二维Ti3C2-S复合正极的制备和电化学性能毕业论文
2020-05-24 12:34:32
摘 要
目前市场上的LIBs,由于其理论比容量大小受限而很难满足社会发展的要求。但Li-S电池用硫作为正极,其理论比容量可高达1675 mA·h/g,其理论能量密度可高达2600瓦时/千克,硫的低毒性,低成本及硫资源丰富,使Li-S电池成为最具有发展前景的二次电池体系之一。但S元素导电性差,单质硫为绝缘体,由于Sx2-的穿梭效应,其循环容量衰减较快,活性物质的利用效率较低。新型二维过渡金属C/N化合物MXene,其化学式为Mn 1Xn,M是过渡金属,X是C或者N,n=1、2、3。据报道,MXene具有良好的导电性、透光性、磁性、低温热电性和能量存储等诸多新颖的性能。而Ti3C2纸具有优于石墨烯纸的导电性,出色的机械柔性和强度而有望在锂硫电池领域得到应用。
本实验采用HCl和LiF作为腐蚀剂,对Ti3AlC2 MAX相进行腐蚀制备出相应的多层Ti3C2 MXene,然后剥离得到少层/单层的Ti3C2 MXene,并制备Ti3C2 MXene纸和与多壁碳纳米管复合的Ti3C2 MXene结构。将Ti3C2 MXene与硫采用熔融蒸汽法、原位还原法制成锂硫电池正极,研究碳纳米管复合、硫的复合方式和载硫量等对Ti3C2-S复合正极的化学组成、显微结构和电化学性能等的影响。结果表明,原位还原法的载硫效果较好,其硫的百分含量可以达到70%左右,但是含硫量高并不一定说明硫的利用率高,本实验通过原位还原法分别制备了含硫量为60%wt,70%wt的正极复合材料,结果表明含硫量为60%时,首次比容量在1210mA·h/g,30次循环后,比容量稍有下降,为1000 mA·h/g,后期循环性能比较稳定,30次循环至100次循环时,比容量衰减不明显。熔融蒸汽法制得的复合正极的电化学性能表明:含硫量为17%时,首次比容量在1150mA·h/g,但第二次循环比容量就下降的比较快,比容量只有800 mA·h/g左右, 100次循环后,比容量下降较多,只有450 mA·h/g左右,后期循环性能比较稳定,但比容量不高。本实验采用SDBS修饰MW-CNTs,再采用原位还原法进行载硫,结果表明,电池的首次放电比容量为1283mA·h/g,推测是因为硫的颗粒大小减小,且导电性好的MW-CNTs包裹在硫颗粒上,提高了整体材料的导电性和活性物质利用率。由交流阻抗谱图可以清楚地看出,含MW-CNTs的电池内阻要小于未加入碳管的MXene@S复合正极的内阻,这间接地说明了MW-CNTs改善了MXene@S复合正极的电子电导率。
关键词:锂硫电池 MXene 二维材料 Ti3C2-S复合正极 电化学性能
Preparation and electrochemical properties of two-dimensional Ti3C2-S composite cathode
ABSTRACT
Nowadays, lithium batteries are difficult to meet the requirements of the development of society due to their limited theoretical capacity. However, Li-S batteries’ theoretical capacity can reach 1675 mA·h / g with sulfur as their positive electrode, and the theoretical energy density of Li-S batteries can reach 2,600 W / kg. The sulfer’s low toxicity, richness in nature and low-cost make Li- S batteries to become one of the most promising secondary battery system. MXene is a new two-dimensional transition metal carbides or carbonitrides, its formula is Mn 1Xn, M represents a transition metal, X represents the element of carbon or nitrogen, n = 1,2,3. Currently MXene surface preparation is accompanied by functional groups. Researches show that MXene has good electrical conductivity, and many other innovative performance transparency, magnetism, and low-temperature thermoelectric energy storage in lithium-sulfur batteries which are expected to be widely used in the field.
In this article, we use HCl and LiF as the etchant to etch Ti3AlC2 MAX phase to prepare the corresponding multilayered Ti3C2 MXene, and then strip it to get single layer or monolayer Ti3C2 MXene, and compose Ti3C2 MXene paper and multi-walled carbon nanotube complexed Ti3C2MXene paper.
