助烧剂对常压烧结SiC基陶瓷性能的影响毕业论文
2020-06-12 20:20:55
摘 要
SiC材料是一种高性能结构材料,在无机非金属领域有着特别重要的地位和应用。但由于SiC具有很强的极性共价键,使得烧结制备过程较为复杂,且烧成温度高,能耗大,极大地限制了SiC的应用和商品化发展。而常压烧结可以降低烧成温度,节省成本,所以它愈来愈成为材料工作者的研究重点。
本文从SiC、AlN的性质和应用出发,综述了SiC和AlN的发展历史和烧结机理的研究现状。以研究目标和前人实验经验为基础,以SiC为主,添加第二相AlN,采用MgO-Sm2O3-Y2O3(摩尔比MgO:Sm2O3:Y2O3=2:1.5:1)为烧结助剂,在1850℃Ar气氛下保温1h来制备高致密的碳化硅基陶瓷,简称为MSYSA复相陶瓷。
本实验主要研究通过改变SiC含量、MgO-Sm2O3-Y2O3含量和MgO-La2O3含量及烧结温度对试样性能的影响。性能影响的探究包括通过测得显气孔率和体积密度、分析物相组成和断面形貌及抗弯强度。最后对比得到不同试样之间的性能差异,分析数据,得到本实验的结论。
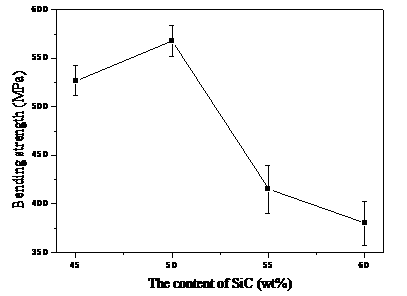
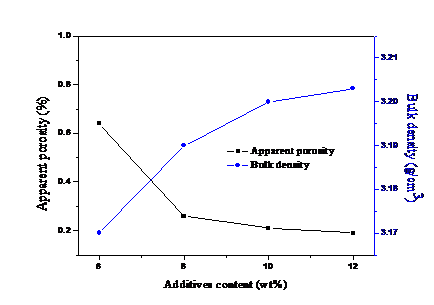
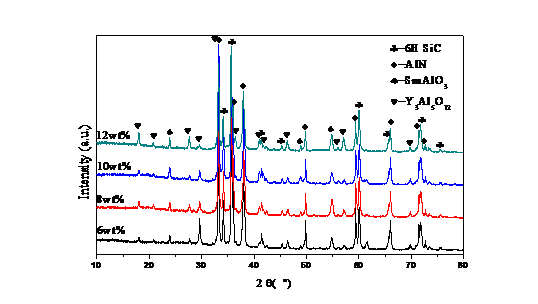
以MgO-Sm2O3-Y2O3为复合烧结助剂,采用常压烧结的工艺在氩气气氛中分别制备一系列的SiC-AlN复相陶瓷。在氩气气氛中1850 ℃保温1 h,添加10%的烧结助剂MgO-Sm2O3-Y2O3,当SiC含量为50wt%时,显气孔率低于0.3%,各项性能达到最好。随着含量的增加,气孔逐渐增大,性能也随着变差。在氩气气氛中1850 ℃保温1h,加入45wt%的SiC,当MgO-Sm2O3-Y2O3含量为12%时,显气孔率达0.19%,添加的烧结助剂含量越多,气孔率随着降低,样品较致密,抗弯强度最高达578MPa。在氩气气氛中不同温度下保温1h,加入45%的SiC和10%wt的MgO-Sm2O3-Y2O3助剂,当烧结温度为1900℃时,样品的气孔率达0.2%以下,抗弯强度最大为576MPa,性能随烧结温度的增加逐渐改善。同时,根据不同烧结助剂制备的SiC基陶瓷的性能对比实验可得出,本实验所采用的烧结助剂MgO-Sm2O3-Y2O3更好地提高SiC基陶瓷的性能。
关键词:SiC;AlN;烧结助剂;常压烧结;抗弯强度
ABSTRACT
Silicon carbide is a high-performance structural materials, and has a particularly important position and application.in the field of inorganic non-metallic. However, Silicon carbide has a strong polar covalent bond, resulting in more complex sintering preparation process, high sintering temperature and energy consumption. It greatly limits the application of SiC and commercial development. But the atmospheric pressure sintering can low the fsintering temperature and cost, so tnere are more and more material workers to focus on this study.
