论文总字数:23143字
目 录
1 引言 1
2 材料和方法 2
2.1 资料来源 2
2.2 研究方法 3
2.3 技术路线图 3
3 结果分析 4
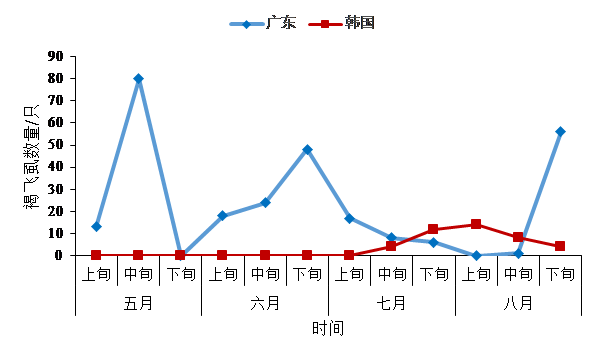
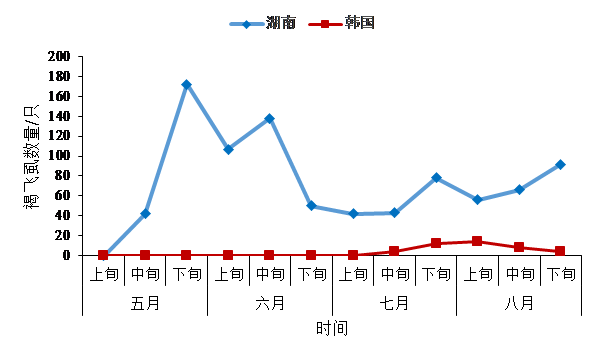
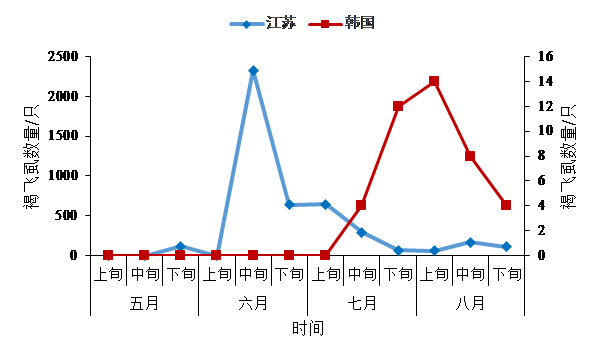
3.1 2016年韩国褐飞虱虫情简介 4
3.2 褐飞虱迁飞的分析和推测 6
3.3 大气环流形势分析 8
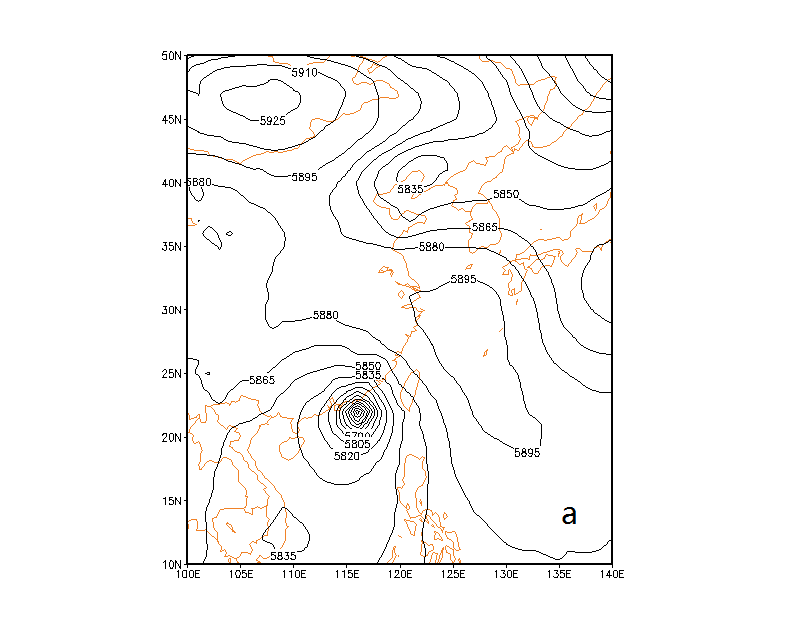
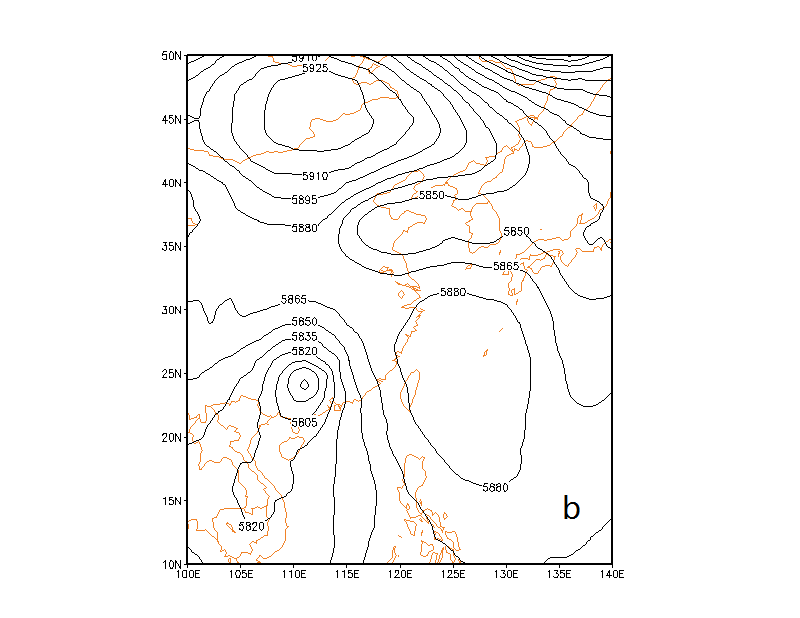
3.3.1 500hPa高度形势分析 8
3.3.2 700hPa高度形势分析 10
3.3.3 850hPa高度形势分析 10
3.3.4 地面天气形势分析 12
3.3.5 大气环流形势分析结果 13
3.4 大气动力场分析 13
3.4.1 风场分析 13
3.4.2 垂直速度场分析 14
3.4.3 大气动力场分析结果 17
3.5 基于HYSPLIT的褐飞虱后向迁飞轨迹分析 18
4 结论与讨论 19
4.1 结论 19
4.2 讨论 19
参考文献 19
致谢 22
褐飞虱迁入韩国的大气环流背景及虫源地分析
——以2016年为例
杨诗俊
, China
Abstract: Brown planthopper (BPH), Nilapavata lugens (stål), is a kind of migratory pest with the characteristic of transnational and trans-boundary migration in a long distance and it has brought about a great damage to the rice production of many nations and regions. The research of BPH’s transnational migration is necessary to the management of BPH in the world.
