碳载镍制备及其对镁基氢化物储氢性能的影响毕业论文
2020-05-24 12:34:46
摘 要
氢经济促使社会研发高效、经济、安全的储氢材料,金属镁由于资源丰富、价格低廉、环境友好和储氢容量高等优点,被认为是非常有应用前景的储氢材料,然而其热力学稳定性和吸放氢动力学的性能限制了它的市场化应用进程。本课题组采用氢化燃烧合成与机械球磨的复合制备工艺(Hydriding Combustion Synthesis and Mechanical Milling,HCS MM)显著改善了镁基储氢材料的吸放氢性能,然而其吸放氢温度依旧较高。本课题拟制备不同碳载镍催化剂并通过X射线衍射技术(XRD)、扫描电子显微分析(SEM)、透射电子显微分析(TEM)、差示扫描量热仪分析(DSC)和压力-组分-温度(PCT)研究其微观物相结构及其对镁基氢化物的影响,揭示吸放氢性能与材料结构的内在联系。
本文采用溶液化学还原法制备纳米Ni,高温煅烧法制备碳载镍催化剂,并研究了不同碳载镍催化剂微观结构及其对镁基储氢材料的吸放氢温度的影响。研究表明:纳米Ni在放氢温度方面的催化效果优于微米Ni;合成的Ni/CR催化剂能够明显改善MgH2的放氢热力学性能,在3.0MPa氢压,最佳吸氢温度250oC,其在100s内吸氢量达到5.8wt%;对MgH2-Ni/CR样品的吸放氢曲线进行拟合,结果表明,在放氢过程中Mg晶核的三维扩散过程是其主要的控速步骤。计算得到MgH2-Ni/CR的放氢活化能为86.32KJ/mol,而商业版MgH2的放氢活化能为153 kJ/mol,对比发现Ni@CR的添加有效的降低了体系的活化能,表现出优异的放氢动力学性能。
关键词: 镁基储氢材料 碳载镍催化剂 碳棒 储氢性能
ABSTRACT
The burgeoning of hydrogen economy prompts a lot of scientists to study efficient, economical and safe hydrogen storage materials. Mg is widely considered as a promising, candidate among hydrogen storage materials with great application prospect due to abundance in nature, low cost, environment friendliness and high capacity for hydrogen storage. However, the application of magnesium hydride is severely restricted by its high thermodynamic stability and sluggish hydrogen sorption/desorption kinetics. A combined process of hydriding combustion synthesis (HCS) and mechanical milling (MM) was proposed by our group to prepare Mg-based hydrogen storage materials with excellent properties, but the absorption/desorption temperature was still a technical problem. This research intends to prepare different types of carbon supported Ni catalysts, analyze their microstructures and the influence of them on Mg-based hydride by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) and pressure-composition-temperature (PCT), and explore the interrelationship between the hydriding/dehydriding properties and the microstructures of the HCS MM products.
Nanometer nickel was prepared by solution chemical reduction and carbon supported nickel catalyst by being sintered at high temperature. The paper studied the microstructure and explored the effect of hydrogen absorption/desorption temperature of magnesium-based hydrogen storage material. The results show that nano-Ni is superior than micron Ni with respect to hydrogen desorption. Synthetic Ni/CR catalyst can significantly improve the thermal performance of MgH2, requiring only 100s to reach 5.8wt% hydrogen absorption capacity at 250℃ in 3.0MPa hydrogen pressure. When fitting the hydrogen absorption/desorption curves of MgH2-Ni/CR sample, it is found that the diffusion process of Mg crystal nucleus is the main rate-controlling step in hydrogen desorption. The dehydrogenation activation energy of MgH2-Ni/CR is 86.32KJ/mol, while the commercial MgH2 is 153KJ/mol. It is confirmed that compared with commercial MgH2, Ni/CR effectively reduces the activation energy of the system, showing excellent kinetics performance of desorption .
