论文总字数:22950字
目 录
摘要 1
Abstract 2
1.绪论 3
1.1 g-C3N4的制备 3
1.2 g-C3N4的形貌 3
1.3 g-C3N4的应用 4
2. S原子掺杂g-C3N4的特性研究 6
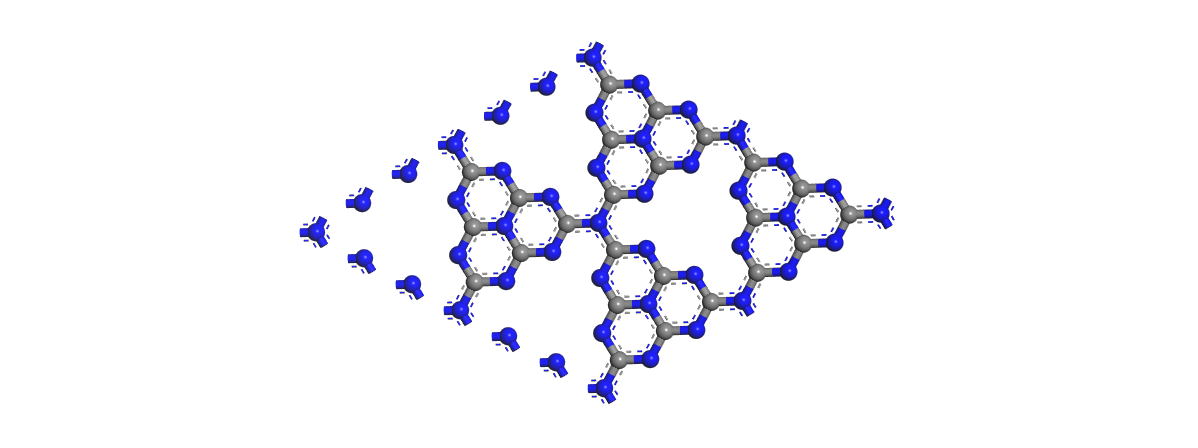
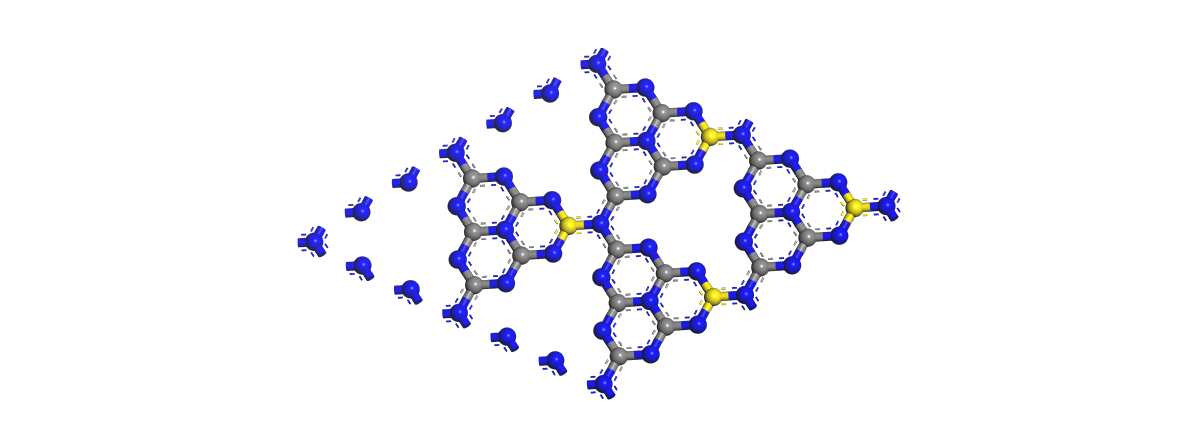
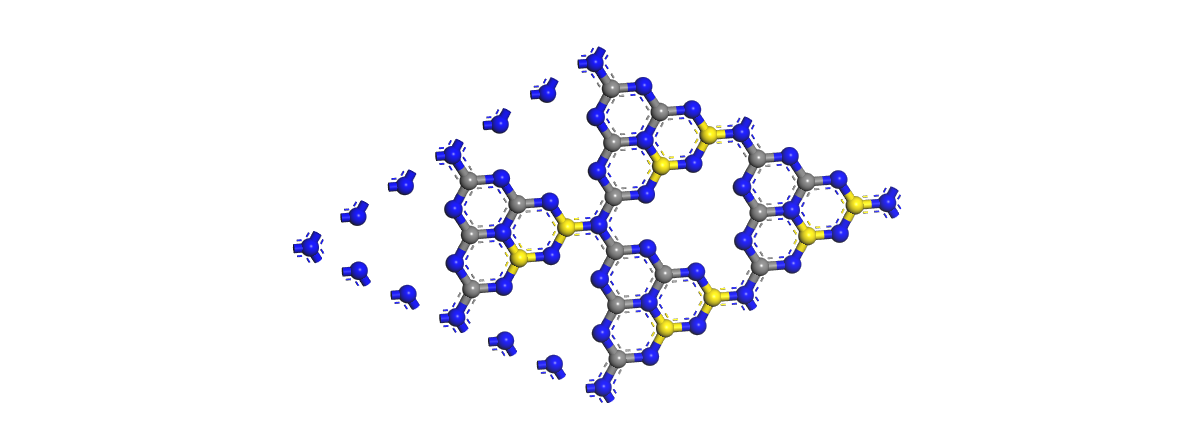
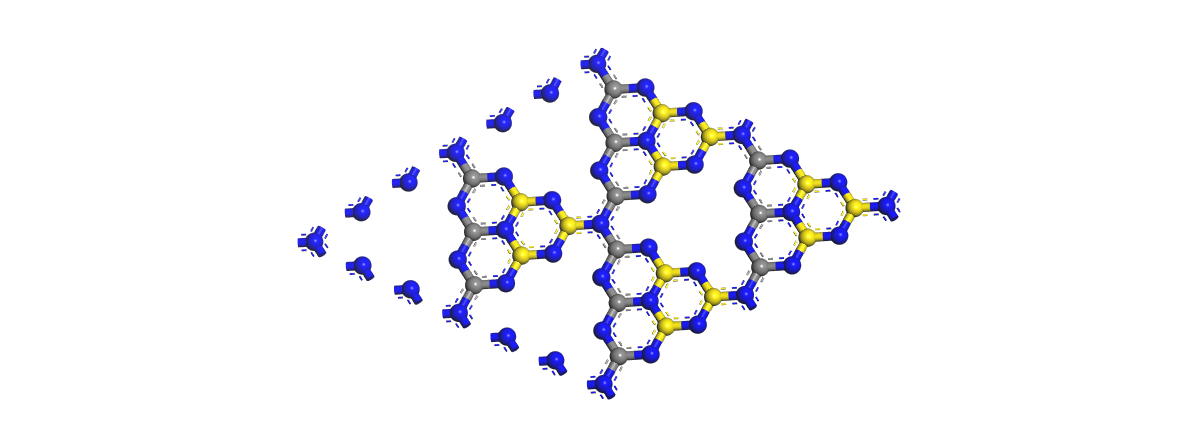
2.1理性模型和计算方法 6
2.2不同浓度S掺杂g-C3N4的电子特性研究 8
2.2.1能带结构 8
2.2.2 态密度(简称TDOS)和分波态密度(简称PDOS) 9
2.3 不同浓度S掺杂g-C3N4的光学特性研究 14
3. P原子掺杂g-C3N4的特性研究 22
3.1模型的建立和计算 22
3.2 不同浓度P掺杂的g-C3N4电子性质的研究 24
3.2.1能带结构 24
3.2.2 态密度图和分波态密度图 25
3.3 不同浓度P掺杂g-C3N4的光学特性研究 30
4 结论 38
参考文献 39
致谢...................................................................................40
二维碳氮化合物的光电特性研究
秦玉霜
,China
Abstract:In this paper based on the first principle, to pure g-C3N4 and doped with different concentrations of S and P of g-C3N4 were calculated, including the band structure, density of States and optical properties. The results show that the pure two-dimensional g-C3N4 light absorption region mainly in blue and ultraviolet region, consistent with the experimental results reported.
