论文总字数:14903字
目 录
1引言 5
2 热线含水量仪原理 6
3 分析用雾的微物理特征 6
4 传感器导线特性分析 7
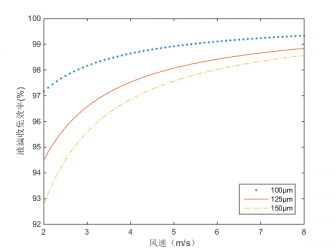
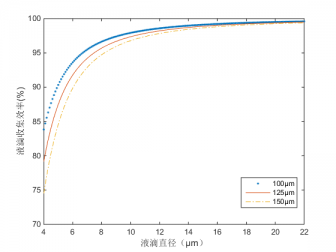
4.1热线直径对收集效率的影响 7
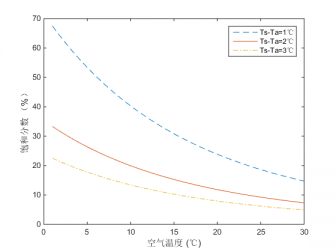
4.2热线温度对测量性能的影响 9
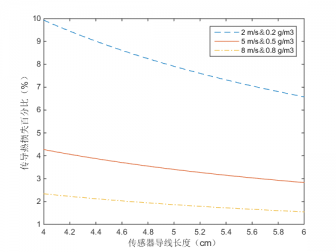
4.3热线长度的性能分析 12
4.4 对热线材质的分析 14
5结论 15
6讨论 15
参考文献 16
致谢 18
热线雾含水量仪收集效率与性能分析
孟凡煜
,China
Abstract:In order to investigate the effect of sensor wires on the collection efficiency of the hot-wire liquid water content meter,this paper uses the droplet distribution data of a typical advection fog .Starting from the sensor wire,the diameter of the wire,the temperature of the wire,the length of the wire and the material of the wire were calculated and analyzed.The results show that the droplet collection efficiency of the thinner wire diameter is larger.The larger the difference between the temperature and the air temperature of the wire,the smaller the fraction of the saturation of the surface of the wire,the better the collection of dropletsWith regard to the length of the sensor wire,the longer the wire,the smaller the percentage of conduction power lost as a percentage of the total power and the greater the power used to evaporate the droplet.The resistivity and resistivity temperature coefficient of the wire are related to the sensitivity of the instrument,and the higher the resistivity and resistivity temperature coefficient,the higher the sensitivity.Finally,based on the content of the study, and combined with the actual,we put forward a more practical hotline water meter wire parameters:the choice of annealing platinum wire for the production of wire diameter of 125μm,length of about 5cm,and the air temperature difference of about 2 °C.
Key words:liquid water content;the hot-wire liquid water content meter;collection efficiency
1引言
液态水含量(LWC)在云雾研究,天气预报,人工影响天气和环境科学等项目的研究中都是非常重要的。LWC与雾,云和露的无机与有机物含量相关[1]~[2]。因此它也被当做是重要指标在雾或者云的观测项目中(Berton, 2008; Carrillo et al., 2008)。而对于液态水含量的测量,最主要的是确定采集器的收集效率。
随着时间的发展,人们对雾水收集器的效率的研究也逐渐深入。
Schemenauer 和 Joe (1989)的研究指出,大型雾收集器是由1mm宽的扁平聚丙烯带制造成的双层网组成。在2到8m/s的风速下,通过观察到的液滴,一毫米宽的扁平聚丙烯带的理论收集效率大约为75到 95%。在收集效率的现场观测中,一个大型雾收集器的网格中心线,收集效率大约为66%(3.5–6.5 m s−1; 11 μm MVD)。这与单一扁平聚丙烯带收集效率的理论值是很吻合的。然而,在较低风速下,大型雾收集器的收集效率下降到26% (1.9 m s−1; 15 μm MVD)[3]。
通过空气动力学分析,Rivera (2011)认为对于一个典型的大型雾收集器,其最大的收集效率应为30%左右。Rivera提出了一种简单的叠加模型来分析遮阳系数和纤维特性对与雾水收集器(Fog water collectors)的气动收集效率(Aerodynamic Collection Efficiency)的影响。该模型表明,在遮阳系数位于0.5到0.6之间时,对于特定的网格模拟,雾水收集器的气动收集效率达到最大值[4]。
Baumgardner等(2011)描述了使用机载测量的方法去探测LWC。Carrillo等(2008)描述了一种经济的光学云雾探测器,经过校准,该探测器也可以用于LWC的测量。然而,该文提出的设计是处于非常低的研究预算而用于大型远程无线传感网络(Collins et al., 2006)。 因此,这些设备因为成本和功率要求相对较高而被淘汰了[5]~[7]。
测量液态水,冰,或者总水量,液态水通过与一个或多个加热元件接触,使得其本身蒸发。在地面风速影响下,大粒径总液态水含量探头将有较低的沉积效率。为了提高标准传感器坐在地面条件下的沉积效率,可以通过一种用于实验室测量的方法(e.g., Keith et al., 1986),即移动传感器(例如装在一个旋转臂上)来人为的提高相对速度。或者通过抽气,使气体加速经过探头(如液滴测量技术、热线液态水传感器)[8]。
非常小直径的雾滴分布测量探头适用于地面或气球或直升机运载的仪器平台。KLD实验室便携式滴计数器可以测量液滴的直径分布(Dodge,1987)。然而这些仪器过于精密或昂贵,难以在大规模自动式地面遥感系统中实现[9]。
约翰逊–威廉姆斯云水计和联邦科学与工业研究组织(CSIRO,or King)液态水探针已成为最常用的机载LWC探针(作为比较,见Feind et al., 2000)[10]。 LWC热线探头用于蒸发和收集水滴。通过相对速度,环境温度,导线温度和保持导线温度所需电量等数据,我们可以计算得出LWC。
2 热线含水量仪原理
热线含水量仪是通过维持传感器导线温度恒定,根据消耗的功率来计算LWC的。
保持导线温度所需的电功率是导线几何形状和温度以及相对速度、温度和LWC的函数。该导线通常被假定为垂直于风。热线垂直于平流雾的功率平衡如公式(1)所示[11]。
 (1)
(1)
其中, 是热线含水量仪消耗的总功率,
是热线含水量仪消耗的总功率, 是加热和蒸发撞击到热线上的水滴消耗的功率,
是加热和蒸发撞击到热线上的水滴消耗的功率, 是因为空气对流冷却热线,而将热线维持在恒定温度所需要的功率,
是因为空气对流冷却热线,而将热线维持在恒定温度所需要的功率, 是电能在导线中传导所消耗的功率。
是电能在导线中传导所消耗的功率。 ,因为导线的时间响应很短(大约1秒)而被忽略。
,因为导线的时间响应很短(大约1秒)而被忽略。
方程(1)中所示的蒸发项(即 )可以用传感器导线长度(
)可以用传感器导线长度( )、直径(
)、直径( )、温度(
)、温度( )、空气温度(
)、空气温度( )、热容量(
)、热容量( )、蒸发潜热(
)、蒸发潜热( )和LWF(即速度(
)和LWF(即速度( )和LWC(
)和LWC( )的乘积)来表示:
)的乘积)来表示:
 (2)
(2)
通过连列方程(1)和方程(2),我们可以求解得出lwc:
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:14903字
相关图片展示:
该课题毕业论文、开题报告、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找;


