论文总字数:23173字
目 录
摘要..............................................1
ABSTRACT..........................................2
一 绪论...........................................3
1.1 选题的意义与目的......................................................3
1.2 国内外研究现状........................................................3
1.3 纳米线的拉伸性能......................................................3
1.4 分子动力学............................................................3
1.4.1 分子动力学模拟计算的基本原理与方法..............................3
1.4.1.1 基本原理..................................................3
1.4.1.2 牛顿运动方程式的数值解法..................................5
1.4.2 势函数..........................................................6
1.4.2.1 对势......................................................6
1.4.2.2 多体势....................................................7
1.4.3 分子动力学模拟的系综............................................7
1.4.4 控温控压方法....................................................8
1.4.5 边界条件........................................................9
1.4.6 本文主要的物理量的计算公式.....................................10
1.4.7 有关热力学性质的计算...........................................10
1.5 小结.................................................................11
二 铜纳米线模拟体系的确定................................12
三 温度对于铜纳米线拉伸塑性形变的影响....................13
3.1 分子动力学模拟的主要过程.............................................13
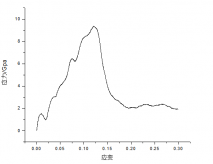
3.2 300K温度下铜纳米线的应力-应变曲线....................................13
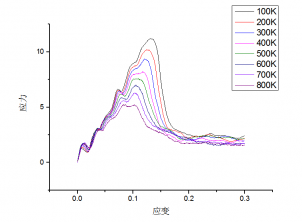
3.3 温度变化对于铜纳米线应力-应变关系的影响..............................13
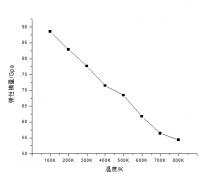
3.4 温度对于铜纳米线弹性模量和屈服强度的影响.............................15
3.5 小结.................................................................16
四 横截面积尺寸对于铜纳米线拉伸塑性形变的影响............17
4.1 分子动力学模拟的主要过程.............................................17
4.2 拉伸过程中的横截面积尺寸为10a0×10a0的铜纳米线.......................18
4.3 不同横截面积尺寸与铜纳米线应力-应变曲线之间关系的分析................20
4.4 横截面积尺寸对于铜纳米线的弹性模量与屈服强度的影响...................21
4.5 小结.................................................................22
五 应变速率对于铜纳米线拉伸塑性形变的影响................23
5.1 分子动力学模拟的主要过程.............................................23
5.2 拉伸过程中应变速率为5.0e10s-1的铜纳米线的结构形貌与应力-应变曲线.....23
5.3 在不同的拉伸应变速率下铜纳米线的应力-应变曲线分析....................26
5.4 在不同的拉伸应变速率下铜纳米线的屈服强度与弹性模量的分析.............27
5.5 小结.................................................................29
六 总结..................................................30
参考文献.................................................30
致谢.....................................................33
铜纳米线[100]方向上拉伸塑性形变的分子动力学研究
刘观海
,China
Abstract: The purpose of this paper is to investigate the effect of cross-sectional area, tensile strain rate and simulated temperature on the tensile plastic deformation of copper nanowires. First, the size of the system of the copper nanowire model was determined, and then the stretching direction of the copper nanowires was established as the X axis [100] direction.
During the stretching process of copper nanowires, the tensile process of copper nanowires was observed and the stress - strain curves were drawn by using origin software. The resulting stress-strain curves are then analyzed and the elastic modulus of the copper nanowires is obtained. The magnitude of the stress corresponding to the highest point of the curve is called the yield strength.
Using the control variable method, six copper nanowires models with different cross - sectional sizes were established to study the effect of cross - section size on the tensile plastic deformation of copper nanowires. By analyzing the obtained stress-strain curve, it can be seen that the smaller the cross-sectional area of copper nanowires, the greater the strain corresponding to the yield point. Its elastic modulus increases with the cross-sectional area size; the yield strength is also true.
Using the control variable method, six copper nanowire models with different strain rates were established to study the effect of tensile strain rate on the tensile plastic deformation of copper nanowires. By analyzing the stress - strain curves of the copper nanowires, it is shown that the higher the strain rate, the higher the yield strength of the copper nanowires and the earlier. And the elastic modulus is inversely proportional to the strain rate.
Using the control variable method, eight copper nanowire models at different ambient temperatures were established to study the effect of ambient temperature on the tensile plastic deformation of copper nanowires. The results show that the elastic modulus and the yield strength of the copper nanowires show a linear decrease when the temperature becomes high.
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:23173字
相关图片展示:
该课题毕业论文、开题报告、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找;