孔性配位聚合物在二氧化碳选择性捕获的研究毕业论文
2020-06-17 21:38:17
摘 要
金属有机骨架(Metal-Organic Frameworks,MOFs),作为一种新型材料,自上世纪90年代被合成以来,以其优异的孔性能和巨大的应用潜力而得到蓬勃发展。考虑到MOF特殊的孔道结构,允许部分气体通过,部分气体截留,是理想的气体吸附材料。因此如何设计出具有特定孔径和比表面积且对特定气体具有高的选择性和透过率的功能性MOF材料仍然是目前实验室主要研究方向之一。
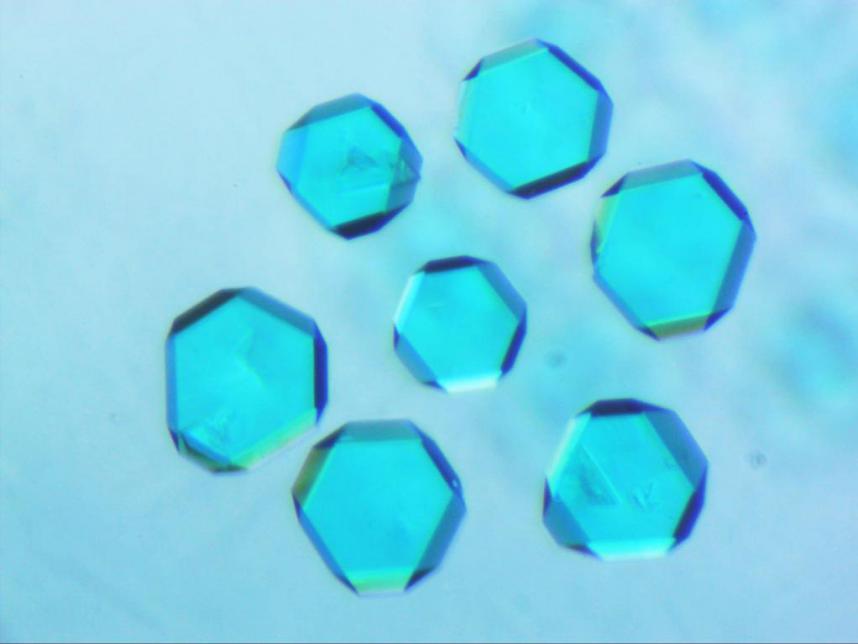
本论文的实验内容是以制备具有较高CO2吸附性能和选择性的MOF为目的,设计、合成有机配体以及培养生长高结晶度的晶体,并对晶体的结构和性能进行表征。实验中主要通过酯化、取代和suzuki等一系列反应有机合成配体4’-(4-甲基-咪唑-1-基)-联苯-3,5-二羧酸,用核磁共振氢谱确认其纯度。利用溶剂热法使配体和金属盐配合反应生长晶体,探索不同溶剂体系对培养晶体的影响。利用单晶X 射线衍射确定其晶体结构。在继续合成孔性配位聚合物材料的基础上,通过红外、热重分析、X 射线粉末衍射以及CH4、N2、CO2等气体的吸附研究,准确测定其孔径、热稳定性、比表面积、气体吸附性能和CO2选择性等数据,最终总结优化结构设计。
关键词:功能性MOF 配体合成 晶体培养 CO2捕获
The study of porous coordination polymers on selective
capture of CO2
Abstract
Metal organic frameworks, as a new material, since the 90s of last century has been synthesized, has developed vigorously due to their excellent pore property and tremendous potential applications. Considering the MOF has a special pore structure, which allows part of the gas pass through and trap the rest, is the ideal gas adsorption material.So how to design a functional MOF material with specific pore size, surface area and high selectivity and transmittance for specific gas is still one of the main research directions of the current laboratory.
The experimental substance of this thesis is design, synthesize organic ligand and cultivate crystals with high crystallinity as well as characterize structure and performance of the crystal for the purpose of preparing MOFs with higher CO2 adsorption properties and selectivity. In our experiments, the ligand called 4’-(4-methyl-imidazol-1-yl)-biphenyl-3,5-dicaboxylic acid was synthesized by esterification, substitution, suzuki and other series of organic reaction, the purity was confirmed by NMR spectroscopy. We used solvothermal method to allow the growth of crystals with the reaction of the ligands and metal salts, the effects of different solvent systems on the culture of the crystal also have been investigated.The structure of the crystal was measured by single crystal X-ray diffraction.On the basis of proceeding the synthesis of porous coordination polymers,we collected the characteristic datum of the crystal such as pore size, thermal stability, specific surface area, gas adsorption capacity and CO2 selectivity mainly by infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, X-ray powder diffraction as well as adsorption of CH4, N2 and CO2 ,etc. Finally,we summarized and optimized the structural design.
