电镀漂洗水全回收利用处理装置及工艺的研究毕业论文
2020-06-07 21:29:59
摘 要
本研究是在发明专利ZL 2009 10212684.0(循环喷淋法实现电镀废水全部回收利用零排放装置及工艺技术)的基础上改进,原专利未能推广应用的原因是喷淋级数太多导致清洗周期长,同时对复杂工件清洗不易干净。本研究的创新在于:采用了循环喷淋的关键技术,该技术通过循环喷淋可以将逆流漂洗加蒸发浓缩工艺中的很大的漂洗槽缩小几百倍,从而使多级漂洗槽能集中在一很小的空间,从而实现第一级漂洗槽浓度接近镀液浓度可以直接返回镀槽而最后一级水仍能满足清洗要求。因此,本装置解决了现有电镀废水处理技术中存在的问题与不足,可实现电镀废水零排放,能够100%回收从镀槽中带出的镀液,不产生任何废水,所有漂洗水全部回用。
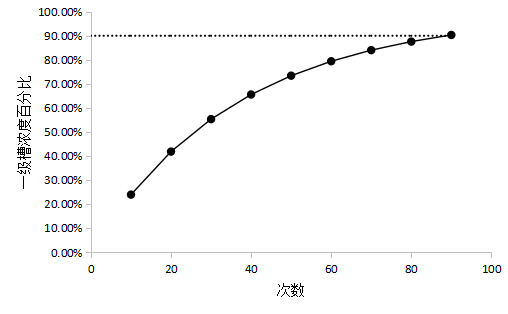
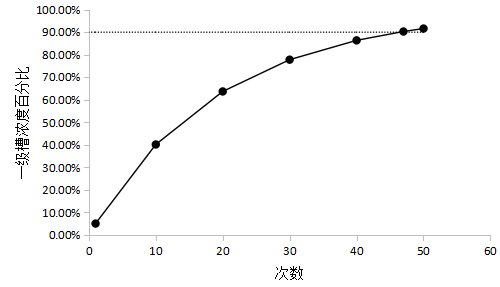
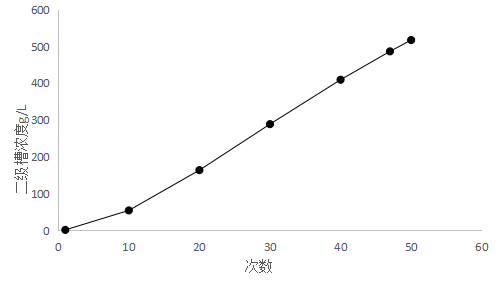
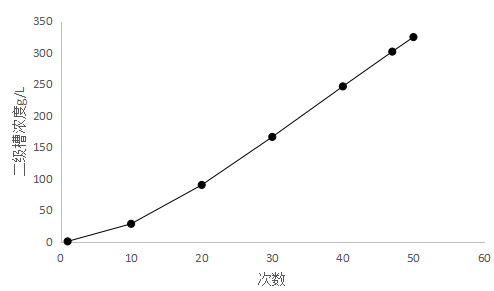
采取氢氧化钠溶液作为模拟镀液来研究一些设计参数,通过多次模拟实验确定,在总漂洗级数固定为3级,且第一级水量为500mL,第二、三级水量均为32000mL,总水量为64500mL时,经过喷淋漂洗,第一级清洗浓缩槽模拟镀液浓度为原模拟镀液浓度的90%,且最后一级清洗浓缩槽模拟镀液浓度小于20mg/L。经过研究将原专利中至少8级以上的喷淋级数减少至三级,即一个喷淋清洗浓缩槽,一个漂洗浓缩槽和一个逆流漂洗槽实现对新建电镀生产线漂洗水的全部回收利用。喷淋系统(a)中的清洗水量根据第一级漂洗系统和第二级漂洗系统的水量来确定,当第一级漂洗系统和第二级漂洗系统的水量相同时,喷淋系统(a)中的清洗水量为第一级漂洗系统和第二级漂洗系统的水量的1/64,在实际应用过程中可以进行调整。当喷淋系统中镀液浓度达到倒槽浓度时,第二级漂洗系统的镀液浓度超过20mg/L时,可以通过减小喷淋系统(a)中的清洗水量或增加第一级漂洗系统和第二级漂洗系统的水量来调整直到满足第二级漂洗系统的镀液浓度小于20mg/L的清洗要求。
关键词:电镀模拟溶液 喷淋浓缩槽 漂洗液 漂洗槽
Abstract
This study is improved on the basis of the invention patent ZL 2009 10212684.0. The patent refers to the devices and process technology which can achieve all the recycling of electroplating wastewater zero-discharge by using circulating spray method. The original patent failed to find widespread use because of its long cleaning cycle caused by too much spray. At the same time, it is not easy to clean out the complex parts. The innovation of this study is the use of the key technology of circulating sprinkling, reducing the number of rinsing tanks in the countercurrent rinse and evaporative enrichment process by a cycle of spray, making the multi-stage rinse tank be concentrated in a very small space, is to achieve the first level of rinse tank concentration close to the bath concentration can be directly returned to the tank and the last level of water can still meet the cleaning requirements. Therefore, the device can solve the problems and shortcomings of existing electroplating wastewater treatment technology, and achieve zero discharge of electroplating wastewater. The device does not produce any waste water and make all the rinse water all back use for the 100% recovery from the plating tank out of the bath.
