Contents
1. Introduction 1
1.1 Impact of Air Pollution on Daily Life 1
1.2 Major Influential Meteorological Factors within the ABL 1
1.3 Previous Research and Development 3
1.4 Main Content of the Thesis 4
2. Governing Equations and Methods 4
2.1 Governing Equations 5
2.2 Numerical Schemes 6
3. Results and Discussions 7
3.1 Verification of the Model 7
3.1.1 Theoretical Solution 7
3.1.2 Numerical Solution 9
3.2 Two-Dimensional Diffusion Simulation 12
3.2.1 Pollutant Diffusion of Three Point Sources 13
3.2.1.1 Right Triangle Distribution 13
3.2.1.2 Linear Distribution 17
3.2.2 Pollutant Diffusion of Four Point Sources 21
3.2.2.1 Square Distribution 21
3.2.2.2 Triangular Distribution 23
3.2.2.3 Linear Distribution 25
3.3 Three-Dimensional Diffusion Simulation 28
3.3.1 Diffusion when Eddy Diffusivity Remains Constant 29
3.3.1.1 No Wind Speed Condition 30
3.3.1.2 Components of Wind Speed Equal 1 m/s 31
3.3.2 Eddy Diffusivity Equals an Empirical Expression 33
4. Conclusions 36
References 37
Acknowledgements 41
Simulations of Pollutant Diffusion under Different Meteorological Conditions
Li, Zhijie
School of Atmospheric Physics , NUIST , Nanjing 210044 , China
Abstract : Pollutant enters into the atmospheric boundary layer (ABL) after discharged from surface pollution sources, which has a great influence on human life. The diffusion of pollutant within the ABL is affected by various meteorological conditions, such as radiation, wind speed and turbulent mixing. In order to estimate the effect of different factors on the diffusion, especially the wind speed, in this thesis, finite difference method is used to solve the diffusion equation of pollutant. The solution is firstly compared with the theoretical solution, which verifies the correctness of the numerical model. Moreover, the numerical model is then extended to three dimensions. By considering the vertical mixing between different layers, based on the one-dimensional and two-dimensional models. In this thesis, we obtained the spatial and temporal evolution of pollutants under different wind speed conditions for different types of pollutant source distribution, which is of guiding significance for the planning and locating of industrial zones in cities.
Keywords : Diffusion equation; Meteorological condition; Three-dimensional simulation; Distribution types
1. Introduction
The value of pollutant concentration in local area is affected by two factors, the emission source[1] and the meteorological conditions[2-3]. Pollutant emitted from sources is the root cause of atmospheric pollution[1]. However, within a certain time period, the releasing rate of pollutant from sources can be considered as constant. Therefore, meteorological conditions have become the decisive factor which significantly influence the air quality.
1.1 Impact of Air Pollution on Daily Life
Most pollutant sources are close to the surface of the Earth. Pollutant emitted from sources enters into the atmospheric boundary layer (ABL) firstly, and usually stays within it. It is in this shallow layer that our dwellings are constructed, our crops are cultivated and most of our activities take place[3]. Therefore, high-concentration pollutant events within the ABL have pronouncedly negative influences on human life in many aspects. Species of pollutant entering into the ABL mainly include CO, NOx, SO2 and ozone[4]. The primary pollutants can be converted into secondary pollutants, such as acid precipitation, photochemical smog and aerosol haze, after a series of complicated oxidation[5][8].
In construction industry, acid precipitation has a corrosive effect on marble stones and sculptures due to the effective component of [5-7]. Moreover, the strong oxidizability of photochemical can shorten the life span of materials[8-10].
For the agriculture and forest, a high concentration of ozone damages the structure of leaves, leading a reduction in crop yield and forest degeneration[11][12]. In addition, climate change mainly resulted from increasing concentration of CO2 has influenced the species of plant distribution and their growth period[13].
In human life, all of these pollutant are toxic to the health of human in the aspect of skin, eyes, respiratory and so on[14-16]. Moreover, the present of photochemical smog and aerosol haze can decrease the air visibility, which leads to the traffic jam[17].
Due to the existence of polluted air in the ABL, changes in atmospheric composition and structure within it can have a direct impact on human life.
1.2 Major Influential Meteorological Factors within the ABL
In most cases, the atmosphere can dilute pollutants to levels that humans can afford due to their own purification capabilities. However, under different meteorological conditions, the diffusion and dilution capacity of the atmosphere is also different. The meteorological factors which can affect atmospheric diffusion mainly include: wind and turbulence, vertical distribution of temperature, radiation and cloud, and properties of the underlying surface[3].
- The diffusion capacity of the atmosphere within the ABL depends on the turbulent mixing to a large extent. Turbulence presents as irregular and random activities, and it can mix smoke plumes with ambient air, mainly in the vertical direction[3][18].
- Wind Speed (especially the mean wind) can transports quantities out of the local area in a relatively short time period, such as heat, momentum, moisture, and the pollutants. The value of transport flux is dominated in the horizontal direction by the mean wind[3][18].
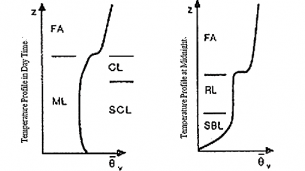
- The stability of the atmosphere is one of the most important factors that affect the atmospheric diffusion. When , where denotes the potential temperature, the atmospheric stratification is stable which is known as an inversion temperature layer. A high degree of stability inhibits the diffusion of pollutants[19]. On the contrary, means that the stratification is unstable. An unstable state can enhance vertical convection which contributes to diffusion of pollutants. Figure 1 shows the vertical profile of virtual potential temperature in the ABL in the day time and at midnight[3].
- Clouds have indirect effects on the diffusion. When the clouds present in the mixing layer, we can call the mixing layer subcloud layer[3]. Clouds can reflect solar radiation, which reduces direct solar radiation reaching the ground. Moreover, clouds strengthen the reverse radiation of the atmosphere and reduce the long-wave radiation on the ground. Therefore, the clouds can reduce the vertical gradient of the temperature, and therefore, affect the atmospheric stability [20].
- Properties of the underlying surface also influence the transport and dilution of the pollutant. Properties of underlying surface mainly affect the meteorological conditions in two aspects. First, the thermal properties in the horizontal direction of the underlying surface can change the distribution of atmospheric temperature within the ABL by the thermal process. The second aspect is the dynamic process. The wind shear in the boundary layer is changed to affect the intensity of turbulence in the boundary layer, due to friction force by different roughness of the underlying surface[3].
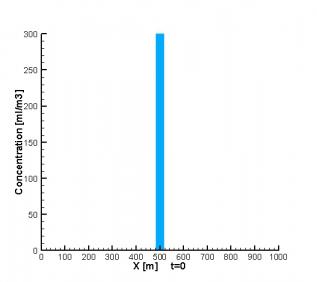
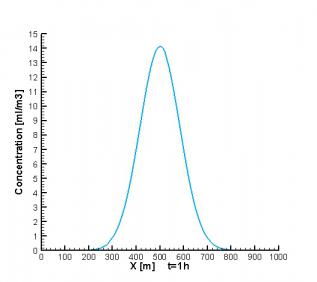
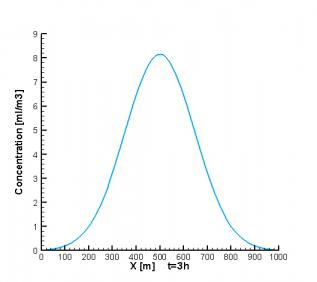
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:78046字
相关图片展示:
该课题毕业论文、开题报告、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找;


