腺苷化结构域Aden6pro在大肠杆菌中的融合表达毕业论文
2020-06-14 16:24:05
摘 要
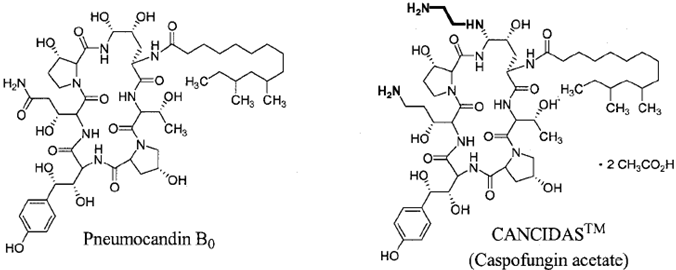
丝状真菌Glarea lozoyensis发酵生产抗生素前体纽莫康定B0的过程中, C0 是主要的结构类似物,C0的存在给B0的分离纯化造成了极大的困难。
纽莫康定B0结构中的羟基脯氨酸是通过NRPS途径引入的,因此C0结构的形成可能跟NRPS第6位的腺苷化结构域(Adenpro6)的底物识别机制相关。因此异源表达adenpro6,对了解NPRS的底物识别机制具有重要意义。
本论文考察了adenpro6基因连接到pET28a,pSJ5和pESC-Leu 三种载体上的蛋白表达情况。在BL21中pET28a-adenpro6可溶性表达蛋白量较少。因此以大肠杆菌为宿主,对密码子进行优化,选用高可溶性表达载体pSJ5,但pSJ5-adenpro6可溶性表达蛋白量仍不理想。进而构建了pESC-adenpro6载体,拟在采用酿酒酵母中表达。
关键词:纽莫康定B0 腺苷化结构域 酿酒酵母
Abstract
Filamentous fungus Glarea lozoyensis fermentation production of antibiotic precursors in the process of Pneumocandin B0, C0 is the main structural analogues. The presence or absence of C0 has resulted in great difficulty in the separation and purification of B0.
The hydroxyproline in the Pneumocandin B0 structure is introduced through the NRPS pathway, so the formation of the C0 structure may be related to the substrate recognition mechanism of the adenylated domain (Adenpro6) at position 6 of NRPS. Therefore,heterologous expression of adenpro6, to understand the NPRS substrate recognition mechanism is of great significance.
