论文总字数:20953字
目 录
摘要.....................................................Ⅰ
Abstract.................................................Ⅱ
0.引言....................................................1
1.研究地区和研究方法......................................1
1.1 资料来源................................................................1
1.2 研究地区概况............................................................1
1.3 研究方法................................................................2
1.3.1 标准化降水指数SPI .................................................2
1.3.2 气象干旱年份的确定(MDY)...........................................3
1.3.3 危险性分析(DHI)...................................................3
1.3.4 暴露性分析(E).....................................................4
1.3.5 干旱综合风险评估....................................................4
1.3.6 反距离权重法(IDW).................................................5
1.4 数据处理................................................................5
2.结果与分析..............................................5
2.1 气象干旱年份的确定......................................................5
2.2 夏玉米干旱特征分析......................................................6
2.2.1 干旱时间变化特征....................................................6
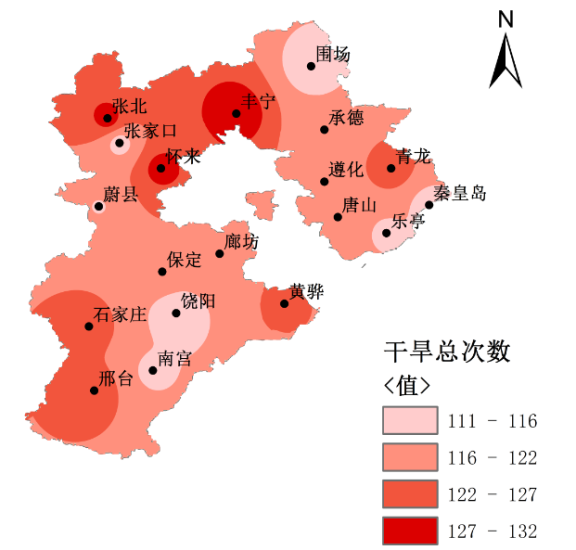
2.2.2 干旱空间分布特征....................................................7
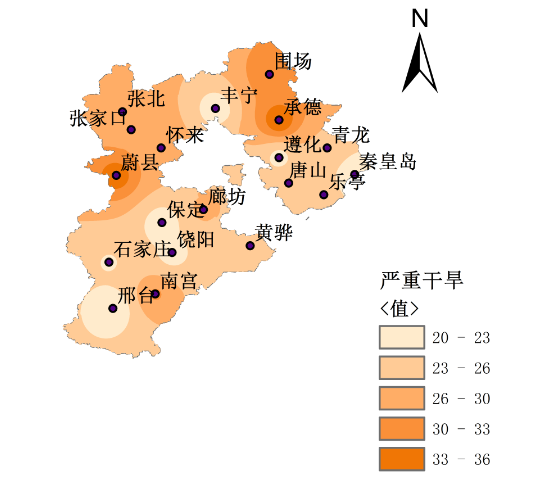
2.3 夏玉米干旱危险性指数....................................................8
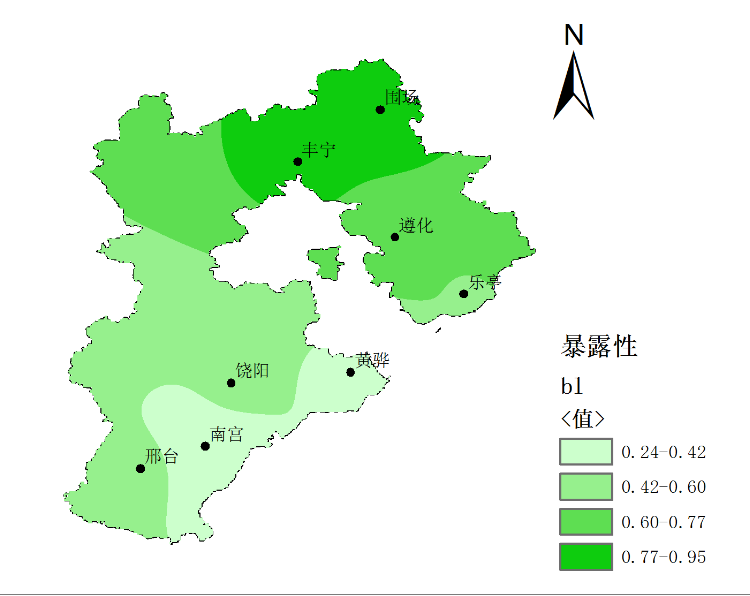
2.4 夏玉米干旱暴露性指数...................................................10
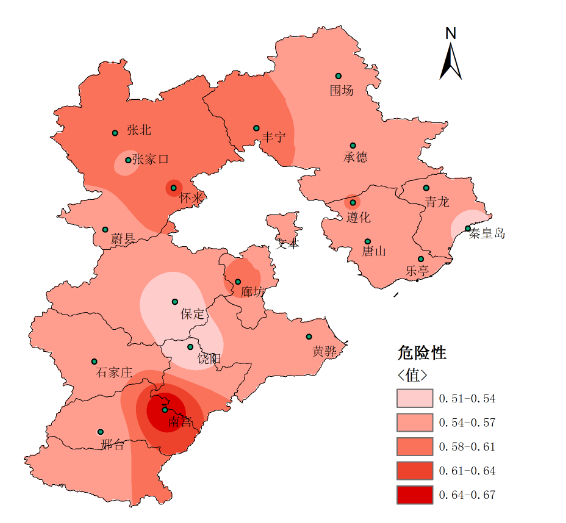
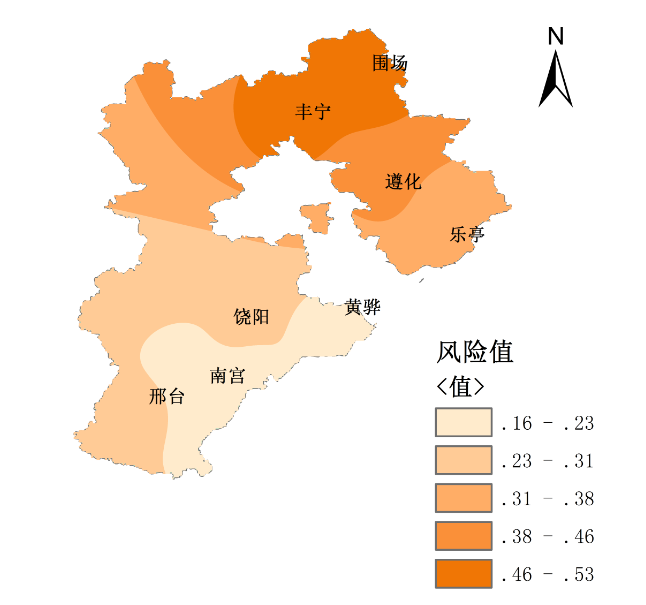
2.5 夏玉米干旱风险综合评估.................................................10
- 讨论...................................................11
- 结论...................................................13
参考文献.................................................13
致谢.....................................................16
河北省夏玉米生长季干旱特征及干旱灾害风险评估
陈曦
,China
Abstract:Drought is one of the meteorological disasters affecting grain production in China. It has an important effect on ensuring grain yield and guiding agricultural production to conduct a study on drought characteristics analysis and to establish a reasonable risk assessment model of drought disaster. Based on the meteorological data,summer maize sown area and yield data of 19 sites in Hebei Province, the occurrence of drought years in Hebei Province was analyzed, and uses the theoretical framework of drought risk assessment to establish drought risk assessment model, according to hazard risk , vulnerability and the drought characteristics of summer-maize growing season. The results showed:(1)The high incidence area was concentrated in the central of Hebei Province, in which the frequency of drought occurred nearly 50% in Huailai and Weixian. Meanwhile,The drought frequency in both of northward and southward gradually decreased, as the frequency of eastern area was the lowest. (2) The harm index of Hebei Province tended to be overall high , more than 0.5. High value distributed in the southern and western area.The highest station, Nangong whose dangerous index attained to 0.67.(3)Exposure of Hebei Province had a decline from north to south, the northern Weichang station exposed the highest, reaching 0.95. (4) Compared to exposure,distribution of drought risk had the same tendency,from north to south, a decline happened.The highest risk of drought in the Weichang station, reaching 0.53. (5) Drought characteristics of summer maize showed,drought frequency increased througout June to September,which was a period when summer maize grew while drought degrees developed . From spatial distribution,drought characteristics and occurrence were the highest in the northwest, southwest and eastern parts of Hebei Province, and the serious drought occured in the Midwest.
Keywords: Standardized Precipitation Index(SPI); Summer-maize;Drought characteristics;Drought risk assessment
0.引言
影响我国作物产量的气象灾害中,干旱造成的经济损失十分惊人。据统计,每年由于干旱造成的作物减产约占因气象灾害导致的经济总损失的50%[1]。依据IPCC第五次评估结果,未来地表温度将会持续升高,同时中纬度地区的平均降水会减少[2-3],使干旱发生的频率增多,强度更强,因此,干旱风险评估引起了许多研究人员和决策部门的重视。在我国黄淮海区域,夏玉米生长季处于盛夏,气温高,蒸散量大,水分分布不均匀,干旱频率高,而河北省位于黄淮海北部[4],是我国玉米主产区之一,其总产量近年来始终维持着较高水平,但由于水资源分布不均匀,不合理应用,使得河北省发生干旱的频率逐年增加,据相关部门统计,河北省春旱发生的频率为60%~80%,初夏时节干旱发生率为55%~90%[4],并且干旱持续时间长,范围广,造成玉米减产。
针对目前的干旱状况,不少学者根据旱灾的各种特点以及不同的指数,取得众多研究进展。国内的学者,郝晶晶[5]等利用PDSI指数分析指出,在未来的60a里,干旱将成为黄淮海平原长期面临的气候灾害;李森[6]等对逐年干燥度变化趋势的分析表明,黄淮海地区干湿区域间的差别有愈加显著的趋势,即半干旱区会更干旱,而半湿润和湿润区的湿润度程度增加;武建军[7]等对黄淮海平原干湿状况研究表明,研究区域内有相当大面积的区域呈现偏干趋势;沙莎等[8]学者认为植被状态指数(VCI)能更好描述干旱情况,结合遥感监测,被广泛应用与各种研究业务;目前来说,干旱评估结合了多种手段,卫星监测与各类干旱指数共同使用,通过监测植被的生长状况分析干旱情况,例如NDVI指数。国外学者从其它角度解释干旱成因,Abdoul-Raouf Sayadi Maazou等[9]利用生物学方法描述干旱特征,从基因学角度和玉米转基因品种入手,发现玉米在开花期和灌浆期易受干旱危害;Vicente-Serranoetal[10]等通过标准化降水指数的基础上,引入潜在蒸散,构建标准化降水蒸散指数,该指数适用于气候变暖背景下的干旱监测与评估,该方法融合了PDSI对蒸散的响应,而标准化降水指数的多种优点在全球各区域的应用检验中得到了很好的验证,目前用于多尺度的干旱监测与评估。近两年针对不同作物、作物生育期,干旱风险评估和干旱特征的分析很多[11-19],但较少学者利用标准化降水指数(SPI)对河北省夏玉米生长季干旱特征进行描述并建立干旱风险评估模型。
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:20953字
相关图片展示:
该课题毕业论文、开题报告、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找;


