论文总字数:30363字
摘 要
本次课题研究的内容围绕缺陷对石墨烯摩擦力的影响而展开,运用C语言编程实现分子动力学模拟,模拟原子力显微镜(AFM)对硅探针在石墨烯表面施加力的作用后石墨烯摩擦力的变化进行观测,并将结果与完美石墨烯的数据图像相对比,分析讨论得出缺陷的存在对于石墨烯摩擦力的影响。其中原程序为完美石墨烯的模型,在此程序基础上引入各类缺陷,如最典型的空位缺陷(又包括单原子空位缺陷和双原子空位缺陷)、SW(Stone-Wales)拓扑缺陷、增原子缺陷和其他非拓扑缺陷等,改写程序后通过并行计算机模拟运行程序得到相关数据,利用Matlab等软件处理后绘制图像,分析并得出结果。
在对支撑石墨烯的缺陷对其摩擦力影响的研究中,本文列出了两类共四种缺陷,从结果上看都使石墨烯相应位置的摩擦力产生了较大的增幅,平均摩擦力都明显大于完美石墨烯。原因在于缺陷的引入导致缺陷处的能量骤增,增大了探针移动需要消耗的能量;此外在缺陷处形成的褶皱也会产生阻碍作用。而缺陷的位置和浓度在本文的研究中并未对摩擦力产生较大影响。
关键词:石墨烯;缺陷;摩擦力;分子动力学
The Effects of Defects on Friction of Graphene
02011111 Xu Chen-qi
Supervised by Wang Yu-juan
Abstract:Graphene has broad research prospects and great application value due to its unique characteristics. It has been expected to be an ideal material for micro- and nano-applications, and a revolutionary solid-state lubricant. However, there have only been a few works investigating the tribological properties of graphene, and even less knowledge about the relationship between defects and frictions. Studying the effects of defects on friction properties of graphene can not only help people understand the mechanism of tribology and effects of defects, but also improve the preparation technology of graphene in daily production.
The study works on the effects of defects on the friction of graphene. C program is used for molecular dynamics simulation to simulate the Atomic Force Microscope (AFM), which focuses on the observation of variation of friction of graphene as the silicon probe brings forces on the surface of graphene. The results would be compared with the statistic and graphs of perfect graphene model and thus analyzed to find the effects on friction of graphene when defects occurs. The original program is the model of perfect graphene, and different defects would be introduced into the model, such as vacancy defect, Stone-Wales defect, ad-atom defect and other topological defects. The super computer is applied for simulation and calculation, and Matlab programs are responsible for data processing and image graphing. The statistic would be analyzed to find out the conclusions.
During the study of the effect of defects on friction of graphene, this article focuses on the two types of defects. The results show that the defects lead to the obvious increase of friction of graphene, and the average of friction is greater than the perfect graphene. One of the reasons is that the defect results in the dramatic increase of energy in the place of defect, which increases the energy that the probe needs to move. Also the wrinkle formed at defect would block the probe. The location and concentration of defects in this study did not affect the friction of graphene.
Key words:Graphene; Defect; Friction; Molecular Dynamics
目 录
摘要………………………………………………………………………………………………Ⅰ
Abstract…………………………………………………………………………………………Ⅱ
目录………………………………………………………………………………………………Ⅲ
第一章 绪论………………………………………………………………………………………1