In this paper, we examined the protein expression of adenpro6 gene linked to pET28a, pSJ5 and pESC-Leu. In BL21, pET28a-adenpro6 has less soluble protein. Therefore, the protein was optimized by using Escherichia coli as the host, and the high soluble expression vector pSJ5 was selected, but the amount of pSJ5-adenpro6 soluble protein was still unsatisfactory. And then constructed pESC-adenpro6 vector, intended to be expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Keywords:Pneumocandin B0;Adenylated domain;Saccharomyces cerevisiae
目录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 文献综述 1
1.1 卡泊芬净及纽莫康定B0的理化性质 1
1.2纽莫康定B0的生物合成途径 1
1.3 腺苷化结构域 3
1.4大肠杆菌表达系统 3
1.5 包涵体 3
1.6 酿酒酵母表达系统 4
第二章 实验材料 1
2.1 实验仪器 1
2.3 试剂配制及器材操作 3
2.3.1试剂配制 3
2.3.2 器材操作 3
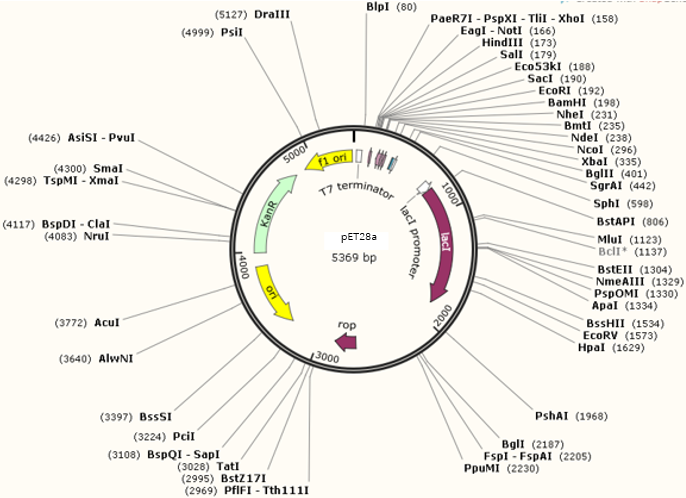
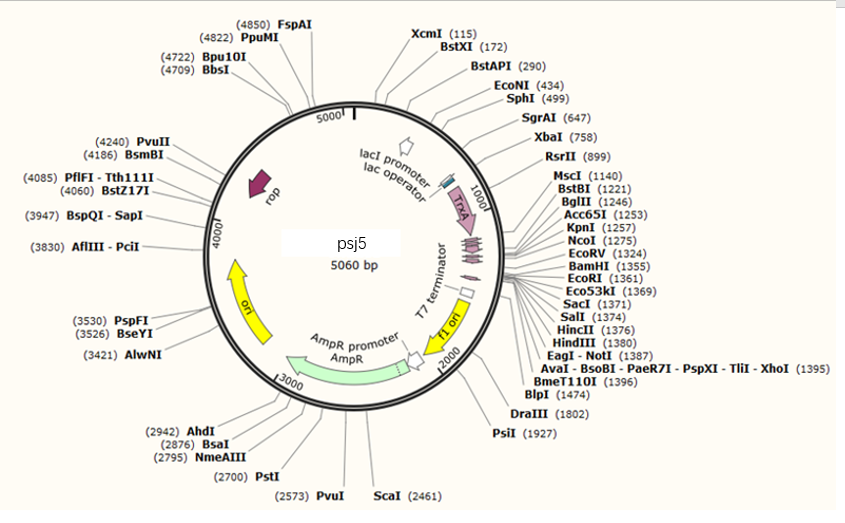
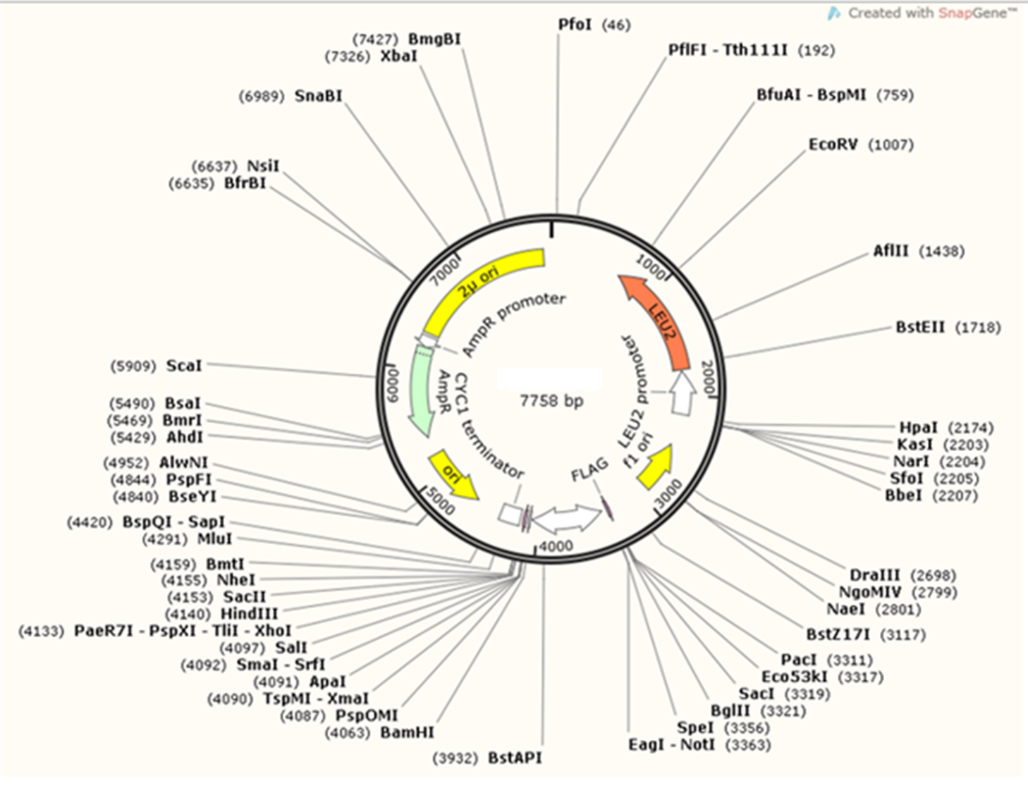
2.4 质粒图谱 5
第三章 实验方法 1
3.1 G. lozoyensis Q1 cDNA 的制备 1
3.2引物设计 1
3.3聚合酶链式反应(PCR) 1
3.4 琼脂糖凝胶电泳 3
3.5 片段连接 3
3.5.1 T载体连接 3
3.5.2 表达载体的连接 3
3.6 双酶切 4
3.7 转化 4
3.7.1 E coli的转化 4
