论文总字数:28528字
目 录
摘要 I
Abstract II
1引言 1
1.1研究目的及意义 1
1.2研究进展 1
1.2.1湖泊温室气体排放的研究进展 1
1.2.2水体温室气体影响因素研究 2
1.2.3通量测量方法研究 2
1.3问题提出 3
2材料与方法 3
2.1太湖概况 3
2.2采样和分析方法 4
2.2.1采样方法 4
2.2.2气体处理和分析方法 4
2.3温室气体浓度和通量的计算方法 4
2.3.1水体中CH4、CO2和N2O浓度计算方法 4
2.3.2水气界面CO2、CH4交换通量的计算方法 5
3结果与分析 5
3.1水体CH4、CO2、N2O浓度的时间变化和季节变化 5
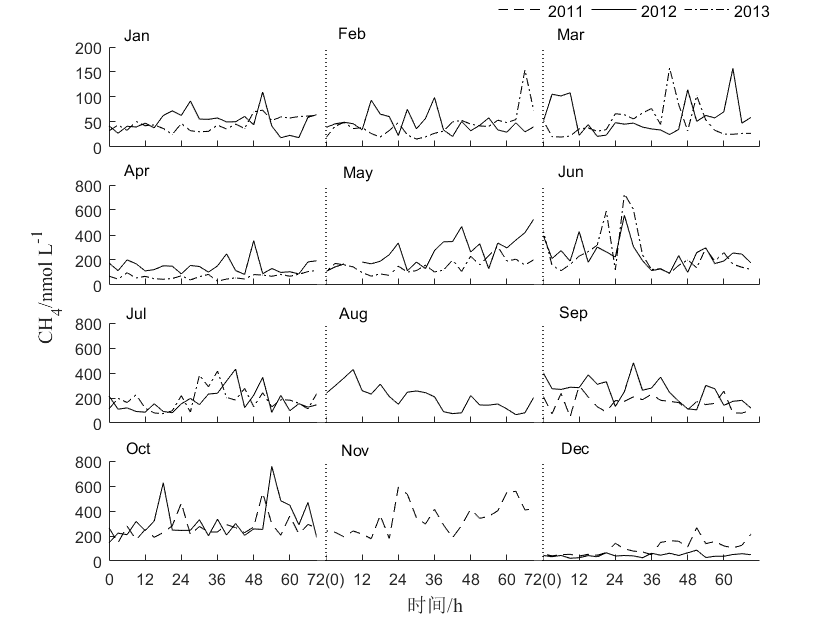
3.1.1水体CH4浓度的时间序列 5
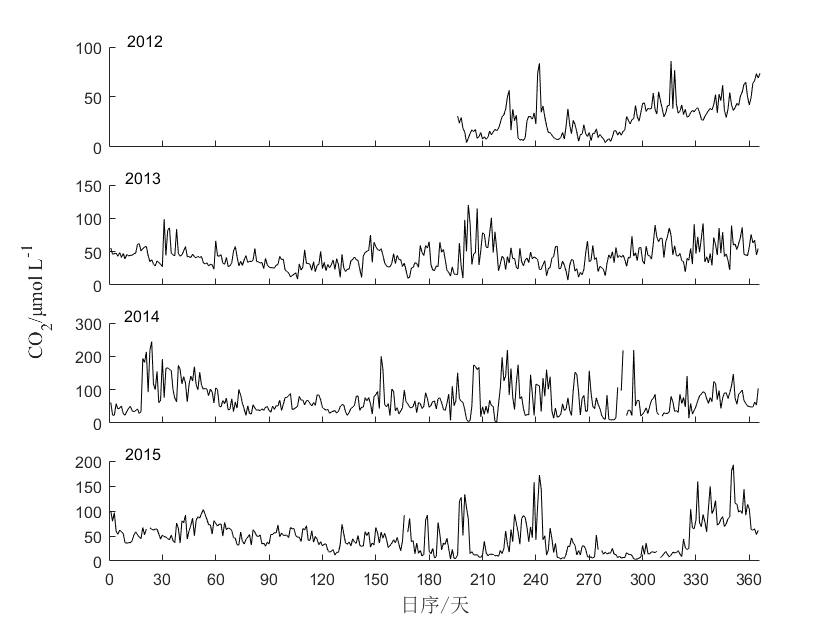
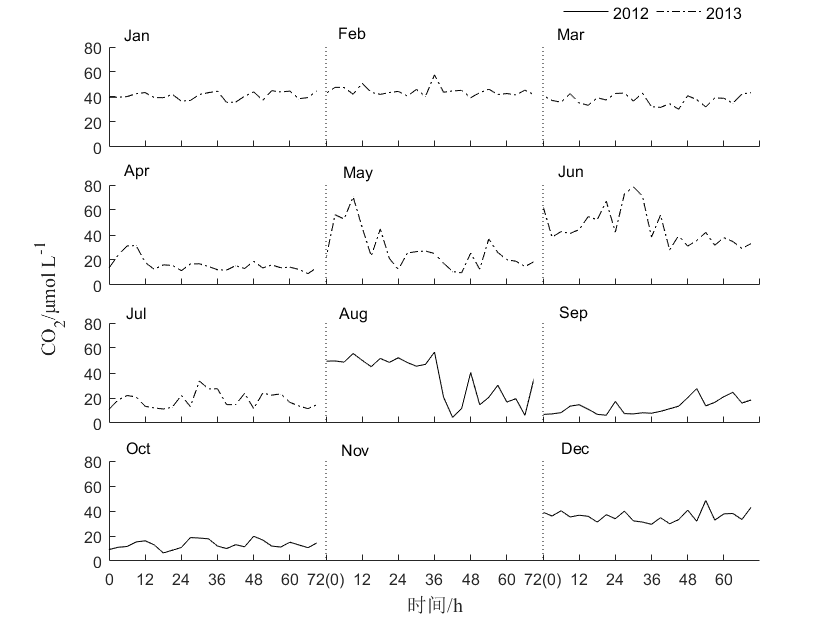
3.1.2水体CO2浓度的时间序列 6
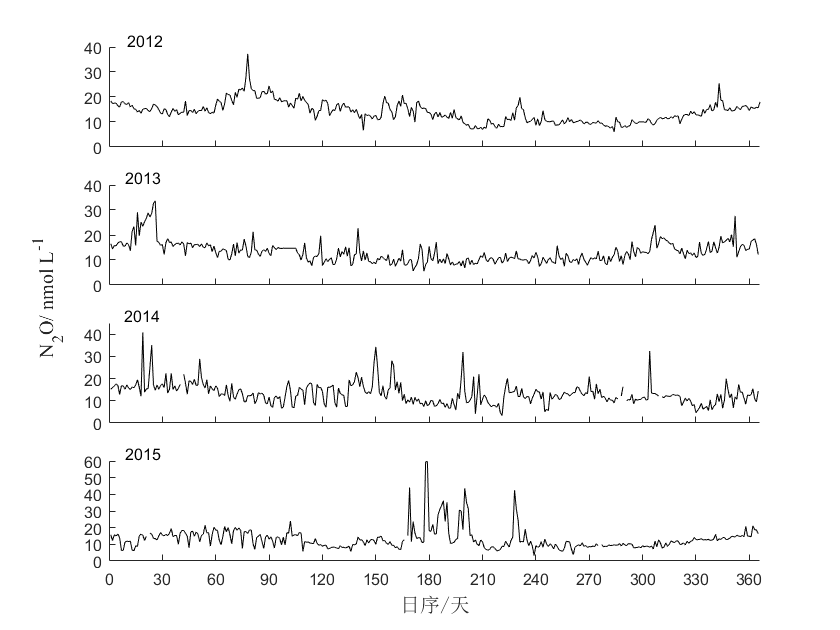
3.1.3水体N2O浓度的时间序列 7
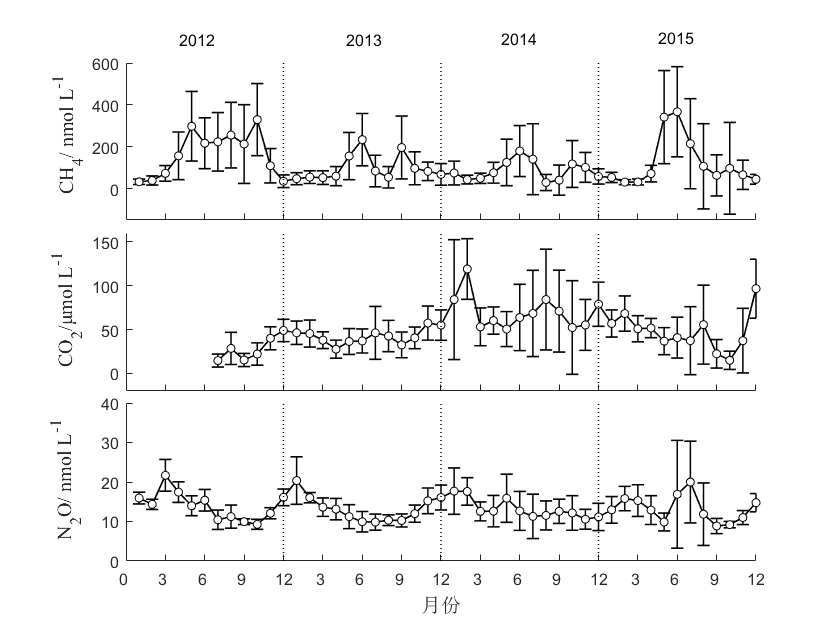
3.1.4水体CO2、CH4和N2O浓度的季节变化 7
3.2水体CH4、CO2和N2O浓度的日变化 9
3.2.1水体CH4浓度的日变化 9
3.2.2水体CO2浓度的日变化 10
3.2.3水体N2O浓度的日变化 11
3.2.4水体CO2、CH4和N2O浓度日变化: 11
3.3水体CH4、CO2、N2O浓度的深度廓线 13
3.3.1水体CH4浓度的深度廓线 13
3.3.2水体CO2浓度的深度廓线 13
3.3.3水体N2O浓度的深度廓线 15
3.4水气界面CH4和CO2的通量变化及影响因素 15
3.4.1水气界面CH4通量的时间序列 15
3.4.2水气界面CO2通量的时间序列 16
3.4.3太湖水气界面CH4、CO2通量与气象因素的关系 17
4讨论 18
4.1太湖水气界面CH4、CO2通量的影响因素研究 18
4.2太湖CH4、CO2通量与其他湖泊的研究结果对比 18
5结论 19
参考文献 20
致谢 23
太湖湖水温室气体浓度时空变化和水-气界面通量研究
韦婷婷
, China
Abstract: With the long-term observation on CH4, CO2 and N2O concentrations of lake water in the Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu employing the gradient diffusion method, the spatiotemporal variation of the CH4, CO2, N2O concentration in lake water and the fluxes at the water-air interface in Lake Taihu, and the influence of meteorological factors were analyzed. The results indicated: (1) The