论文总字数:21032字
目 录
第一章 绪论 1
1.1研究背景 1
1.2液相氧化研究现状 2
1.3 本实验研究的目的及意义 2
第二章 实验过程 3
2.1实验仪器及试剂 3
2.2 实验过程 4
2.2.1 实验试剂的配制 4
2.2.2 实验步骤 4
2.3 实验样品的测定 5
2.3.1 样品的在线测定 5
2.3.2 样品的离线测定 6
第三章 实验结果与分析 8
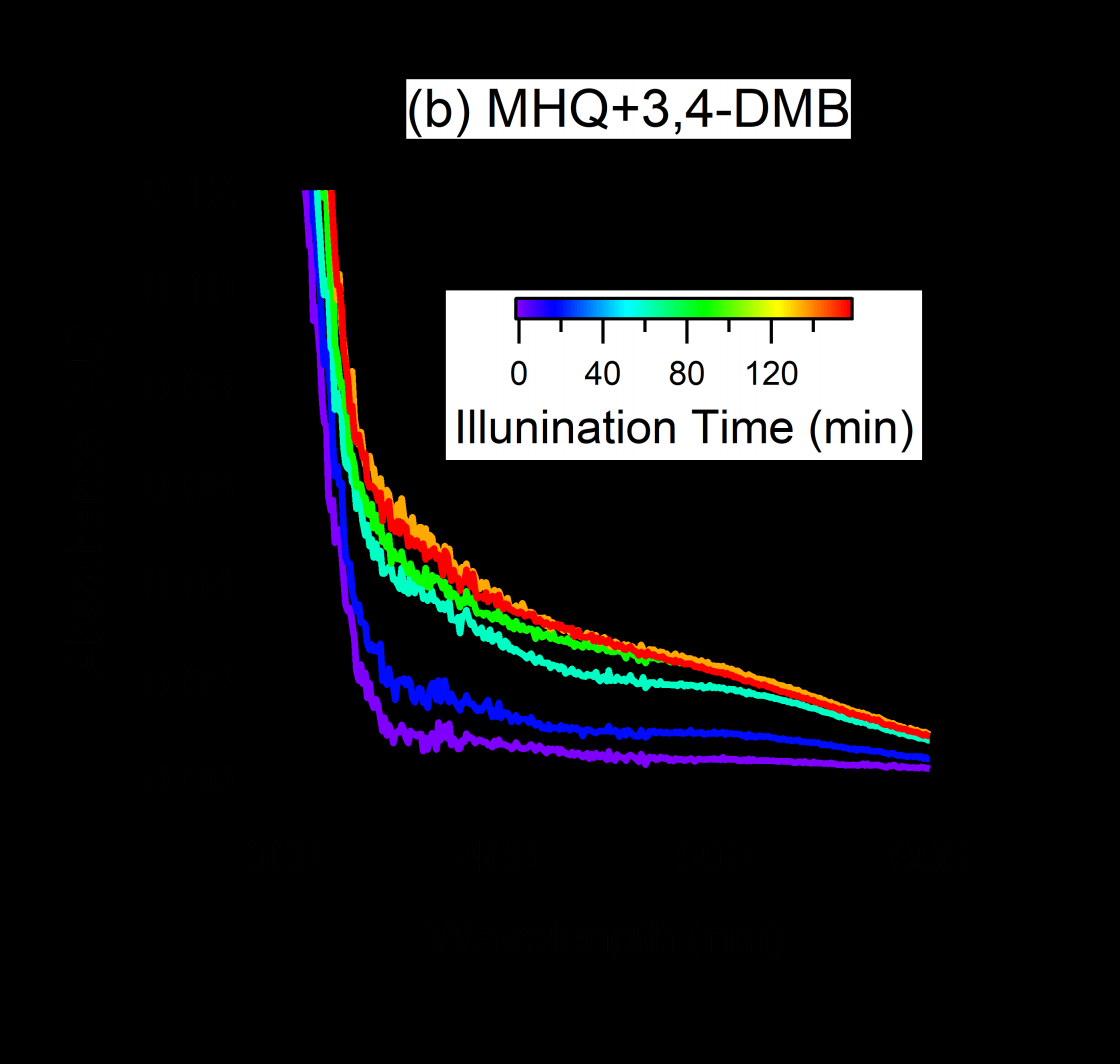
3.1 甲氧基对苯二酚反应降解规律 8
3.1.1前体物降解规律 8
3.1.2 确定反应物降解常数(kd)及半数反应时间 8
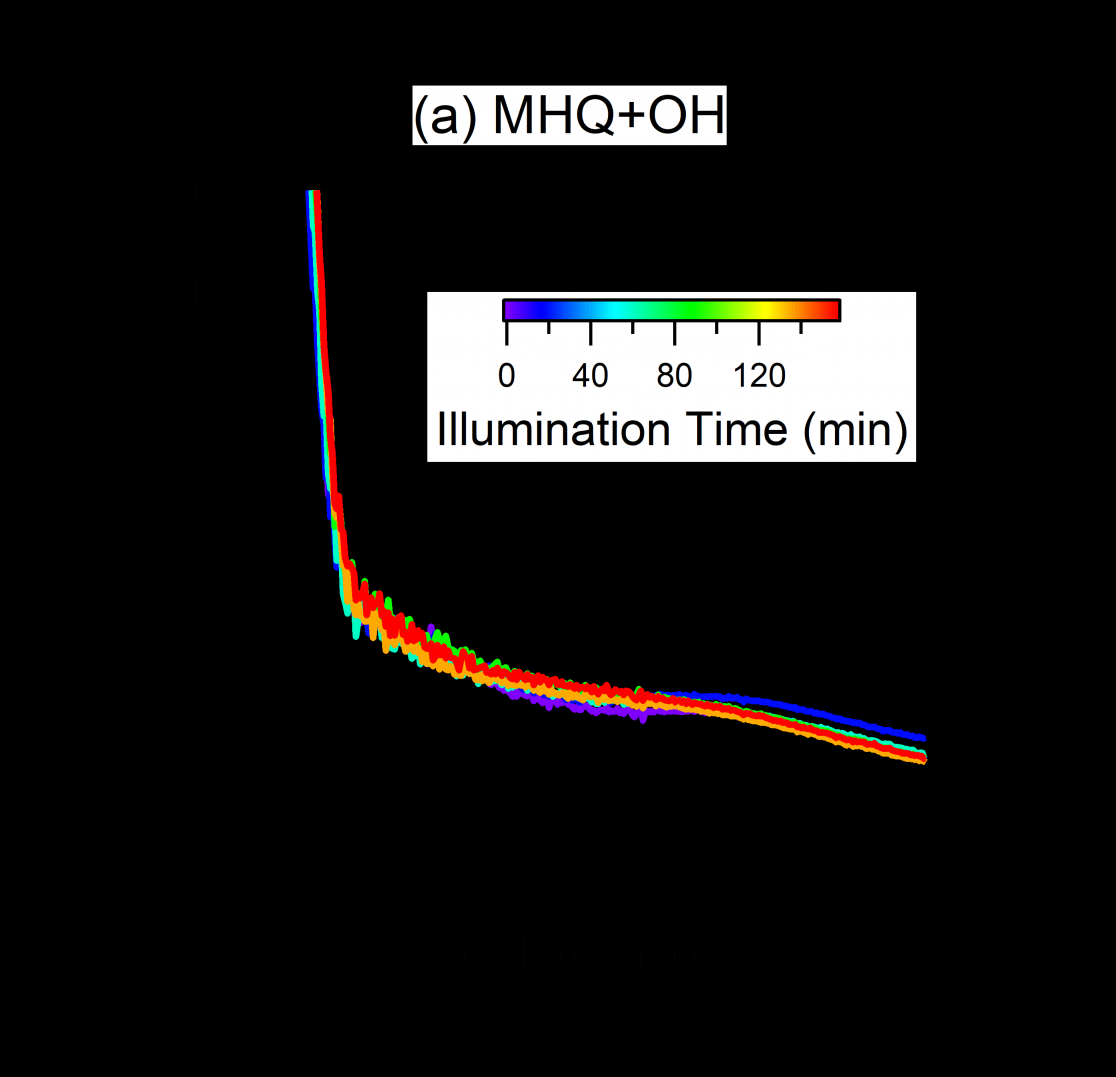
3.2反应产物的光学性质 9
3.2.1 光谱图分析 9
3.2.2 分析其质量吸收系数(MAC) 10
3.3反应产物的氧化程度 11
3.3.1质谱图分析及不同氧化物的影响 11
3.4 反应产率分析 12
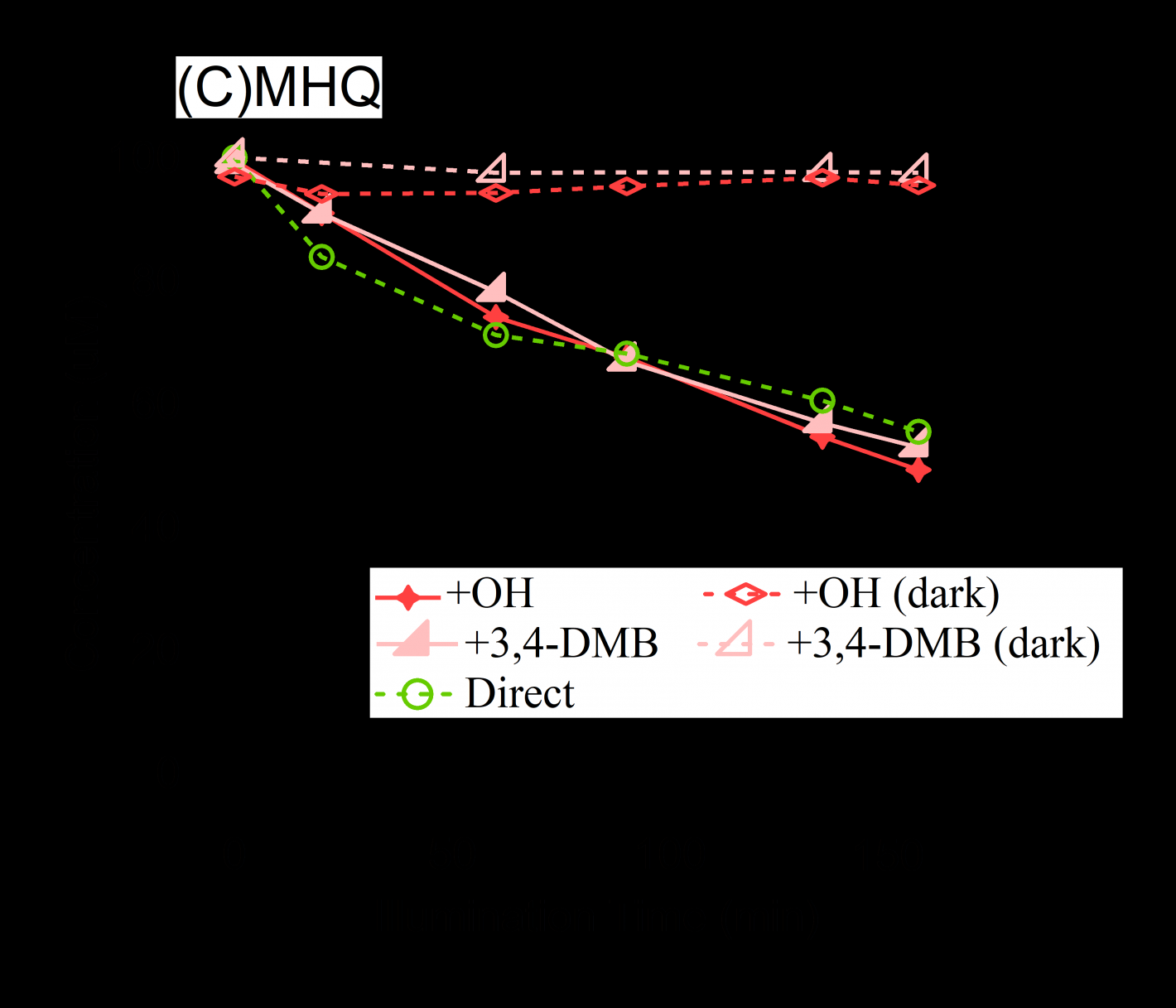
3.4.1比较反应产物的O/C、H/C、OSc 12
3.4.2 分析产物的f44vsf43图及VK图 13
第四章 总结与展望 15
4.1本实验主要结论 15
4.2本实验的不足与展望 15
参考文献 16
致谢 18
生物质燃烧产物甲氧基对苯二酚液相光化学氧化研究
欧阳
, China