3.7.2 酿酒酵母的转化 5
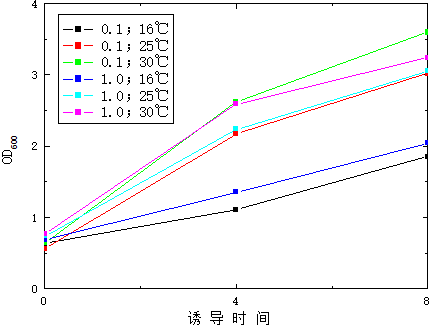
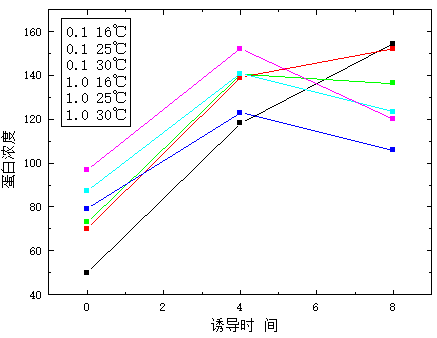
3.8 重组菌株的诱导表达与粗酶液的制备 5
3.8.1 BL21-pET28a的诱导表达与处理 5
3.8.2 BL21-pSJ5的诱导表达与处理 5
3.9 粗酶液的制备 6
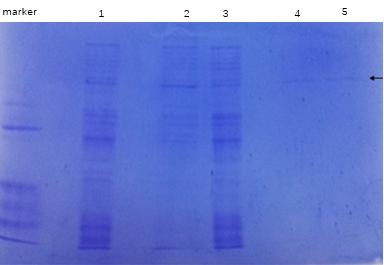
3.9 SDS-PAGE电泳检测目的蛋白 6
第四章 实验结果及分析 8
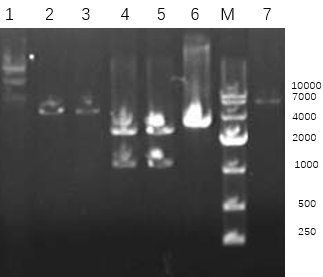
4.1 腺苷化结构域基因(adnpro6)在E coli pET28a载体上的表达: 8
4.1.1目的基因扩增: 8
4.1.2重组菌株的诱导表达: 9
4.2 adnpro6基因在 E coli Psj5载体上的表达: 10
4.2.1表达载体的构建 10
4.2.2 BL21-pSJ5- adnpro6*重组菌株的表达 10
4.3 adnpro6基因在酿酒酵母亮氨酸缺陷型载体上的表达: 12
4.3.1 腺苷化巯基化结构域基因(adnpro6)的构建 12
4.3.2 adnpro6**和pESC-Leu双酶切 12
4.3.3 adnpro6**与pESC-Leu的连接与验证 13
4.3.4 pESC-Leu-adnpro6**的转化 14
第五章 结果与展望 15
参考文献 16
致谢 18
第一章 文献综述
1.1 卡泊芬净及纽莫康定B0的理化性质
纽莫康定( Pneumocandin )类棘白菌素化合物是Merck公司科学家发现并命名的, 生产菌为Glarea lozoyensis[1],其主要生产A0 和B0 两种有效产物。其中,纽莫康定B0为一种极性产物,易溶于乙醇,纯化时可用乙醇对其进行提取。通过对药效较好的B0进行修饰,可以得到一种水溶性的半合成衍生物卡泊芬净( Caspofungin )。卡泊芬净已经广泛运用于医治念珠菌败血症、念珠菌所引发的感染、两性霉素B脂质体制剂和/或伊曲康唑的侵袭性曲霉病[2]。醋酸卡泊芬净可以抑制多种丝状真菌与酵母菌的细胞壁中所含有的β(1,3)-D-葡聚糖的合成[3]。哺乳类动物的细胞中不存在 β(1,3) -D-葡聚糖,因此卡泊芬净成为一种高效且对人体无害的抗真菌药物。
相关图片展示:
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



