LiMn2O4锂离子筛吸附分离基础研究毕业论文
2020-06-19 21:53:04
摘 要
随着当代高新技术的不断进步,锂资源需要量剧烈增加。目前陆地上的锂储量已经远远供不应求。人们开始谋求从储量丰富的盐卤湖和海洋资源中提取锂资源,也就是液态锂资源。海水中锂资源储量巨大,总储量大约是陆地上锂储量的10000倍。所以如何从海水中提取锂成了当今科学界一个热门话题。锂离子吸附法是当前工艺最简单且成本最低的提取锂的方法。研究表明,离子筛型的吸附剂可以循环的用来吸收海水中的锂离子,能够更好地从液体中提取锂资源。
本文主要介绍了以KMnO4、LiCl·H2O和CH3CH2OH为原料通过水热合成法,经过酸洗处理后的锂离子筛λ-MnO2,在不同吸附液PH、不同吸附时间、不同脱附时间、不同酸洗浓度等实验条件下的吸附容量,考察了λ-MnO2离子筛静态吸附动力学、等温线实验以及热力学行为,对比分析多组实验数据从而得出最佳的吸附实验条件。
λ-MnO2离子筛的吸附分离基础研究实验结果表明:λ-MnO2离子筛在12h达到吸附平衡,饱和吸附量为23.4mg/g,在偏碱性环境中吸附为佳;λ-MnO2对Li 的吸附主要为化学吸附,具有均匀的吸附活性位且发生单分子层吸附;λ-MnO2离子筛吸锂是一个自发的吸热过程,对Li 的选择性大于H ,对Li 最大吸附量达到6.256mg/g,尤其是镁锂分离效果显著,分离因子达到1270.67;脱附时间为0.5h时,离子筛的脱附效果最佳,此时Li 的脱附量达到最大吸附量的97%,Mn2 的溶损仅为4%。由此可知对λ-MnO2离子筛锂离子具有较高的吸附容量,可用来循环吸附。
Abstract
With the continuous innovation of high and new technology, more and more lithium is needed. But now the land reserves of lithium has been far short of request. People are seeking new methods to draw lithium from the brine lake and sea resources. The total reserves of lithium reserves in the sea is very large and is about one million times of it on land. So how to extract lithium from seawater has become a hot topic in today's scientific community. Adsorption method is seen as a good method and it is simple and lower cost. Researchs show that ion-sieve adsorbent can be reused for many times, so it is considered to be a good material for extraction of lithium from the liquid.
Under different experimental conditions, such as pH, different adsorption time, different desorption time and different pickling concentration, the adsorption capacity of the lithium ion sieves λ-MnO2, which were treated by acid-water treatment with KMnO4, LiCl · H2O and CH3CH2OH as raw materials, were introduced in this paper. And the static adsorption kinetics, isothermal experiment and thermodynamic behavior of λ-MnO2 ion sieve were investigated. Then the optimum adsorption conditions were obtained by analyzing the experimental data.
