论文总字数:19428字
目 录
摘要………………………………………………………………………I
Abstract……………………………………………………………….….II
1 引言……………………….…………….……………………………1
1.1 研究背景……………………….…………….………………………………………………1
1.2 研究进展……………………….…………….…………………………………………1
1.2.1 水体温室气体通量的主流研究方法……………………….……….…….……1
1.2.2 水体温室气体排放的途径……………………….…………….…….…………2
1.3 研究内容……………………….…………….…………………………………………3
2 研究区域与研究资料…….…………….……………………………3
2.1 全椒县鱼塘站点简介……………………….…………….…….………...……………3
2.1.1 全椒县地理位置及气候特征……………………….………….….……………3
2.1.2 全椒县鱼塘水体水文特征……………………….…………….….……………4
2.2 资料与方法……………………….…………….………………………………………4
2.2.1 CO2通量计算方法——薄边界层法…………………….….…………….……4
2.2.2 CO2浓度测定方法——顶空平衡法………………………..…………….……4
2.2.3 其他气象要素观测的仪器和方法……………………….….………….………5
3 结果分析…….…………….…………..………..……………………5
3.1 鱼塘水体气象要素的时间变化特征……………………….………...…..……………5
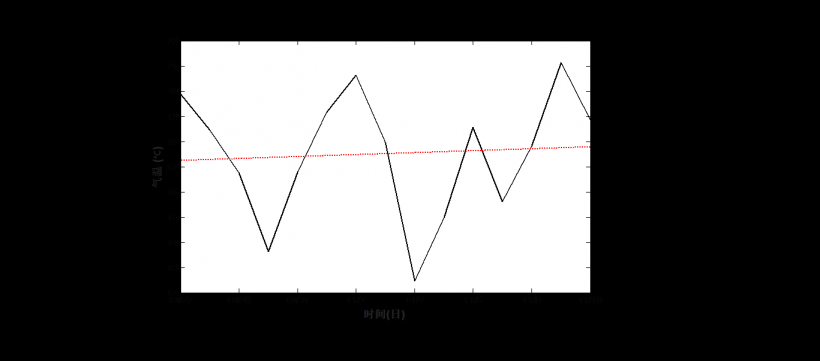
3.1.1 气温变化特征……………………….…………….……………………….……5
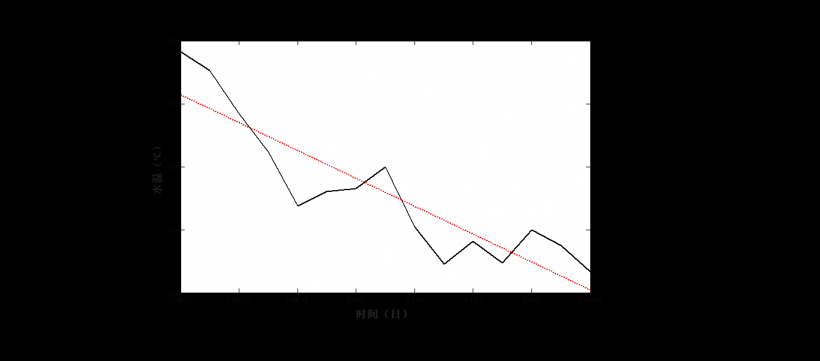
3.1.2 水温变化特征……………………….…………….……………….……………6
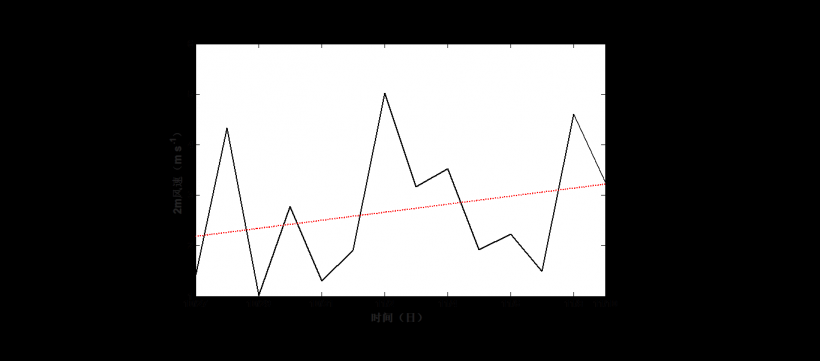
3.1.3 风速变化特征……………………….…………….………………….…………6
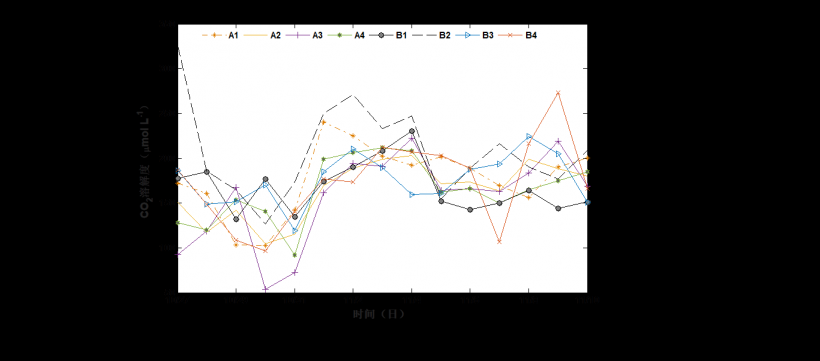
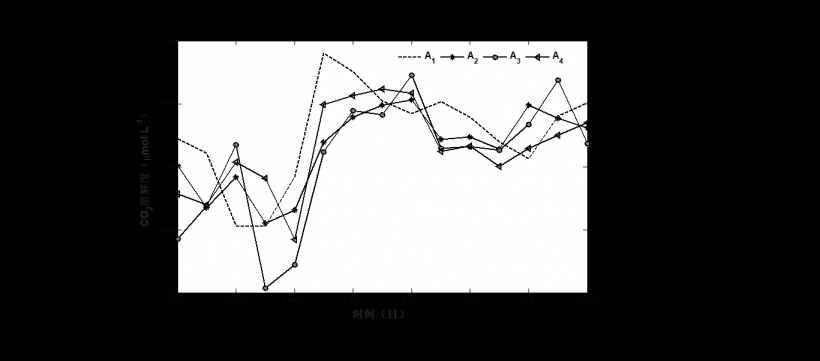
3.2 鱼塘水体CO2溶解度的时间变化特征……………………….…………….…………7
3.3 鱼塘水体CO2溶解度的影响因素……………………….…………….………..……10
3.3.1 鱼塘水体CO2溶解度与气温的关系……………………….…….………...…10
3.3.2 鱼塘水体CO2溶解度与水温的关系……………………….……...……….…10
3.3.3 鱼塘水体CO2溶解度与风速的关系……………………….…………………11
3.4 鱼塘水体CO2通量的时间变化特征……………………….……………...…………12
3.5 鱼塘水体CO2通量的影响因素……………………….…………….……..…………14
3.5.1 鱼塘水体CO2通量与气温的关系……………………….…………...…….…14
3.5.2 鱼塘水体CO2通量与水温的关系……………………….……..……….……15
3.5.3 鱼塘水体CO2通量与风速的关系……………………….……..……….……16
4 结论….………….………….………….………….………..….……16
4.1 鱼塘水体CO2通量的时空变化特征……………………….………….….…………16
4.2 鱼塘水体CO2通量的影响因素……………………….…….……….………………17
4.3 本文研究特色…………………………..……………….…………….………………17
参考文献….………….………….………….………….………….……17
致谢….………….………….………….………….…………….………20
基于薄边界层法的鱼塘CO2通量观测研究
余俊瑞