Based on the properties and applications of SiC and AlN, the development history of SiC and AlN and the research status of sintering mechanism are reviewed. MgO-Sm2O3-Y2O3 (molar ratio MgO: Sm2O3: Y2O3 = 2: 1.5: 1) was used as the sintering additive, and the second phase AlN was added based on the experimental target and the previous experimental experience in 1850℃Ar atmosphere for 1 h to prepare high-density silicon carbide-based ceramics, referred to as MSYSA composite ceramic.
In this experiment, the effects of SiC content, MgO-Sm2O3-Y2O3 content and MgO-La2O3 content and sintering temperature on the properties of the samples were investigated. The study of the influence of properties includes the determination of apparent porosity and bulk density, analytic phase composition and cross-sectional morphology and flexural strength. Finally, we compare the performance difference between different samples, analyze the data, get the conclusion of this experiment.
A series of SiC-AlN composite ceramics were prepared by argon atmosphere at room temperature using MgO-Sm2O3-Y2O3 as the composite sintering additive. In the argon atmosphere at 1850 ℃ for 1 h, when adding 10% of the sintering aid MgO-Sm2O3-Y2O3 and the SiC content of 45wt%, the sample have its best performance, whose apparent porosity is less than 0.3%. As the content increases, the stomata gradually increases and the performance decreases. In the argon atmosphere at 1850 ℃ for 1 h, adding 45% of SiC, when MgO-Sm2O3-Y2O3 content of 12%, the
apparent porosity of 0.19%, the additional sintering additives content, the porosity decreased, and the sample is more dense, bending strength up to 578MPa. In the argon atmosphere at different temperatures for 1 h, adding 45% of SiC and 10% MgO-Sm2O3-Y2O3 additives, when the sintering temperature of 1900 ℃, the sample porosity is 0.2% or less, and bending