Abstract: Biomass combustion products play an important role in atmospheric aerosols, and are also one of the important sources of aerosols. In the atmosphere, after various physical or chemical processes to form secondary organic aerosols, the atmospheric liquid phase reactions have been discovered. The aqSOA generated in the reaction in the liquid phase in the atmosphere may be one of the important routes of SOA in the atmosphere, but its laws are still unknown. This experiment simulates the photochemical reaction of methoxyquinone (MHQ) with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and 3,4-dimethoxybenzaldehyde (3,4-DMB), simultaneously The methoxy hydroquinone solution without any oxidizing agent is directly subjected to very liquid photochemical reaction itself, and the product is used offline (including HPLC, UV-VIS and total organic Carbon analyzer (TOC) and on-line (Aerosol Mass Spectrometer (SP-AMS)) series of analytical methods determined the reaction kinetics, product light absorption properties, oxidation properties, and yields as follows:
(1) MHQ in the liquid phase forms a triplet excited state under light irradiation conditions and undergoes direct photodegradation reaction. The reaction rate was almost unchanged after adding 3,4-DMB or H 2 O 2 . In the liquid phase photochemical reaction of MHQ, the reaction rate after the addition of oxidant hydrogen peroxide and 3,4-dimethoxybenzaldehyde is very similar to the rate of direct photodegradation reaction.