Key words: Functional MOF;ligand synthesis;crystal cultivation;CO2 removal
目 录
摘 要 Ⅰ
Abstract Ⅱ
第一章 概述 1
1.1 孔性配位聚合物简介 1
1.2 MOF材料的合成与活化方法 2
1.2.1 溶剂热法 3
1.2.2 微波辅助法 3
1.2.3 超声合成法 4
1.2.4 电化学合成法 4
1.2.5 机械合成 5
1.2.6 MOF材料的活化方法 5
1.3 MOF材料的应用 5
1.3.1 气体储存 6
1.3.2 分离纯化 7
1.3.3 药物输送 8
1.3.4 催化 8
1.3.5 电化学中的应用 8
1.3.6 MOF材料的跨学科研究 9
1.4 本课题选题依据与研究内容 10
1.4.1 选题依据 10
1.4.2 研究内容 10
第二章 实验部分 11
2.1 实验仪器与试剂 11
2.2 配体的合成 12
2.3 配体结构表征 13
2.3.1 核磁共振结果分析 13
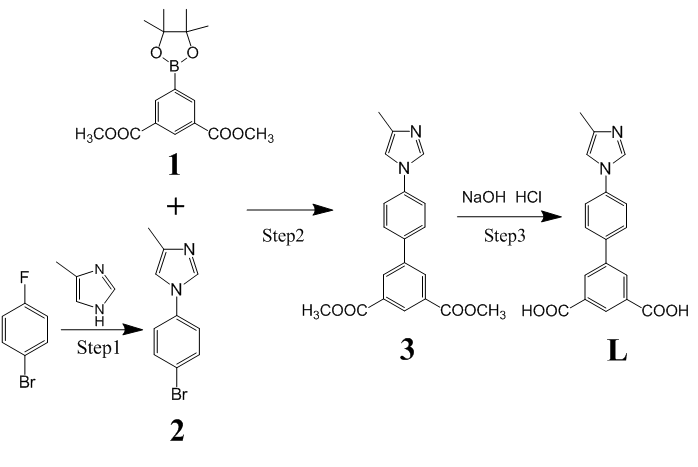
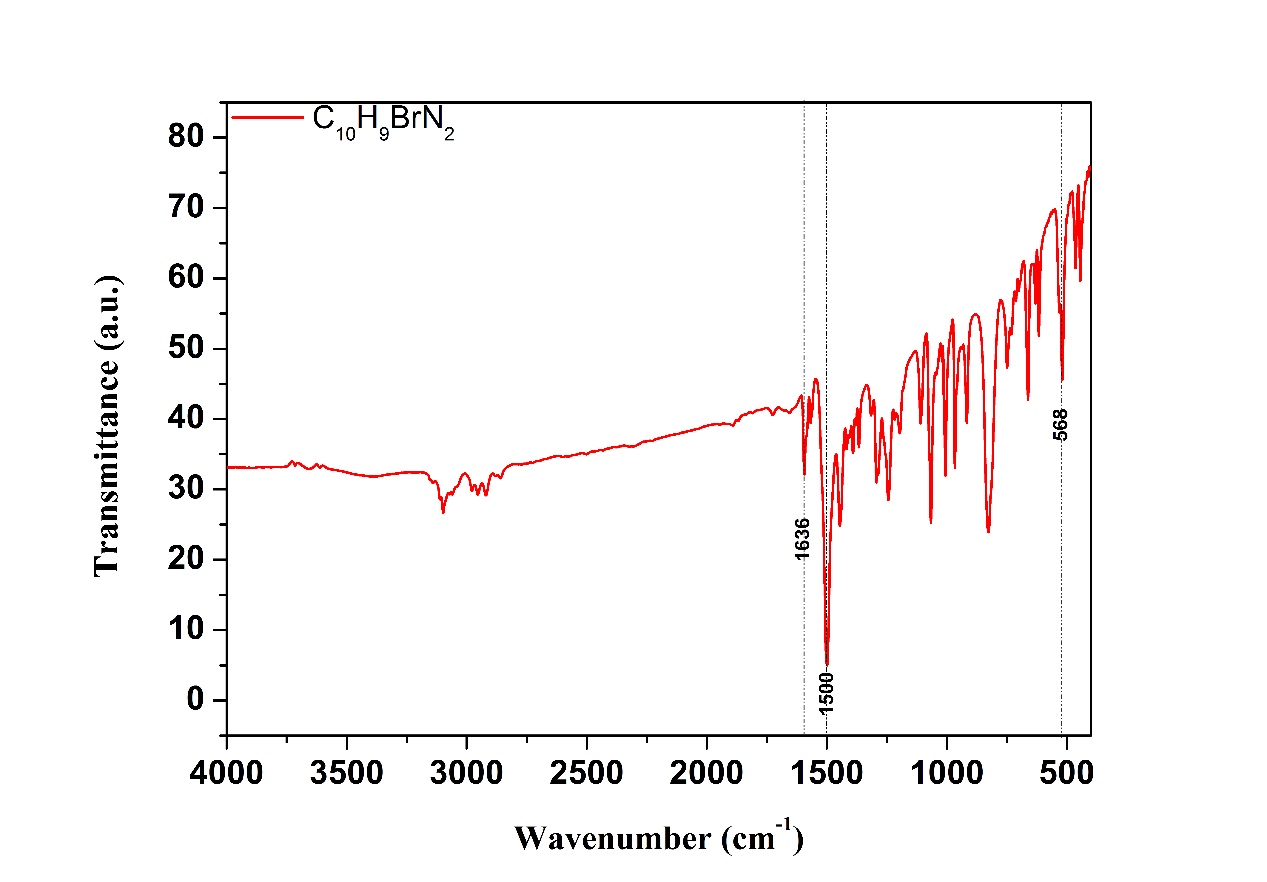
2.2.2 红外光谱结果分析 14
2.4 晶体的培养 16
2.5 晶体的表征 18
2.5.1 X-射线单晶结构分析 18
2.5.2 红外光谱结果分析 20
2.5.3 粉末X射线衍射分析(XRD) 21
2.5.4 热重分析 22
2.5.5 晶体的N2吸附等温线的测定 22
2.5 晶体的吸附性能测定 23
2.6 晶体的水稳定性研究 25
2.7 结论与展望 26