strength have a maximum of 576MPa. The performance with the sintering temperature increases gradually improved. At the same time, according to the performance comparison experiment of MSYSA composite ceramics prepared by different sintering auxiliaries, the sintering aid MgO-Sm2O3-Y2O3 used in this experiment can improve the performance of SiC-based ceramics better.
Key Word:SiC; AlN; Sintering aids; Atmospheric pressure sintering; Bending strenth
目 录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT i
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 引言 1
1.2 发展历史 1
1.2.1 碳化硅的发展历史 1
1.2.2 氮化铝的发展历史 2
1.3 实验体系中组分的基本性质 2
1.3.1 SiC的性能特点及应用 2
1.3.2 AlN的性能特点及应用 2
1.3.3 SiC-AlN复相材料的性能特点 3
1.4 SiC陶瓷烧结机理的研究现状 3
1.4.1 固相烧结 4
1.4.2 液相烧结 4
1.5 研究的意义与内容 5
1.5.1 研究意义 5
1.5.2 研究内容 5
第二章 实验工艺及测试方法 7
2.1 实验原料 7
2.2 实验仪器及设备 7
2.3 制备工艺 8
2.4 表征及性能测试 9
2.4.1 显气孔率及体积密度 9
2.4.2 物相组成分析 9
2.4.3 显微结构分析 9
2.4.4 抗弯强度 9
第三章 MSYSA复相陶瓷常压烧结的探索 11
3.1 SiC含量对MSYSA复相陶瓷性能影响 11
3.1.1 烧结性能 11
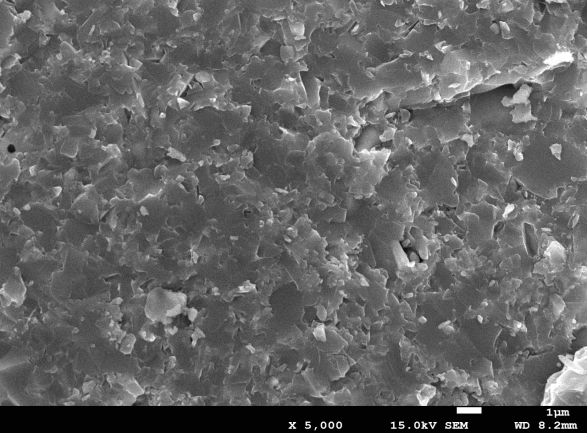
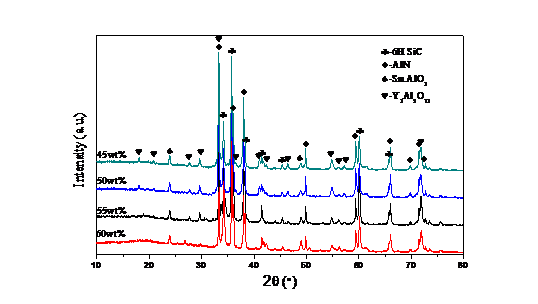
3.1.2 物相组成及显微形貌分析 12
3.1.3 抗弯强度 14
3.2 MgO-Sm2O3-Y2O3含量对MSYSA复相陶瓷性能的影响 15
3.2.1 烧结性能 15
3.2.2 物相组成及显微形貌分析 16
3.2.3 抗弯强度 18
3.3 烧结温度对MSYSA复相陶瓷性能的影响 19
3.3.1 烧结性能 19
3.3.2 物相组成与显微形貌分析 20
3.3.3 抗弯强度 21
3.4 MgO-La2O3含量对SiC基陶瓷性能的影响 22
3.4.1 烧结性能 23
3.5 本章小结 23
第四章 结论和展望 25
4.1 主要结论 25
4.2 展望 25
参考文献 27
致谢 30
第1章 绪论
1.1 引言
随着现代工业的快速发展,应用于高性能领域的材料越来越不能满足其要求,从而需要开发各种新型高性能结构材料。由于碳化硅(SiC)陶瓷具有特殊的结构,从而其性能在各方面都是极为优秀的,因此广泛用于工业领域,并引起了人们的普遍重视。但由于碳化硅陶瓷的难烧结性,同时它的制备工艺复杂,生产成本昂贵,所以探索能够降低碳化硅陶瓷烧成温度、节省生产成本的烧结工艺是当前研究的重点,同时SiC仍有诸多优良性能尚待被发掘。
氮化铝(AlN)陶瓷在热性能、电性能、力学性能等多方面显示出了独特优良之处,从而引起了国内外研究者的广泛关注,随着现代科学技术的飞速发展,各种所用材料的性能要求也有了一个新的高度,需要更多大的研究与探索[1]。同时,AlN材料的制备工艺尚待深入的研究和改进,这对提高氮化铝生产量和商业化发展具有重要意义。
相关图片展示:
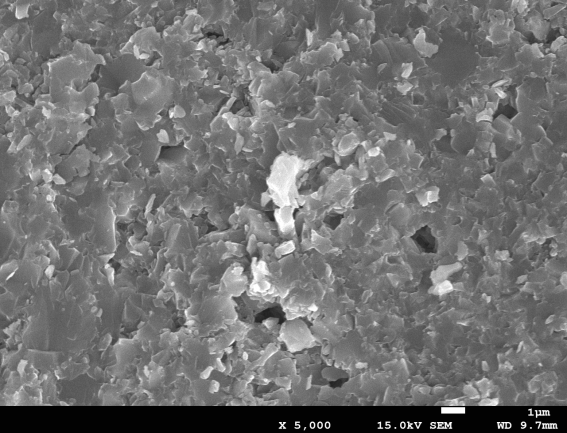
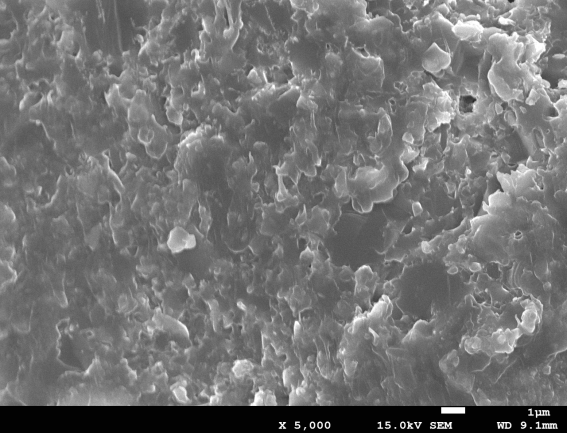

课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