Key words: Mg-based hydrogen storage materials; carbon supported nickel catalyst; carbon rod; hydrogen storage property
目 录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 引言 1
1.2 储氢方式及其分类 2
1.2.1 气态储氢 2
1.2.2 液态储氢 3
1.2.3 固态储氢 3
1.3 储氢合金 4
1.3.1 储氢合金的分类 4
1.3.2 储氢合金的储氢机理 6
1.4 镁基储氢材料的概述 7
1.4.1 镁基储氢材料的纳米化改性 7
1.4.2 镁基储氢材料的合金化改性 8
1.4.3 镁基储氢材料的复合化改性 8
1.4.4 镁基储氢材料的催化改性 9
1.5 本课题的问题提出及研究内容 10
第二章 实验方法 12
2.1 实验原料与试剂 12
2.2 材料的合成设备 12
2.3 材料的制备 13
2.3.1 纳米Ni的制备 13
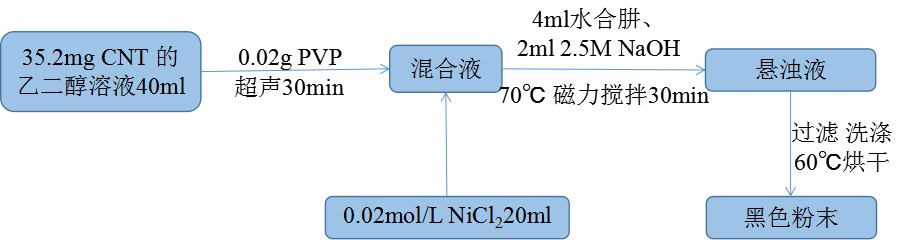
2.3.2 碳棒载镍的制备 14
2.3.3 碳纳米管载镍的制备 14
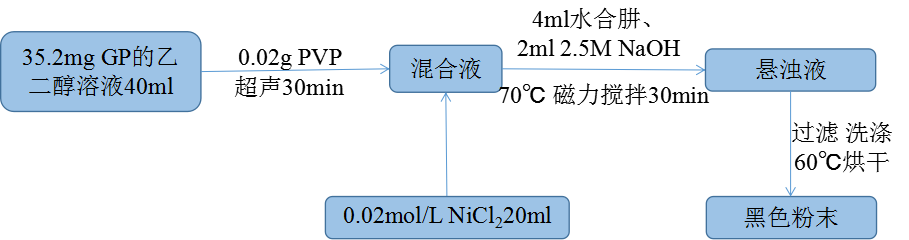
2.3.4 石墨烯纳米片载镍的制备 15
2.4 材料的微观分析及表征 15
2.4.1 X射线衍射分析 15
2.4.2 扫描电子显微镜分析 15
2.4.3 透射电子显微镜分析 16
2.5 储氢性能测试及表征 16
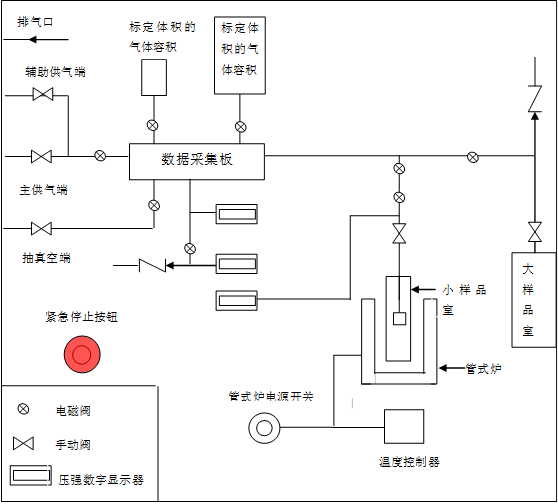
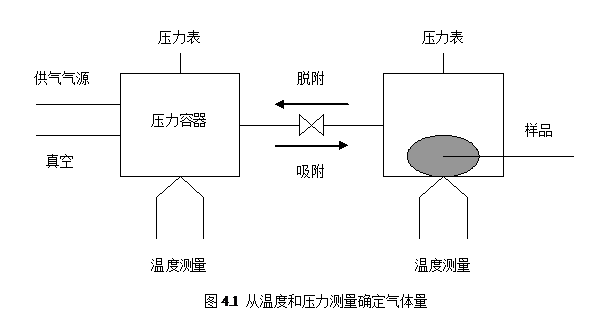
2.5.1 P-C-T测试仪 16
2.5.2 热分析 18
第三章 不同碳载镍对MgH2体系储氢性能的影响 19
3.1、纳米镍的微观结构及其对MgH2性能的影响 19
3.1.1 纳米镍的微结构分析 19
