论文总字数:37021字
摘 要
随着智能移动终端的数量不断增长,传统的多输入多输出(MIMO,multiple-input, multiple-output)技术受天线数量的限制难以满足未来移动通信网络的性能需求。大规模MIMO技术在基站端配置数十根甚至数百根以上天线,可以深度挖掘利用空间维度资源,大幅提升了无线通信的频谱利用率和功率利用率,是新一代移动通信系统的关键技术。由于大规模MIMO系统中多用户的检测涉及到大维矩阵求逆,复杂度较高,本论文在考虑检测性能的同时,研究大规模MIMO系统多用户上行低复杂度接收方法。
首先,本文总结了大规模MIMO系统的已有接收方法并重点研究了迭代检测译码的软干扰抵消(SIC)MMSE算法。在大规模MIMO系统中当基站天线数为 ,用户数为
,用户数为 且
且 时,线性检测方法可以达到近似最优的性能。综合考虑各线性检测算法的性能及实现复杂度,本文重点研究MMSE检测方法。为适应
时,线性检测方法可以达到近似最优的性能。综合考虑各线性检测算法的性能及实现复杂度,本文重点研究MMSE检测方法。为适应 的系统的检测需求,以SIC MMSE为例研究迭代检测译码算法。
的系统的检测需求,以SIC MMSE为例研究迭代检测译码算法。
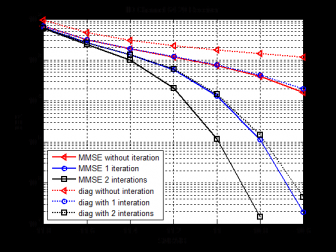
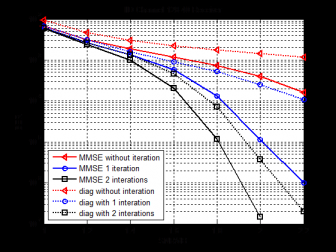
然后,本文提出了基于近似子空间投影的低复杂度检测算法。此算法利用矩阵求逆引理对MMSE检测算法进行子空间投影,再对投影矩阵进行对角矩阵近似,极大的降低了矩阵求逆的复杂度。为进一步提高此近似算法的检测性能,对此检测过程进行迭代,仿真结果表明,在较少次(两次)迭代之后,此近似算法的性能可以很好的接近MMSE迭代检测算法。
最后,本文在分析大规模MIMO系统的信道模型和空间特性的基础上,提出基于信道波束域功率分布特征的选择波束接收来进行降复杂度的检测方案。由于大规模MIMO系统中,波束域的信道具有能量集中的特性,对每个用户的发送信号选择能量集中的若干波束进行检测和译码,将MMSE检测方法的高维矩阵求逆变为低维矩阵求逆。仿真结果表明,合理选择接收波束的数目,能够在保证检测性能的同时降低检测复杂度。
关键词:大规模MIMO,低复杂度,上行检测,子空间投影,选择波束
Abstract
With the growing number of smart mobile devices, the traditional MIMO technology with restricted number of antennas is unable to meet the requirement of the spectrum and power efficiency. Massive MIMO technology, which has the potential to further tap the space of wireless resources and greatly improve the spectrum efficiency, is the key technology for future mobile communication systems. However, it requires the inversion of large-dimensional matrix in massive MIMO with high computational complexity. In this paper, we study low-complexity uplink detection in massive MIMO.
Firstly, we proposed some kinds of detection algorithms in massive MIMO, focusing on the soft interference cancellation detector. The linear detection can achieve near optimal performance when the number of antennas in base station  is larger than the number of users
is larger than the number of users  . Taking the performance and implementation complexity into consideration, this paper focuses on the MMSE detection. In the case where the number of antennas in base station is close to the number of users, the iterative receiver is considered. And we focus on the iterative SIC MMSE detector.
. Taking the performance and implementation complexity into consideration, this paper focuses on the MMSE detection. In the case where the number of antennas in base station is close to the number of users, the iterative receiver is considered. And we focus on the iterative SIC MMSE detector.