After doping S and P, the band gap decreases, near the Fermi level appeared the new band, which is beneficial to the electron transition. At the same time between the wavelength 600-1000nm, light absorption efficiency is significantly enhanced. This showed that doping significantly enhances the absorption efficiency in the light of the visible and near infrared region. By changing the doping concentration of impurities, won the best doping concentration. According to the density of states and other information, to S and P controlling the band gap makes a detailed analysis, combined with absorption spectra, confirmed the results of the research. The results of this paper are expected to provide theoretical support for improving the utilization efficiency of g-C3N4 in the light of the sun, and to provide theoretical support for the efficient photocatalytic degradation and decomposition of aquatic hydrogen.
Key words: g-C3N4 ;band density of states ;density ;optical properties ;doping.
1.绪论
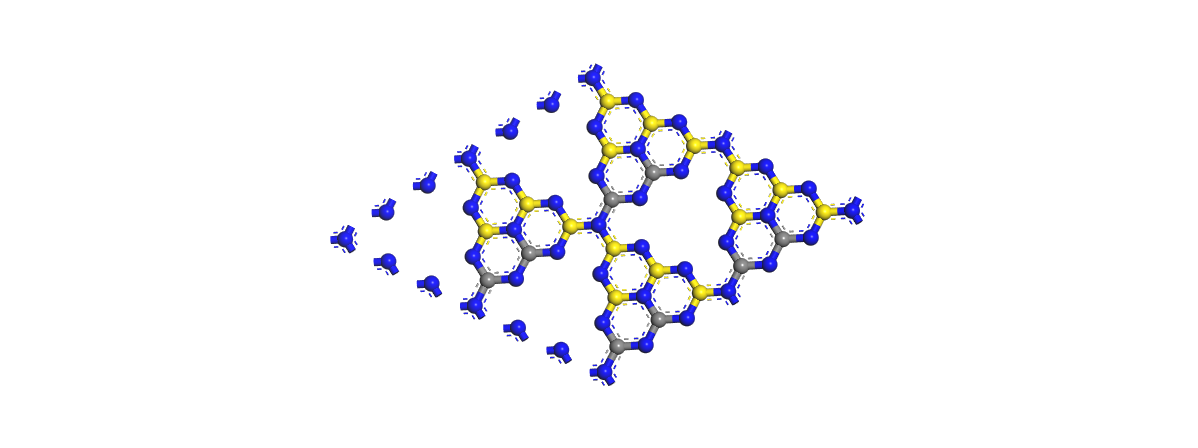
1989年,Liu和Cohen[1]用C原子替换了β-Si3N4晶体中的Si原子,采用第一赝势能带法,通过局域密度近似,预言了自然界中存在β-C3N4的存在。到了1996年,Teter和Hemley[2]采用第一性原理的方法对C3N4进行了重新计算,发现了g-C3N4(石墨相)的存在,它是软质相,与石墨烯结构类似,图1-1为g-C3N4的二维平面结构图。