We use melted sulfur steam method and in-situ reduction method to prepare lithium-sulfur battery positive electrode materials and research on the effect of carbon nanotubes, composite mode and sulfur loading to performance of chemical composition, microstructure and electrochemical effect . We found that: in-situ reduction of the sulfur method is better, the sulfer percent could reach 70%, but the high sulfur content does not mean high sulfur utilization.In this experiment we prepared 60 % wt, 70% wt sulfer composite positive electrode materials, the results showed 60% one, the capacity is 1200mA·h/g for the first time, 30 cycles later, the capacity decreased slightly to 900 mA·h/g or so, the cycle performance is relatively stable after that, from 30 cycles to 100 cycles, the specific capacity remained relatively stable. Steam method were melted electrochemical properties of the composite positive electrode show: sulfur content of 17%, the first specific capacity 1150mA · h / g, but the second cycle than the capacity has dropped more quickly than the capacity of only 800 mA · h / g or so, after 100 cycles, fell more than capacity, only 450 mA · h / g or so, late cycle performance is relatively stable, but not higher than the capacity. In this study, SDBS modified MW-CNTs, then sulfur-situ reduction method, the results show that the battery initial discharge capacity of 1283mA · h / g, presumably because the sulfur particle size is reduced, and good conductivity MW-CNTs wrapped in sulfur particles to