论文总字数:18648字
目 录
1引言 1
1.1研究背景及意义 1
1.2国内外研究进展 1
1.2.1黏粒含量的影响因素 1
1.2.2土壤黏粒含量的空间分布研究 2
2材料与方法 4
2.1研究区概况 4
2.2样本采集 4
2.3数据处理与分析方法 5
2.3.1克里金插值分析 5
2.3.2建模分析 5
3 结果与分析 5
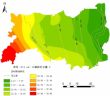
3.1黏粒含量的水平分布 5
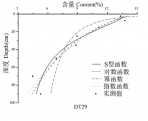
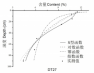
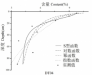
3.2黏粒含量的垂直分布 7
4结论与展望 11
4.1结论 11
4.2存在的问题及展望 12
参考文献 13
致谢 15
东台市滨海土壤黏粒含量的空间分布研究
朱晨霞
, China
Abstract: Soil clay content as a key factor affecting soil fertility, water retention and plant growth has a profound impact on soil properties. Due to the difference of parent material and soil age, the spatial distribution of soil clay content in Dongtai coastal area is very complicated. In this paper, the kriging interpolation method is used to analyze the horizontal distribution of soil clay content in the coastal area of Dongtai City, and it is found that the soil clay content increases gradually from the beach to the inland. It is concluded that the soil clay content gradually increases with the increase of soil age. By analyzing the changes of soil clay content in the east of Fangongdi in Dongtai City, it is found that the law of soil clay content in the north and south lines is not obvious at the same age. In the analysis of the vertical distribution of soil clay content, the power function, logarithmic function, exponential function and S-type function are used to fit the soil clay content, and it is found that the rate of decline in soil clay content is relatively gentle between the soil surface 10-20cm,the rate of decline is significant between 20-40cm,the rate of decline tends to be gentle after 40-50cm,and the law is consistent with the S-type growth curve.In addition, it is found that in the above four models, the S-type function model fits the maximum of R2 between 0.87 and 1.0, which is the best model. The power function model fits the minimum of R2 between 0.62 and 0.89, which is the worst model. Regardless of the parent material of the Yangtze River estuary or the old Yellow River delta sediments, the S-type function model is the best fitting model and the power function model is the worst. With the increase of soil age, S-type function model is always the best fitting model, and the worst fitting model is transformed from exponential function to power function model. It is also necessary to analyze the sectional data of representative soils to determine the optimal and worst model of soil clay content in certain areas. Otherwise, the differences of these certain areas may be covered up. The study of this paper will provide a reference for the study of spatial distribution of soil clay content and the use of different models to fit soil physical and chemical properties.
Key words: clay content; model; spatial distribution
1引言
1.1研究背景及意义
土壤是地球陆地的表面,由矿物质、有机质、水分、空气等物质组成,具有高度的空间异质性。黏粒(单粒直径小于0.002mm)是土壤中最活跃的矿物组分,增加了土壤的多样性,是土壤物理化学性质的基础[1]。黏粒多是由原生矿物风化而成的次生矿物组成[2]。黏粒粒径较小,比表面积大、表面能大,在液体中由于选择性吸附、表面分子解离等而具有带电性。此外,黏粒还具有双电层特性和阳离子交换性等性质[3]。黏粒的阳离子交换性能有助于土壤吸持可供植物生长的养分离子,其离子吸附选择性在土壤作为生长作物和处置废物介质中有一定作用[1]。因此,土壤黏粒含量对土壤保肥性、保水性、通气性以及植物生长等产生影响,土壤黏粒含量的研究对于土壤性质的分析具有重要意义。
到目前为止,国内外学者已经进行了大量关于土壤理化属性垂直分布规律的研究,主要是关于土壤有机碳、全氮等理化性质垂直分布规律的探究,涉及到土壤黏粒含量垂直分布规律的研究却比较少。此外,目前土壤理化性质剖面分布研究主要是通过采集土壤剖面样本,将土壤样本根据深度分层,比较不同层次理化性质平均值的变化规律。这样的研究虽然能够探究出垂直分布的一般规律,但是土壤理化性质的变化在各层之间是连续的,平均值并不能反映在各个层次内部土壤理化性质的连续变化。利用不同函数模型拟合土壤理化性质剖面分布,就可以解决上述问题,模拟出土壤理化性质随深度的连续变化规律。因此,本文将运用剖面拟合方法反映土壤黏粒含量在各深度数值的连续变化过程,探究土壤黏粒含量的垂直分布规律。
ArcGIS地理信息系统主要用于分析和处理一定地理区域内分布的各种现象和过程,具有强大的空间分析、地图制作等功能。本文选取东台市范公堤以东滨海地区作为研究区域,土壤类型主要为潮盐土。由于研究区位于南北两股潮流的汇合处,北线由北而南的沿岸流带来的沉积物主要是旧黄河三角洲物质,南线由南而北的潮流带来了长江河口的沉积物[4-5],土壤黏粒含量或因南北线成土母质的不同而产生差异。研究区自西向东,土壤的发育程度/成土年龄逐渐减小[6],而土壤黏粒含量在东西向或因成土年龄的差异而产生变化。因此,本文将运用ArcGIS软件,将采集的离散数据用插值法呈现整个区域土壤黏粒含量的水平分布,从而探讨东台市滨海地区土壤黏粒含量随成土年龄以及成土母质等因素的差异而产生的黏粒含量的水平变异规律。
1.2国内外研究进展
1.2.1黏粒含量的影响因素
一般而言,随着土壤发育程度/成土年龄的增加,土壤颗粒粒径会逐渐减小,黏粒含量会持续增加,土壤黏粒含量是表征土壤年龄的可靠指示。Burkins D L等[7]通过研究泰奥加和太浩湖各时间序列土壤得出了土壤中黏粒总量随着成土年龄增加而增加的结论。Bockheim J G等[8]通过研究布兰科角(Cape Blanco)和俄亥俄州西南部的阿拉戈角(Cape Arago)附近土壤,得出粉砂和黏粒的相对丰度随成土年龄增加的结论。D. J.Merritts等[9]发现发育于2.9万年海岸阶地的土壤黏粒含量最大达到10%,超过10万年的土壤黏粒含量至少30%,超过24万年的土壤黏粒含量达到40-50%。小于2.9万年阶地土壤Fed少于1%,超过24万年的Fed至少4%,得出最大黏粒百分比是比Fed更可靠的土壤年龄的指示的结论。
土壤黏粒含量还与成土母质有关。范德江等[10]采用X射线衍射物相分析等方法对长江与黄河沉积物中黏土矿物、地化成分组成进行了研究,发现在小于0.005mm粒级中黄河沉积物碳酸盐的含量约为长江的9倍。因而可以推断出,黄河沉积物中土壤黏粒含量高于长江沉积物。
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:18648字
相关图片展示:
该课题毕业论文、开题报告、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找;