average CH4 concentration of lake water in spring, summer, autumn and winter was 124.00, 174.20, 125.96 and 48.04nmol L-1 respectively, which was highest in summer and lowest in winter. The average CO2 concentration of lake water was 45.02, 48.51, 38.31 and 70.66μmol L-1 in spring, summer, autumn and winter respectively, which was highest in winter and lowest in autumn. The average N2O concentration of was 14.19, 12.59, 11.09 and 15.94 nmol L-1 in spring, summer, autumn and winter respectively, with small annual fluctuation and higher value in winter and spring. (2) The CH4 concentration of lake water increased during the night, and reached the maximum at 6:00, and began to decrease after sunrise; the CO2 concentration in lake water was higher at night, decreased after sunrise and then reached the lowest at dusk; the diurnal variation of N2O concentration in water was weak, it decreased after sunrise and increased at night. (3) The CH4 concentration in lake water increased with the depth in spring and summer, and changed significantly at 12:00. The CO2 concentration in lake water changes with depth in the spring and autumn slightly, and it was more stable in autumn and winter; The N2O concentration of lake water did not changed significantly with depth; (4) The average values of CH4 and CO2 flux were 0.12 and 33.24 mmol m-2 d-1. Lake Taihu acted as the source of CH4 and CO2. It was a strong CH4 source in transition between spring and