参考文献 27
致谢 33
第一章 概述
1.1 孔性配位聚合物简介
孔性配位聚合物(Porous Coordination Polymers,PCPs),也被称为金属-有机骨架材料(Metal-Organic Frameworks,MOFs),是一种由金属离子和有机分子通过配位化学形成有机-无机杂化晶型多孔网络结构[1]。MOFs由两个主要组成部分组成:通常被称为“节点”的金属离子或金属离子簇和称为“支柱”或“骨架”的有机分子。大多数MOF由过渡金属构成,例如Zn2 ,Ln3 ,Cu2 和Cd2 等,它们提供了具有不同几何形状的柔性配位环境(例如四面体,三角形,双锥体正方形或金字塔形八面体)[2],基于稀土金属和碱金属或碱土金属的MOFs研究较少;有机单元通常是单,二,三或四价配体,大多为含氧、氮等元素的芳香酸或碱[3]。从微观结构来看,金属-有机骨架是具有潜在空隙的有机配体的配位网络[4]。MOF一般用网状化学合成工艺制备,金属和有机接头的选择决定了MOF的结构和性质。例如,金属的配位特征通过规定多少配体可以结合到金属上并以哪个取向配位来影响孔的尺寸和形状。常见的MOF材料主要有IRMOFs系列(含不同取代基的苯环与金属离子锌络合)、MILs系列(铝、铁、钒、铬等金属与对二苯甲酸等羧酸配体合成)、ZIFs系列(金属离子与咪唑或咪唑衍生物络合成的类分子筛咪唑配位聚合物)、PCN系列,主要可归纳为以下三类:1)含羧酸的官能团位配体而组成的2)有含氮的杂环为配体而组成的3)绿色的生物分子为配体组成的。
相关图片展示:

课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