, China
Abstract:Inland water bodies play important role in global carbon cycle, but the importance of small ponds is seriously underestimated. In this paper, thin boundary layer method was used to measure the CO2 flux at the water-air interface under field condition. The short-term temporal and spatial variabilities of the CO2 flux at the water-air interface of the fish pond in Quanjiao county were investigated, and the meteorological factors affecting the CO2 solubility in the water and the CO2 flux over the fish pond were also analyzed. The experimental results showed that the fish ponds in Quanjiao County were generally the source of atmospheric CO2. During the observation period from 27 October to 10 November 2017, the average CO2 daily flux of Pond A was 135.9 mmol∙m-2∙d-1, and the average CO2 daily flux of the Pond B was 169.9 mmol∙m-2∙d-1. The short-term temporal variation of CO2 flux in fish ponds was mainly due to the fluctuation of meteorological variables. There was no significant correlation between CO2 flux and temperature and water temperature, but there was strong positive correlation between CO2 flux and wind speed. The CO2 flux of fish ponds has a strong spatial variation. The average CO2 flux of fish ponds with contaminated water was significantly greater than the average CO2 flux of fish ponds with clear water. The experimental research results of this paper can provide theoretical reference and concrete data support for the study of terrestrial ecosystem carbon cycle, global warming, and ecological environment management of lakes and fish ponds.
Key words:Small pond; CO2; Concentration; Flux; Fish pond
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:19428字
相关图片展示:
该课题毕业论文、开题报告、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找;


