用的方法是在有轨电车线路密度较高的区域,为有轨电车设立专有的信号灯系统[2],与道路上其他车辆的信号灯系统相互独立又相互协调。为使公共交通信号优先策略更加灵活,有学者提出了在交叉口上游修建间断式公交专用道[3],在保证公交优先的同时又改善了社会车辆的运行条件,是值得借鉴的控制方法。
西门子交通技术集团设计了一套现代有轨电车系统,包含信号控制技术、行车调度系统以及通信系统[4]。其中,信号控制技术包含制动技术、感应传输技术、信标读取技术和车载信息管理技术。行车调度系统则根据行车时刻表以及实时更新的道路信息实现对车辆的调度与管理。
此外,Pitu Mirchandani等人[5]在实时信号控制系统方面也做了研究,提出通过车辆检测技术和交通流分级预测的结合来实现交通信号灯对道路车辆的实时控制,达到干线协调控制的目的。
1.2.2国内研究现状
随着现代化建设的不断推进,我国的经济实现了快速发展,而交通拥堵、环境污染等问题也随之突显出来。有轨电车的建设可以缓解相应的交通问题,且与优先发展公共交通的主题相契合,因此其在交通规划建设的过程中被重新考虑。目前,北京、上海、天津、苏州、武汉、大连等经济较为发达的城市已有运营或规划有轨电车的路线,使之成为多层次城市综合交通体系中的一部分。
李凯,毛励良等人通过分析交叉口交通组成的特性确定各交叉口的信号配时方案,并进一步得出适合于有轨电车运行的配时方案计算公式[6]。杨晓光等人考虑到有轨电车的转弯及优先通行权,按常规方法进行配时会严重影响交通效率,因此借鉴动态TSP控制策略,采用动态配时策略并添加一个有轨电车专用相位,在保证有轨电车的优先通行权的同时最大限度地减小了对其他社会车辆的干扰,保障了其他车辆的通行效率[7]。
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:27273字
相关图片展示:
该课题毕业论文、开题报告、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找;