3.1.2 不同镍催化剂的Mg-Ni体系储氢性能研究 20
3.2 不同碳载镍的物相结构及其对MgH2性能的影响 21
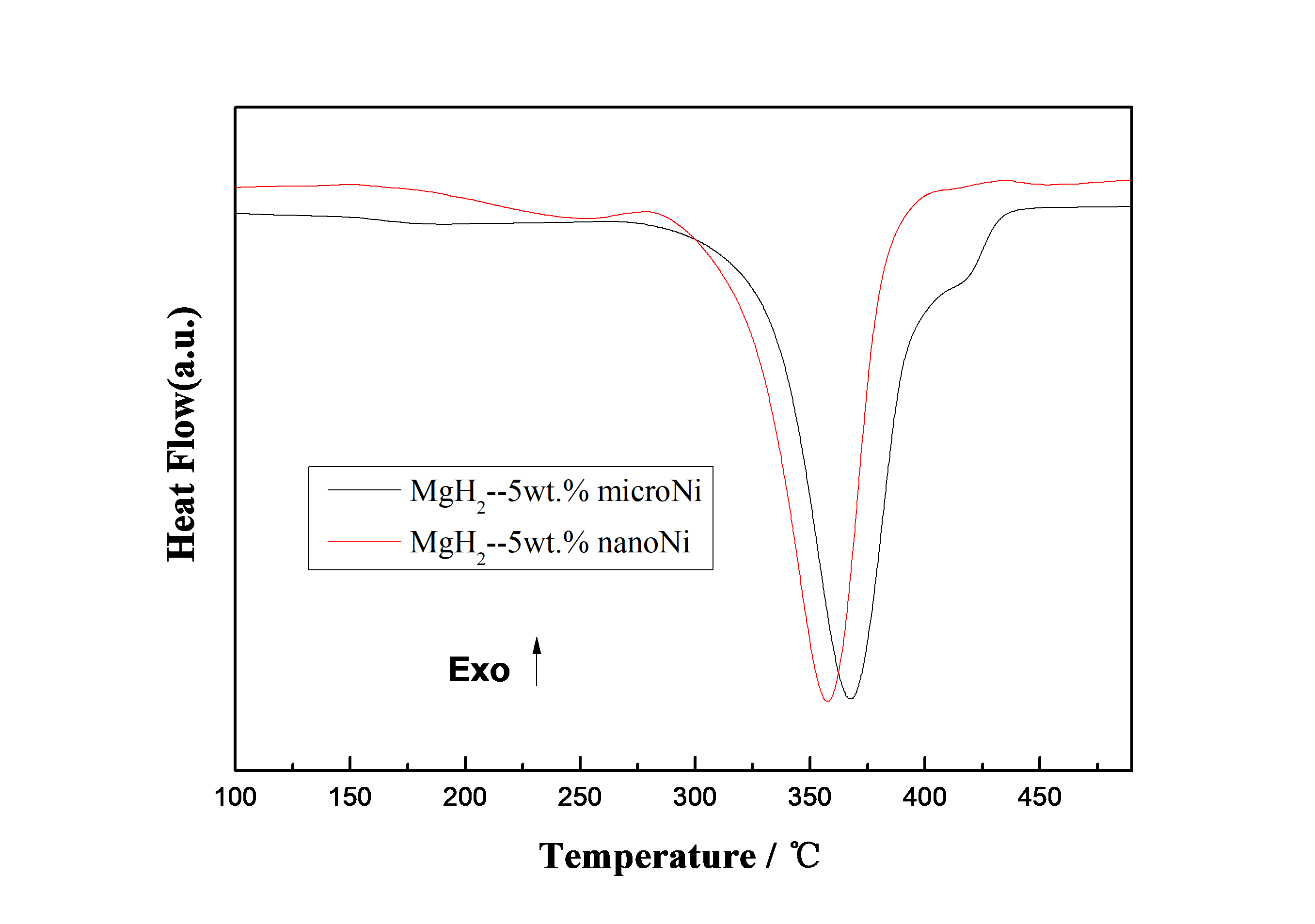
3.2.1 不同碳载镍的物相结构分析 21
3.2.2 不同碳载镍的MgH2-5wt%X体系储氢性能研究 24
第四章 结论和展望 29
4.1 主要结论 29
4.2 展望 30
参考文献 31
致谢 35
第一章 绪论
1.1 引言
回顾社会变迁和历史发展的进程,我们会发现能源在其中有着举足轻重的地位。当前,人类社会的进步越来越依赖于能源,但是,储存有限的煤炭、石油等化石燃料日益枯竭,其过度消耗不仅使能源供给出现了不可持续现状,还造成了环境污染。在这种双重压力下,人们试图寻找新的清洁能源来替代传统的化石能源,以期从根本上解决社会发展所面临的能源危机和环境污染问题。因此,开发可再生能源及其相关技术设备受到了全世界的关注,这有效的推动了太阳能、风能和潮汐能等绿色能源及其相关技术的快速发展。但是,这些清洁能源都在不同程度上具有局限性,如时间局限、空间局限、能源输出的不稳定、能源的转换率低和配套体系不清洁等[1]。
氢能被认为是人类社会未来最理想的清洁能源,原因如下:(1)氢是地球上已知的化学结构最简单、分布范围最广、储存量最大的元素;(2)氢具有高能量密度,标准状况下,燃烧1g的氢气可以产生1.429×105J热能,相当于4.5g焦炭或者3g汽油完全燃烧产生的热能;(3)氢完全燃烧后的产物只有水,对环境没有丝毫污染,水又可以分解为氢气,循环利用。正是如此,使得它在能源载体方面具有不可比拟的优势[2]。但是,要使氢能商业化利用还需要解决氢的制备、储存、运输和转换四个方面的技术难题,而高效的储氢是氢能应用系统中最核心的问题。
相关图片展示:
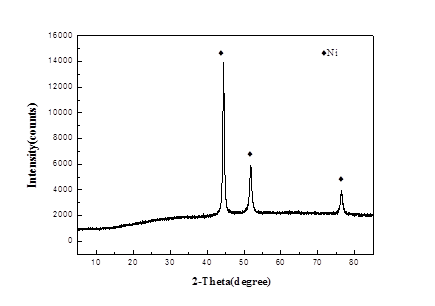

课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