图1-1 g-C3N4的二维平面结构图
1.1 g-C3N4的制备
到目前为止,制备g-C3N4的方法普遍有两种:物理方法和化学方法。物理方法主要包括离子注入、反应溅射、激光溅射等,这些方法能制备出无定形状态的g-C3N4薄膜。另外还可以使用三聚氰氯和氮化锂采用机械球磨的方法制备粉末状的g-C3N4。化学方法包括固相反应、电化学沉积、热聚合等方法,下面我们会重点介绍固相反应发法。
固相反应法采用含有三嗪或七嗪结构的化合物作为反应物,例如C3N3(NH2)3、C3N3Cl3,C6N7(NCNK)3、C6N7Cl3等。因为三嗪结构和七嗪结构不仅可以降低碳氮成键的反应能,而且可以促进类石墨层状晶体结构的产生[3]。
zhang等[4]以三聚氰胺和三聚氰氯固相反应制取g-C3N4,反应条件设置为,压力1.0-1.5GPa,温度500-550℃。实验得到的结晶很好,但是仍然含有杂质C和H。
Guo等[5]将三聚氰氯和氧基钠粉末混合,同时通入适量的苯,在高压釜内反应,温度设置为180-220℃,在高压釜中反应8-12个小时后也得到了结晶很好的g-C3N4晶体,C与N比值为0.72,结果与理论值相当的接近。
Tragl等[6]则使用三聚氰氯作为反应的前驱体,采用Li2(CN2)和Li3(BN2)两种化合物作为氮源,在600℃高温的条件下反应制备g-C3N4晶体。通过使用透射电镜(TEM)、X射线能量色散谱(EDX)、红外光谱(IR)的分析,发现晶体中有两种结构分别为三嗪环结构和七嗪环结构,C与N比值为0.75,与理论值更为接近。
1.2 g-C3N4的形貌
材料的形貌状态通常情况下能影响材料的性能,在合成过程中控制实验的反应条件,或者采用不同的制备方法都可以改变材料的形貌特征。为了得到g-C3N4更多不同的价值,自从人们发现了g-C3N4,就同时尝试了各种方法来制备不同形貌结构的g-C3N4。就现在来看,g-C3N4的纳米片、纳米棒、纳米带等各种各样的结构已经陆续被人们制备出,它们各有其用途。
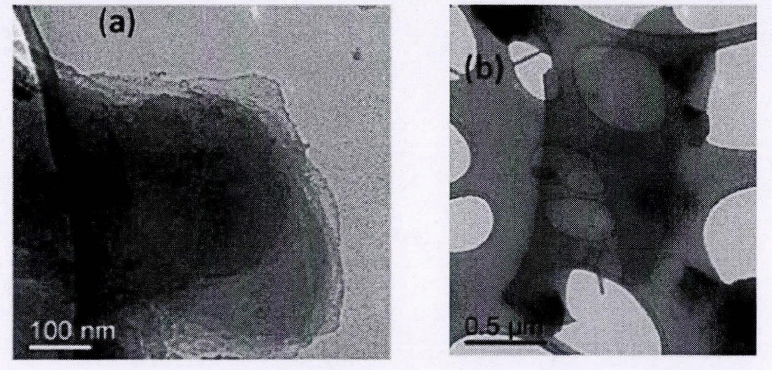
图1-2 g-C3N4纳米片和量子点的透射电镜(TEM)图
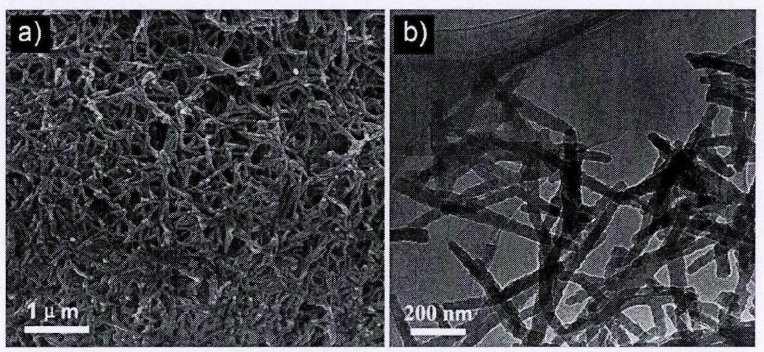
图1-3 g-C3N4纳米棒的扫描电镜(SEM)图和透射电镜(TEM)图
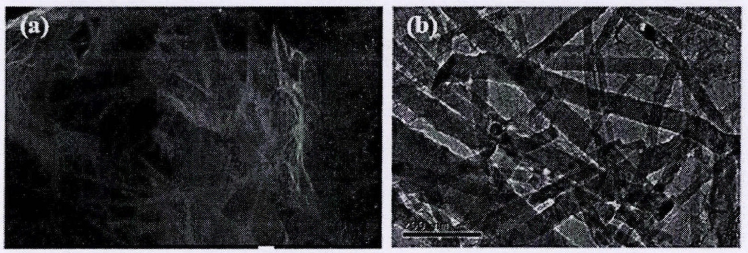
图1-4 g-C3N4纳米带的扫描电镜(SEM)图和透射电镜(TEM)图
1.3 g-C3N4的应用
剩余内容已隐藏,请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:22950字
相关图片展示:
该课题毕业论文、开题报告、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找;