autumn, and lowest in winter. For CO2, the CO2 emission was most intensive in summer, and lower in spring and autumn. (5) There was a significantly positive correlation between wind speed and the CH4 and CO2 fluxes, but the correlation between wind speed and the CH4 flux was unstable. There was a significantly positive correlation between water temperature and the CH4 flux, and there was a unstable positive correlation between water temperature and the CO2 flux. Air pressure was positively correlated with the CH4 flux and CO2 flux positive correlation, and the relationship with CO2 flux may be related to seasonal variation. (6) The seasonal variation of the CH4 flux was relatively stable, and the temporal variabilities of the lakes in different regions were similar, but the seasonal variation of CO2 flux was correlated with the lake characteristics. This study is useful to determine the role of Lake Taihu in the terrestrial carbon cycle, as well as to provide specific data for assessing greenhouse gas emissions from lakes.
Key words:greenhouse gases,flux,concentration,Lake Taihu
1引言
1.1研究目的及意义
在全球范围内的温室气体浓度的升高已经引起不同程度上的气候变化,这已经成为关注热点问题。受到人类活动的影响,大气中温室气体浓度一直保持上升的趋势,目前CO2、CH4和N2O等温室气体的浓度已上升到过去800KA(千年)来的最高水平,全球变暖已经成为一个毋庸置疑的事实[1]。这种气候变化会引起气温升高、海平面上升等现象,还会增加极端气候事件发生的频率,对人类的生产生活以及自然界的存在与发展都有重要的影响。
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:28528字
相关图片展示:
该课题毕业论文、开题报告、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找;