The sodium hydroxide solution was used as the simulated bath to study some design parameters. Through several simulation experiments, the total rinse level was fixed to 3, the total water volume is 64500mL which includes the first grade water was 500mL, the second and third grade water were 32000mL, the concentration of the simulated bath is 90% of the original simulated bath concentration, and the concentration of the simulated cleaning solution is less than 20mg / L. After reducing the spray from at least 8 levels to three, in other words, it is the new plating production line rinse water which can achieve all the recycling by using a spray cleaning concentrated tank, a rinse condensate tank and a countercurrent rinse tank. The amount of cleaning water in the sprinkler system (a) is determined by the amount of water in the first-stage rinse system and the second-stage rinse system. When the amount of water in the first-stage rinse system and the second-stage rinse system is the same, the sprinkler system (a) is 1/64 of the amount of cleaning water for the first-stage rinse system and the second-level rinse system, the amount of water in the practical application of the process can be adjusted. When the bath concentration of the second-stage rinse system exceeds 20 mg / L, the amount of washing water in the sprinkler system (a) or the first-stage rinse system can be increased. And the second-stage rinsing system can adjust the cleaning requirements until the concentration of the bath in the second-stage rinse system is less than 20 mg / L.
Key words:Electroplating simulation solution; Spray the condensate tank; Rinse liquid; Rinse the tank
目录
摘要 II
Abstract III
第一章 综述 1
1.1 电镀废水 1
1.1.1 电镀废水的危害与来源 1
1.1.2 电镀废水的回收 1
1.2 电镀废水的处理现状 1
1.3 电镀废水的处理方式 2
1.3.1 化学法 2
1.3.2 电解法 2
1.3.3 离子交换法 2
1.3.4 膜分离法 3
1.3.4 混合废水的处理 3
1.4 电镀废水的闭路循环 3
1.4.1 清洗镀件 3
1.4.2 自然闭路循环 4
1.4.3 闭路循环技术的优点 4
1.5 反渗透法的应用 4
1.6 研究的内容与意义 4
1.6.1 内容 4
1.6.2 意义 5
第二章 循环喷淋工艺参数设计研究 6
2.1 实验内容 6
2.1.1 实验药品 6
2.1.2 实验仪器 6
2.1.3 实验原理 6
2.2 实验步骤及方法 8
2.2.1 模拟镀件的预处理 8
2.2.2 HCl标准溶液及酚酞指示剂的配制 8
2.2.3 电导率仪测定 9
2.2.4 化学滴定法测定 10
2.3 实验步骤 10
2.3.1 逆流清洗的模拟装置 10
2.3.2 循环逆流清洗的实验步骤 10
2.3.3 NaOH溶液的倒槽 11
2.4 结果与讨论 11
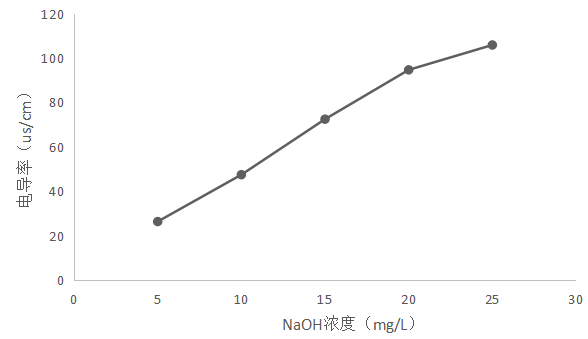
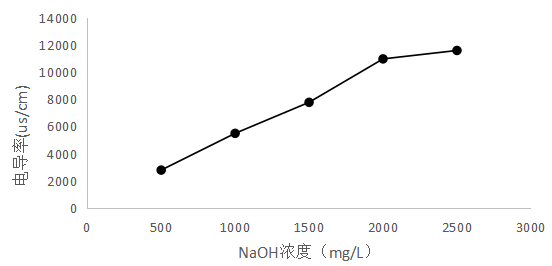
2.4.1 NaOH溶液浓度与电导率的关系 11
2.4.2 确定清洗槽容积 12
2.4.3 模拟镀液倒槽实验结果分析 26
第三章 电镀漂洗水全回收利用处理装置的设计 27
3.1 电镀漂洗水全回收利用处理装置图 27
3.2 工艺流程及原理 27
3.2 与现有技术相比具有的有益效果 28
第四章 结论与展望 30
4.1 结论 30
4.2 展望 30
参考文献 31
第一章 综述
1.1 电镀废水
1.1.1 电镀废水的危害与来源
电镀废水有毒有害物质种类多,毒性大,电镀漂洗废水水量大,重金属浓度低,难于处理,成本高。重金属可进入食物链,经生物富集,最终会达到食物链顶端被人吸收,在人体积累造成慢性中毒,严重危害人体健康。电镀废水的来源一般包括:(1)镀件清洗水;(2)废电镀液;(3)包括冲洗车间,冷凝水,渡槽渗漏或操作管理不当造成的其它废水;(4)设备冷却水;(5)金属表面处理。一般小型电镀企业产生的混合电镀废水含有CN - ,Cr(Ⅵ),Cu 2 ,Zn 2 等毒性重金属,这种混合废物处理起来是极其困难的。电镀漂洗水的处理方式取决于水质状况,有化学法、蒸发浓缩法、生物法、吸附法、离子交换法、膜分离法等。目前,常规化学方法通常可以达到排放标准,但可能不符合回收需要。
1.1.2 电镀废水的回收
相关图片展示:

课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