(2) In the three reactions of MHQ, the absorbance of the reaction product of MHQ and OH in the 300-600 nm band has almost no change with time. The absorbance of MHQ and 3,4-DMB and direct photodegradation reaction increases with the reaction time.
(3) The mass spectrogram of MHQ reaction process shows that the fragmentation process plays a major role in the reaction process; during the reaction, Both O/C and OSc increase with time, while H/C decreases with time, indicating that the oxidation of the reaction product increases over time in the liquid photochemical reaction of MHQ..
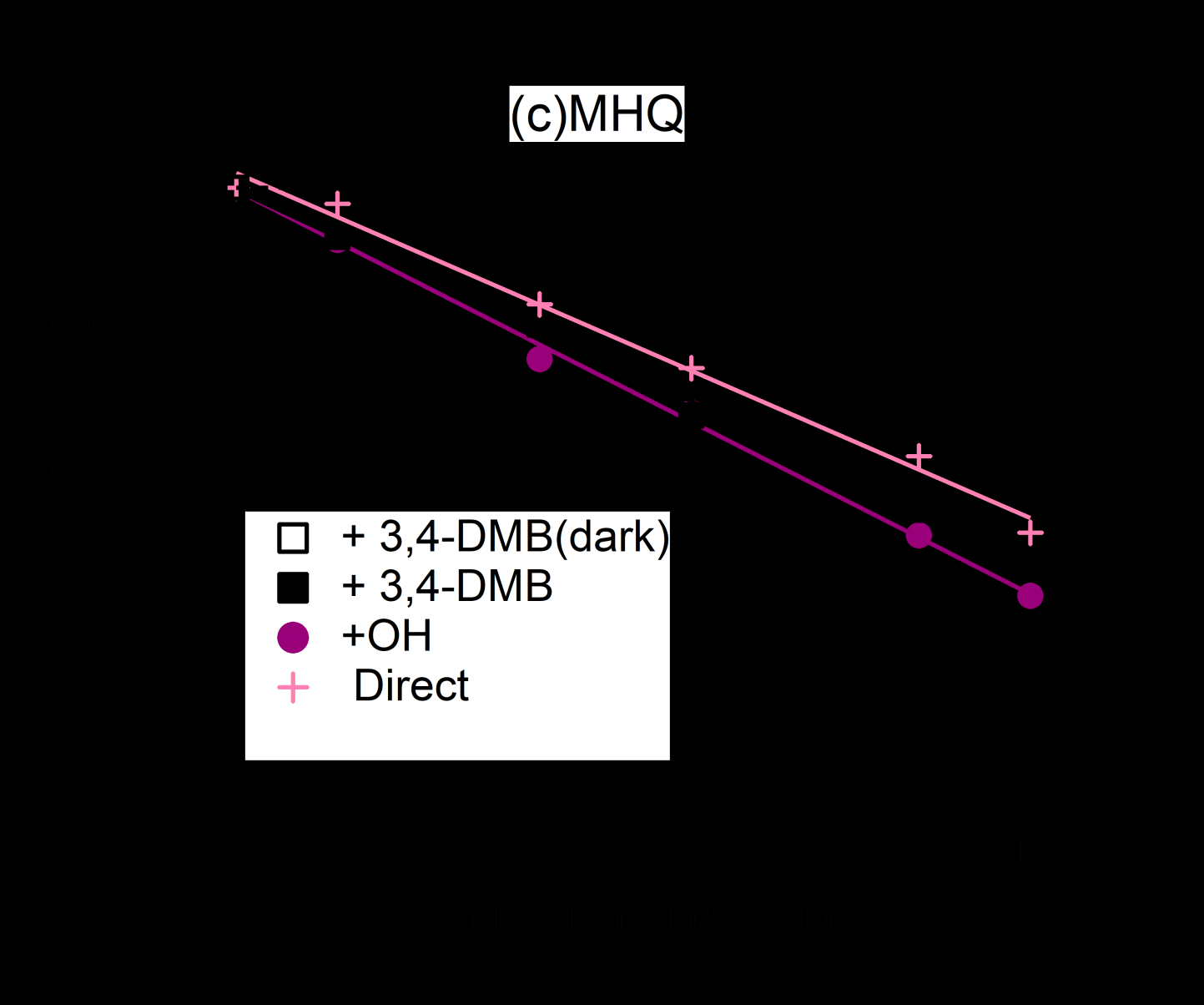
(4) The value of the structure of the reaction product of MHQ and oxidant/SO 4 increases with the increase of the reaction time, which means that there is a continuous production of organic substances during the reaction,MHQ yields range from 110 to 130% with high yields.