In this paper, a great event of BPH’s immigration into the south part of Korea during the period from 1st to 4th August in 2016 was selected a typical case of BPH’s transnational migration, the lighting trap catches of BPH in China and Korea and the related meteorological data were collected to analyze and speculate the emigrating regions, migrating time sections, flight duration and landing areas of BPH’s populations in this event. The impacts of the atmospheric circulation situation at 500hPa, 700hPa, 850hPa, the ground and the effect of horizontal wind speed field at 850hPa and the vertical velocity field at 850hPa, 925hPa, 1000hPa were discussed. The HYSPLIT backward trajectory model was used to check whether the speculation about the emigrating regions, migrating time sections, flight duration and landing areas of BPH’s population was right or not. The results showed as follows:
(1) The analysis of atmospheric circulation situations at 500hPa, 700hPa, 850hPa, the ground indicated that the coordination between the subtropical high pressure on the Western Pacific and the typhoon engendered the south and southwest carrying stream of BPH’s long-distance migration from the pest source areas of the southeast China to the landing area of BPH in the south Korea and it played a key role in this transnational migration of BPH’s populations. The high pressure from the Mongolia plateau moved toward the southeast direction where prevailed the north and northeast horizontal airflow on the sides of south and southeast and it inhibited the northward migration of BPH’s populations and had an important promoting effect on the landing of BPH’s population in the south part of Korea
(2) The distribution of wind speed field at 850hPa level displayed that the southerly wind and southwest wind produced in the east side and northeast side of the typhoon system played a leading role in the transmission of pest sources and the southerly wind and southwest wind in the west side and northwest side of the subtropical high pressure had an important assistant effect.
(3) The diagnosis of the vertical velocity fields at 850hPa,925hPa and 1000hPa showed that the updraft airflow on the BPH’s pest source areas in Jiangsu and Zhejiang of China was advantageous to the emigrating of BPH’s populations and the downdraft airflow on the south part of Korea was favorable to the immigrating of the populations.
(4) The results of HYSPLIT backward trajectory calculation revealed that the BPH’s populations immigrated into the south part of Korea came from the BPH’s pest source areas in Jiangsu and Zhejiang of China and the rice-growing regions of the middle Korea, the main migration period was from 19:00, August 1st to 05:00, August 4th in 2016 and the prevailing migratory height changed from 1500 m to 2000 m.
Key words: Brown planthopper; Transnational migration; Atmospheric background; Pest source areas; HYSPLIT Model (Hybrid Single Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory Model)
1 引言
褐飞虱,Nilaparvata lugens(Stål),是水稻生产中最主要的害虫之一,具有群聚性、远距离迁飞性以及灾变突发性等特点,其广泛分布于中国、朝鲜半岛、日本、东南亚、南亚、太平洋群岛和澳大利亚等国家和地区。过去相当长的一段时间内,褐飞虱在亚洲区域只是在个别的几个国家和地区内间歇性发生,但自从20世纪60年代,尤其是70年代以来,其在亚洲的部分国家和地区相继大范围、高频次的暴发,给当地农业生产带来了严重损失,所以被称为“亚洲水稻上的头号害虫”[1]。虽然从20世纪90年代后期至21世纪初,褐飞虱灾变性迁入的频率和发生程度有所减轻,但此后几十年间,由于生存环境的适宜度提高、褐飞虱种群的抗药性提升、全球气候变化以及全球农业产业结构调整等的影响,褐飞虱的迁入过程和致灾机理趋于复杂化,灾变频率和发生程度有所增加,特别是2005年-2009年连续五年在亚洲出现较大规模的暴发,给相关国家和地区的水稻高产稳产带来严重威胁,危及粮食安全[2; 3]。
关于褐飞虱的远距离迁飞,尤其是跨海迁飞,一直是相关领域的专家学者们关注的重点。早在1927年,日本的村田氏就已经提出了褐飞虱有可能远距离迁入日本的论点,但是苦于没有足够的事实证据来支撑,所以褐飞虱的虫源地问题在日本一直颇有争论[4],直至1967年,朝比奈氏、鹤岗氏等在日本潮岬地区以南的太平洋海洋气象观测站附近发现了褐飞虱种群跨海迁飞的现象[5],同时,永井氏等人在收集了日本全国农业试验站的褐飞虱灯捕资料并加以分析后,证实了日本的褐飞虱有可能是从中国长距离迁飞而来的,这一发现为此后各个国家和地区的科研人员开展相关研究提供了新的思路和方向,促进了相关学科的发展[6]。
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:23143字
相关图片展示:
该课题毕业论文、开题报告、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找;