Then, a low-complexity detection based on approximate subspace mapping is proposed. The matrix inversion lemma is used to get the subspace mapping matrix in MMSE detection. In order to reduce computational complexity, the inversion of subspace matrix is replaced by a diagnal matrix which approaches to its original matrix. And it is required to use the iteration detection with approximate subspace mapping for better performance. Numerical results show that BER performance of the approximation subspace mapping algorithms approaches to the performance of iterative MMSE detection after iteration with a few times(twice).
We study another low-complexity algorithm with beam selection by exploiting the centralized power distribution in massive MIMO channel. Several beams, whose power is dominant, are selected for designing reduced-complexity MMSE detection with the sparse nature of the beam domain channel in massive MIMO. Then the inversion of low-dimensional matrix is required instead of high-dimensional matrix. Simulation result shows that after iteration, the BER performance of the beam selection based method can approach the performance of traditional MMSE detection with lower complexity via the reasonable number of selected beams.
Key words: massive MIMO, low complexity, uplink detecting, subspace mapping, beam selection
符号说明
| 基站天线数 |
| 单个小区中总用户数 |
| 上行链路空间信道矩阵 |
| 矩阵或矢量的共轭转置 |
| 矩阵或适量的转置 |
| 概率质量函数 |
| 概率密度函数 |
| 标量 |
| 向量 |
| 统计平均 |
| 矩阵 |
|
|
|
|
| 第 |
| 求以向量 |
| 求矩阵 |
| 均值为 |
| 矩阵 |
英文缩略词表
AoA | Angle of arrival |
BER | Bit Error Ratio |
CSI | Channel State Information |
DFT | Discrete Fourier Transform |
FDD | Frequency Division Duplexing |
i.i.d | independent and identically distributed |
ISI | Inter-Symbol Interference |
LDPC | Low-density Parity-check |
LTE | Long Term Evolution |
MF | Matched Filter |
MIMO | Multiple-Input Multiple-Output |
MISO | Multiple-Input Single-Output |
ML | Maximum Likelihood |
MMSE | Minimum Mean Square Error |
QAM | Quadrature Amplitude |
RZF | Regularized Zero Forcing |
SIC | Sequence Interference cancellation |
SIMO | Single-Input Multiple-Output |
SINR | Signal-to-Interference-and-Noise Ratio |
SISO | Single-Input Single-Output |
TDD | Time Division Duplexing |
TPE | Truncated Polynomial Expansion |
ULA | Uniform Linear Array |
ZF | Zero Forcing |
4G | 4th Generation Mobile Communication Systems |
5G | 5th Generation Mobile Communication Systems |
目录
摘要 I
Abstract III
符号说明 V
英文缩略词表 VII
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:37021字
相关图片展示:
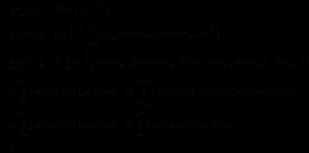
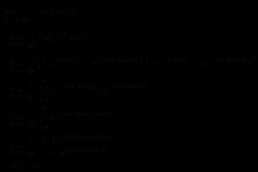
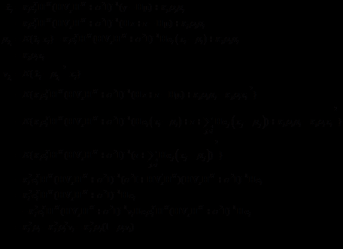
该课题毕业论文、开题报告、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找;









 的绝对值
的绝对值
 或者矩阵
或者矩阵 的Frobenius范数
的Frobenius范数

 第
第 行第
行第 列对应的元素
列对应的元素
 单位矩阵
单位矩阵
 零矩阵
零矩阵
 个元素为1且其他元素为0的列向量
个元素为1且其他元素为0的列向量
 为对角线元素的对角矩阵
为对角线元素的对角矩阵
 对角线元素组成的向量
对角线元素组成的向量
 ,方差为
,方差为 的循环对称复高斯分布
的循环对称复高斯分布
 的迹
的迹