improve the conductivity of the overall material and the active material utilization. Can be clearly seen by the AC impedance spectra containing MW-CNTs battery internal resistance is less than the internal resistance of the carbon tubes not added MXene @ S composite positive electrode, which indirectly illustrates the improved MXene @ S MW-CNTs composite cathode electron conductivity .
Keyword: Lithium-sulfur batteries; MXene; Two-dimensional material; Ti3C2-S composite cathode; electrochemical performance
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 引言 1
1.2锂硫电池简介 1
1.3锂硫电池正极材料研究进展 2
1.3.1硫/多孔碳复合材料 2
1.3.2硫/碳纳米管材料 3
1.3.3硫/石墨烯复合材料 4
1.3.4硫/导电聚合物复合材料 4
1.3.5硫/氧化物复合材料 5
1.4 二维过渡族金属碳/氮化物MXene简介 5
1.4.1 MXene的制备 6
1.4.2 MXene的性能 8
1.4.3 MXene的应用 9
1.5课题提出及意义 11
第二章 实验方法 12
2.1实验原料 12
2.2实验主要设备 12
2.3 实验工艺 13
2.3.1 MAX的腐蚀 13
2.3.2 MXene的剥离 13
2.3.3 MXene Paper的制备 14
2.3.4 不同载硫方法制备复合正极 14
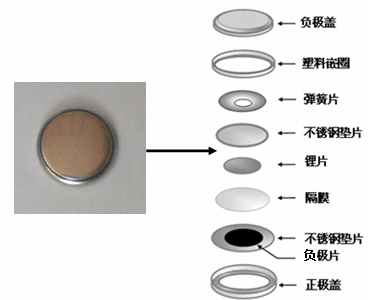
2.3.5 电池组装 14
2.4结构表征和性能测试 15
2.4.1 X射线衍射分析 15
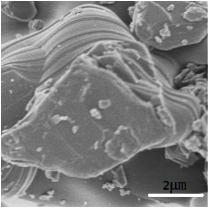
2.4.2 SEM分析 15
2.4.3 X射线光电子能谱分析 16
2.4.4 热重分析(TG-DTA) 16
2.5 电化学性能测试 16
2.5.1 循环伏安测试 16
2.5.2 充放电性能测试 16
第三章 结果与讨论 18
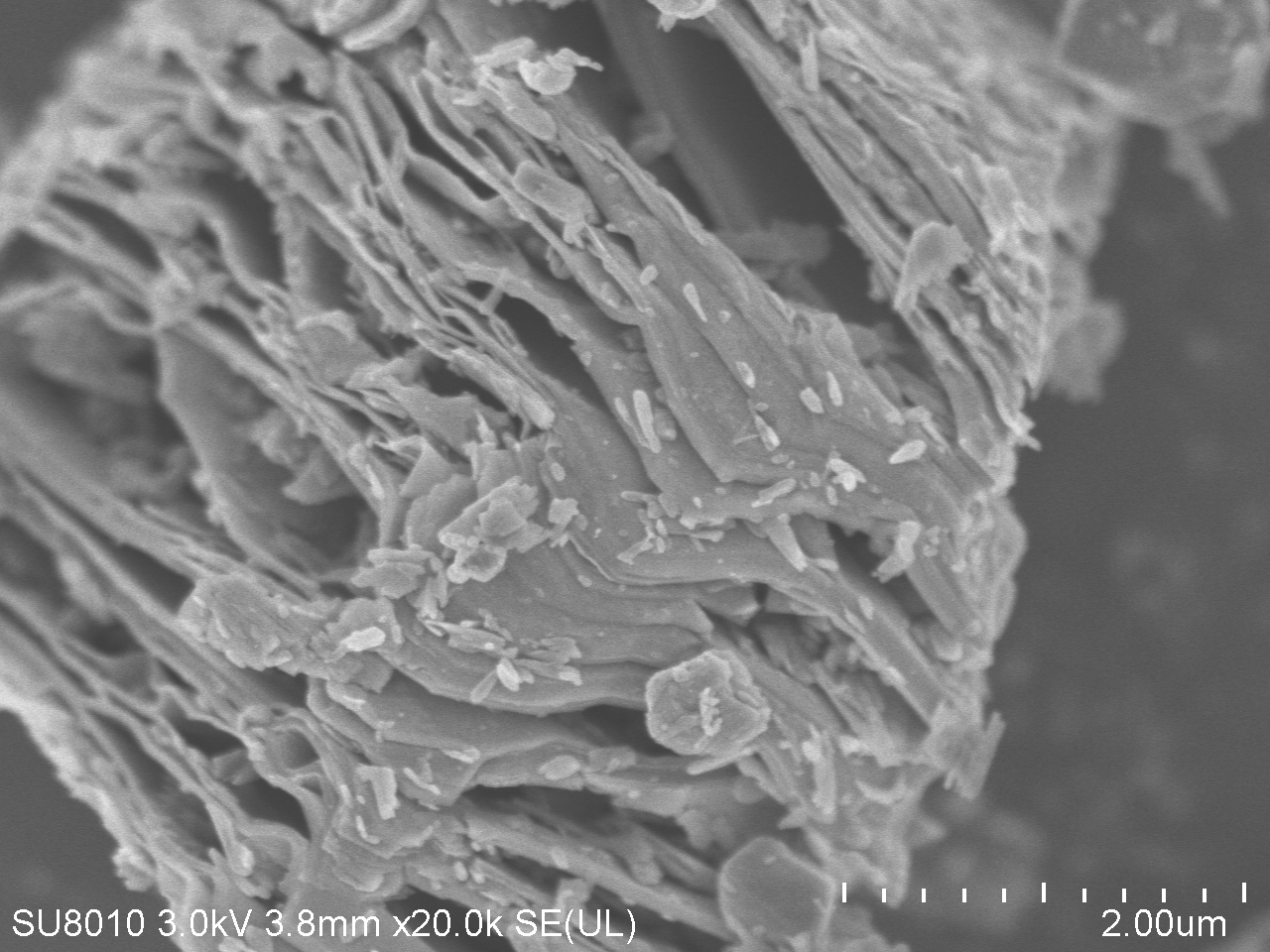
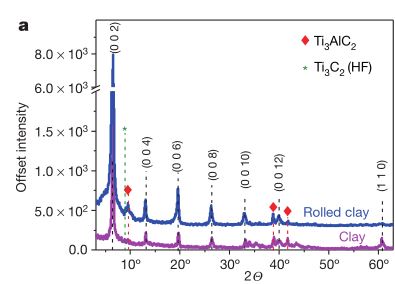
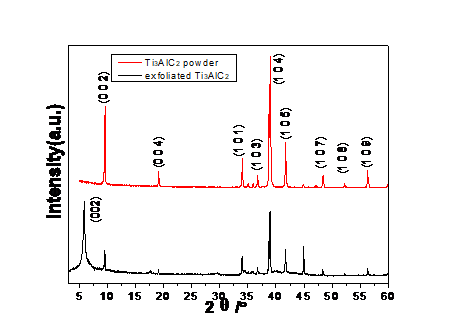
3.1 Ti3AlC2及Ti3C2Tx MXene的表征 18
3.2复合正极材料制备及电化学性能研究 19
3.2.1 原位还原法制备S@ Ti3C2 MXene复合正极材料 19
3.2.2 熔融蒸汽法制备S@ Ti3C2 MXene复合正极材料 24
3.2.3 MW-CNTs对S@ Ti3C2 MXene复合正极材料的影响 27
第四章 结论 30
相关图片展示:


课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