Key words: Secondary organic aerosol, Aqueous phase oxidation, Methoxy hydroquinone
第一章绪论
1.1研究背景
生物质是指利用大气、水、土地等通过光合作用而产生的各种有机体[1],即一切有生命的可以生长的有机物质通称为生物质[2],其主要成分有糖类(纤维素、淀粉、麦芽糖和葡/萄糖)、醛类、酸、醇、酯、苯、酚、胺等,生物质燃烧的主要有露天秸秆焚烧、森林火灾、草原火灾、农村以木材秸秆等为燃料的炊事及采暖活动等形式[3]。生物质燃烧的产物主要有CO2、SO2、氮氧化物、颗粒物、重金属、酸性气体等[4],这些主要成分都是由生物质完全燃烧产生的燃尽污染物;同时还存在一些其他污染物,如植物体内氯的燃烧产物氯化氢,未完全燃烧产物一氧化碳(CO),多环芳烃类污染物等[5]。生物质燃烧的90%是人为因素引起的,而且近百年来已扩展到全球尺度范围。
生物质燃烧对环境有着重要的影响,其导致大气重度污染事件在全国范围内都有所报道,但这些燃烧事件主要发生在农村地区。在印度和东南大地区,生物质燃烧对环境造成的效应尤为严重。碳质气溶胶和水溶性钾是生物质燃烧所排放的主要大气颗粒成分,其中碳质气溶胶的组分占比高达73%,其中60%-90%由有机碳部分组成。而碳质气溶胶在PM2.5中占比高最高达40-60%,对环境有着重要影响。生物质燃烧产物中碳质气溶胶会影响辐射平衡,颗粒物可作为云凝结核,影响降水;另外,生物质燃烧的同时伴有大量烟雾,对能见度造成极大影响,导致交通事故频发;生物质燃烧产物中有温室气体CO2、CH4、N2O,可能导致气候变化;产物中的SO2、氮氧化物等进入大气中,导致酸雨,造成大范围的污染;最后,生物质燃烧产物对人体健康也会有影响,产物中的重金属可能会引起人的头晕头痛、失眠、健忘、神经错乱、结石、癌症等,而排放的二噁英的毒性相当大,对人体伤害极大[6]。但由于生物质密度,燃烧效率,排放因子和燃烧面积的不确定性,目前对生物质燃烧排放的估计显著不同[7],因此对生物质燃烧的研究有待深入。
此前,在香港的一次大气外场观测活动中,研究者发现生物质燃烧有机气溶胶(BBOA)在短时间内极具增加,后究其原因,是当地的中元节,群众焚纸烧香是当地BBOA的来源,从而导致当地大气造成短时间的高浓度的污染。另外也有研究在大火前后的东南亚地区空气中PM2.5浓度和垂直分布情况,研究表明生物质燃烧就是造成雾霾的很大一部分来源。近来生物质燃烧排放的VOC经液相氧化形成液性二次有机气溶胶(aqSOA)的证据也在外场观测中被发现[7,8],有关数据表明在雾水和湿气溶胶中发生的液相反应可以增加大气中棕碳的总量,对光辐射强迫有一定的影响。经估算,在欧洲由生物质燃烧产物液相氧化生成的aqSOA每年排放量高达0.1-0.5Tg,相当于排放的有机气溶胶总量的4-20%。但因外场直接观测的证据不多,有关aqSOA的实际贡献研究还较为匮乏。
1.2液相氧化研究现状
大气中二次有机气溶胶(SOA)形成的路径包括气相氧化和液相氧化。气相氧化指气态前体物在气相中氧化,产物凝结到原有颗粒表面或生成新粒子并长大。液相氧化污染物溶于液相(云滴、雾滴或气溶胶水中),经反应生成低挥发性物质,在水分蒸发后形成颗粒物。先前有关气相氧化的研究较多,但近来研究表明液相反应也是SOA生成的一条重要路径,但有关研究还相对较少。
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:21032字
相关图片展示:
该课题毕业论文、开题报告、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找;