1.1 石墨烯简介………………………………………………………………………………1
1.1.1 石墨烯的结构及性质………………………………………………………………1
1.1.2 石墨烯的应用………………………………………………………………………3
1.2 国内外研究现状…………………………………………………………………………3
1.2.1 石墨烯的超滑研究…………………………………………………………………3
1.2.2 缺陷与摩擦现状分析………………………………………………………………4
1.2.3 石墨烯缺陷简介……………………………………………………………………5
1.3 本课题主要研究内容……………………………………………………………………6
第二章 分子动力学方法…………………………………………………………………………8
2.1 分子动力学方法简介……………………………………………………………………8
2.2 分子动力学模拟的基本步骤……………………………………………………………8
2.2.1 建立石墨烯的分子动力学模型……………………………………………………8
2.2.2 分子的初始位置和速度……………………………………………………………9
2.2.3 势能模型的选取——分子间作用力………………………………………………10
2.2.4 分子运动方程的建立………………………………………………………………10
2.2.5 周期性边界条件……………………………………………………………………11
2.2.6 温度的调节…………………………………………………………………………11
2.2.7 邻居列表的处理……………………………………………………………………12
2.3 分子动力学程序流程……………………………………………………………………13
2.4 本章小结…………………………………………………………………………………13
第三章 缺陷石墨烯与完美石墨烯摩擦特性比较……………………………………………14
3.1完美石墨烯的模拟结果…………………………………………………………………14
3.2 X 30°增原子缺陷石墨烯的模拟结果…………………………………………………17
3.3 中心及三边增原子缺陷石墨烯的模拟结果……………………………………………20
3.4 缺陷石墨烯与完美石墨烯的摩擦特性比较……………………………………………23
3.4.1 完美石墨烯与X 30°增原子缺陷石墨烯对比……………………………………23
3.4.2 完美石墨烯与中心三边增原子缺陷石墨烯对比…………………………………25
第四章 缺陷特性对石墨烯摩擦特性的影响…………………………………………………28
4.1 石墨烯缺陷位置对摩擦力的影响………………………………………………………28
4.2 石墨烯缺陷浓度对摩擦力的影响………………………………………………………31
第五章 结论与展望……………………………………………………………………………35
5.1 总结………………………………………………………………………………………35
5.2 展望………………………………………………………………………………………35
致谢………………………………………………………………………………………………37
参考文献…………………………………………………………………………………………38
缺陷对石墨烯摩擦力的影响
- 绪论
2004年,英国的曼彻斯特大学物理学家Andre Geim和Konstantin Novoselov采用撕胶带的方法成功从石墨中分离出单原子层的石墨烯薄膜,这一发现立即震撼了凝聚态物理界。之前很多物理学家认为单层石墨烯薄膜是一种假设性的物质,其完美的二维形态由于热力学不稳定性在非零温度下是不能稳定存在的。Geim和Novoselov同时也发现了石墨烯在力学、热学、光学和电学性能上具有优异的性能,这引起了全世界的广泛关注,两人也因此共同获得2010年诺贝尔物理学奖。
石墨烯具有极强的机械强度、弯曲强度和导电性能,同时石墨烯优秀的摩擦性能使其成为最佳的纳米润滑剂,应用前景十分广泛,被认为是具有战略意义的新材料。目前,对石墨烯的研究大部分都基于石墨烯为完美的二维平面结构这一假设。然而在实际生产中,石墨烯在制备的过程中不可避免地会产生不同程度的缺陷,亦或是在极端应用环境下工作可能会产生缺陷,从而影响到石墨烯的工作性能,而随着石墨烯被更多的应用到生活的方方面面,这种缺陷可能带来的隐患必须得到重视,因此通过研究各种不同的缺陷对于石墨烯摩擦力的影响,我们能够更好地了解石墨烯的摩擦性能,并发现与各个缺陷相对应的解决方法。
- 石墨烯简介
- 石墨烯的结构及性质
- 石墨烯简介
石墨烯是由碳原子以sp2杂化轨道呈蜂巢晶格排列只有一个原子层厚度的二维晶体超薄材料[1],如图1-1所示,碳原子以6圆环形式周期性排列,以共价键形式连接,键长仅为0.142nm。从几何结构来看,二维平面结构的石墨烯可以作为其他碳基纳米材料的构建单元,它可以包裹形成0维的富勒烯,也可以卷曲形成1维的碳纳米管,还可以层间堆叠形成3维的石墨,也即石墨烯是零维富勒烯(C60),一维碳纳米管(CNT),三维石墨(graphite)等碳的同素异形体的基本结构单元。图1-1为石墨烯构建其他碳基材料的示意图[2]。
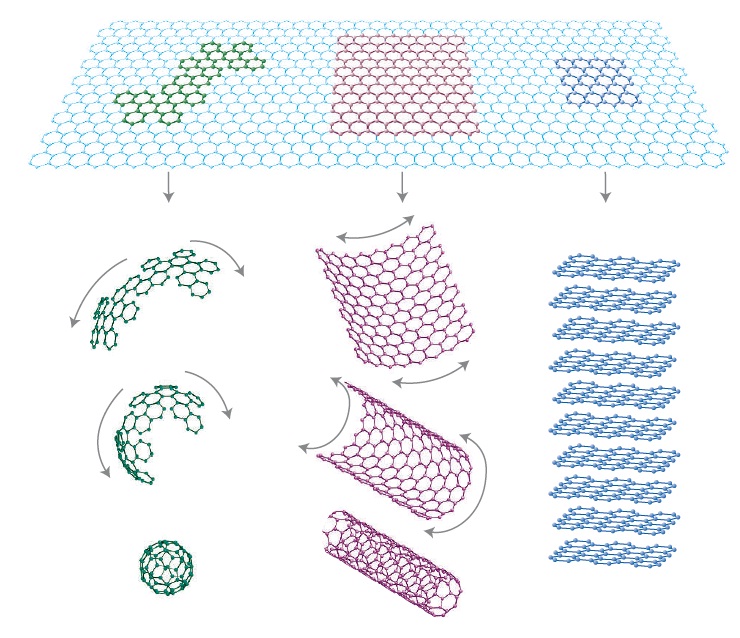
图1-1 石墨烯构建的其它碳基材料
石墨烯作为一种能在常温下稳定存在的二维材料,具有不同于三维材料的优异性质,这些优异的性质使得石墨烯具有广阔的研究前景,也蕴含着巨大的应用价值。具体表现在以下几个方面:
(1)力学性能
石墨烯是目前世界上强度最大的物质。据测算如果将石墨烯制造成现有塑料袋厚度的薄膜,大约能承受两吨物体的压力,其强度是最好钢铁的百倍以上[3]。石墨烯中每个碳原子通过与其他三个碳原子连接,由于σ共价键的键能比较大,并且碳原子之间的相互作用又具有柔韧性,当外力施加在石墨烯上时,晶格不必发生重构,而是产生变形来适应外力的作用。这种特殊的稳定结构使得石墨烯具有极佳的力学性能。2008年,Changgu Lee等人[4]利用原子力显微镜(AFM)压痕实验测量了单层自由悬浮石墨烯的弹性模量和破坏强度,石墨烯的等效弹性模量高达1 TPa,固有破坏强度达到42 N/m。实验证明石墨烯是迄今为止世界上最坚硬的材料。
(2)热学性能
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:30363字
相关图片展示:
该课题毕业论文、开题报告、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找;