The results of the adsorption of λ-MnO2 ion sieve shows that the λ-MnO2 ion sieve reaches the adsorption equilibrium until 12h later and the adsorption capacity is 23.4 mg/g, the adsorption in the alkaline environment is the best. The adsorption is mainly chemical adsorption, with uniform adsorption activity and monolayer adsorption and λ-MnO2 ion sieve lithium is a spontaneous endothermic process, whose selectivity for Li is greater than H and the maximum adsorption capacity of 6.256 mg/G, especially magnesium and lithium, the separation factor is 1270.67. When the desorption time is 0.5h, the desorption effect of ion sieve is the best. At this time, the desorption amount of Li reaches 97% of the maximum adsorption capacity, dissolution of Mn2 is only 4% then. It can be seen that the lithium ion with λ-MnO2 ion sieve has a high adsorption capacity and can be used for cyclic adsorption.
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第一章 文献综述 1
1.1 研究背景 1
1.2 锂离子筛的结构及制备方法 2
1.2.1锂离子筛的结构 2
1.2.2锂离子筛的吸脱附原理 3
1.2.3 锂离子筛的制备方法 4
1.3本文研究内容 5
第二章 实验部分 7
2.1 引言 7
2.2实验试剂及仪器 7
2.3λ-MnO2的简单制备 8
2.4λ-MnO2的吸脱附性能研究 9
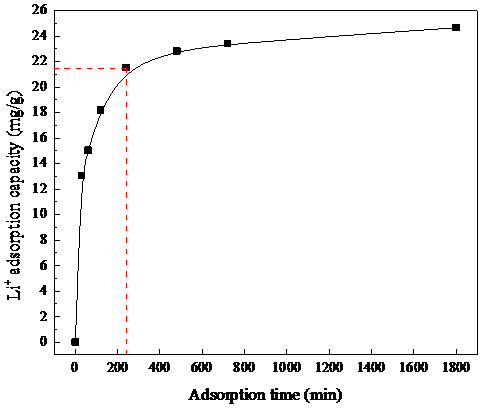
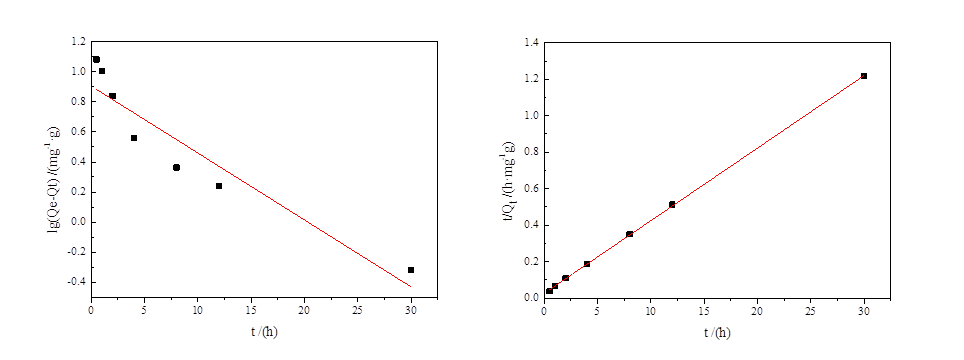
2.4.1吸附动力学研究和模型拟合 9
2.4.2吸附热力学参数 10
2.4.3共存金属离子的分离系数 10
2.4.4脱附性能研究 11
第三章 吸附性能研究结果与讨论 12
3.1 引言 12
3.2同等浓度下的最佳吸附剂量 12
3.3吸附液pH对吸附容量的影响 13
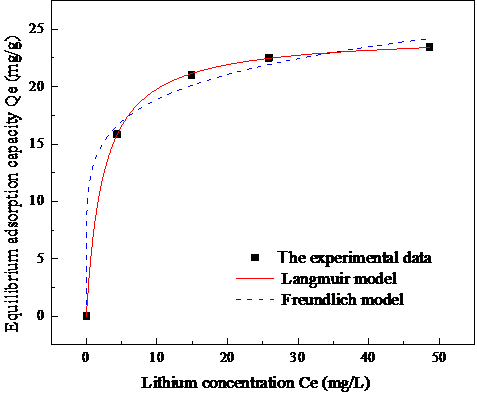
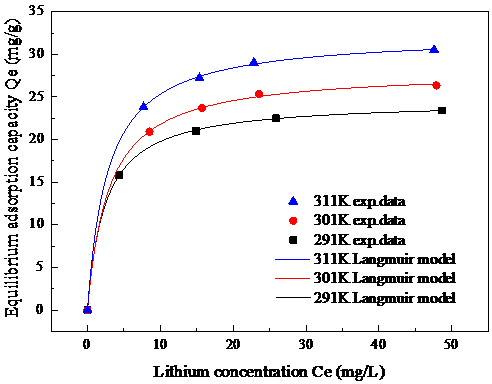
3.4吸附等温线及模型拟合 15
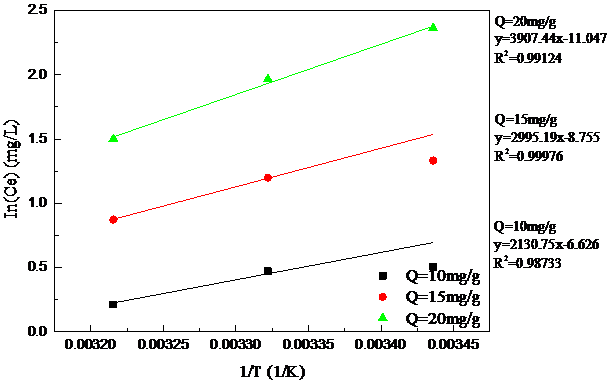
3.5吸附热力学数据 17
3.6共存金属离子的分离系数 18
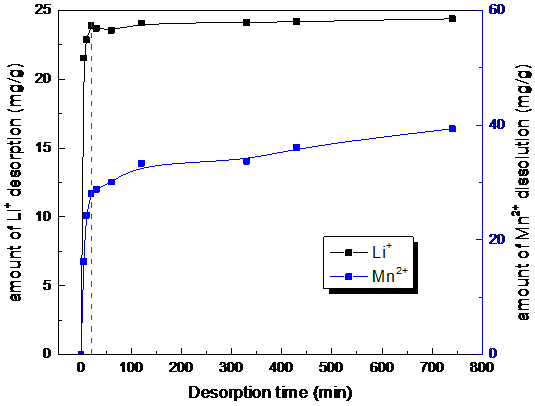
3.7脱附时间对脱附效果的影响 19
3.8酸洗浓度对脱附效果的影响 21
3.9λ-MnO2离子筛的稳定性研究 22
第四章 结论 23
参考文献 24
致谢 26
第一章 文献综述
1.1 研究背景
锂作为最轻的碱金属,是国防科技建设和国民经济中很重要的一种战略物资[1],是国防前沿工业和民用高新技术方面的重要原料。
我国锂资源储量丰富,美国地质调查局2015年发布的研究报告显示,我国已探明的锂资源总储量约为540万t,大概占全世界总储量的13%;其中盐湖类锂资源大约占85%,矿石类锂资源约占15%。
我国生产碳酸锂的主要原材料是锂精矿,而国内锂的供需比大概是1:5,根本不能满足需求,根本原因在于开采锂矿石客观上存在技术难、成本高和能量耗损严重等问题,相比来说盐湖卤水提锂更有前景。近年,中国对锂的开发利用有长足进步[2],但是盐湖卤水锂资源开发与利用现状还是面临很大的难题: 盐湖卤水提锂最主要的影响因素为:卤水中镁锂比高低,卤水中锂的平均浓度,盐湖开采相关区域的交通及气候情况。镁锂比越低,锂的平均浓度越高,越便于开采。
相关图片展示:
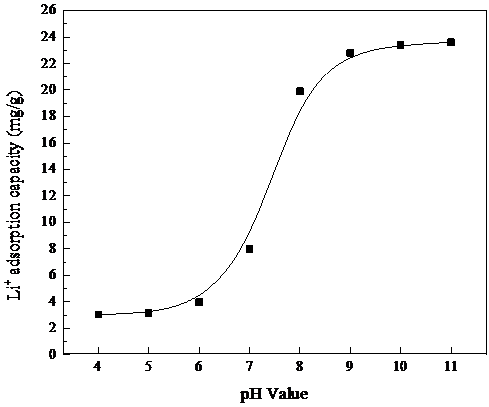
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



