20Cr32Ni1Nb离心铸造合金的高温蠕变性能研究毕业论文
2020-06-21 19:50:47
摘 要
20Cr32Ni1Nb离心铸造合金是广泛使用的高温金属材料。20Cr32Ni1Nb离心铸造合金原始微观结构是在奥氏体基体上分布着一次碳化物的枝晶间网络。因为枝晶间内含有大量的碳化物,形成位错运动的壁垒,而铌的存在又促进了一次碳化物网络的细化,同时减少蠕变裂纹生长。
本课题对20Cr32Ni1Nb钢展开蠕变实验研究,分别在890℃和950℃施加不同应力后,观察20Cr32Ni1Nb的蠕变性能表现,收集数据后绘制蠕变曲线图,观察发现蠕变速率曲线主要由第一蠕变阶段和蠕变第三蠕变阶段组成,第二蠕变阶段很难观察到,最小蠕变速率和断裂时间与应力的关系遵循幂定律。分析蠕变数据可得,20Cr32Ni1Nb合金具有明显的高应力状态和低应力状态,并结合通过显微镜观察到的微观结构,得出第三蠕变阶段在高应力状态的形成原因是截面和颈缩的损失以及孔洞生长,而在低应力状态下是显微结构的退化。同时与25Cr35Ni0.4C钢的蠕变性能展开对比,确定20Cr32Ni1Nb钢更适合作为高温材料。
关键词:20Cr32Ni1Nb钢 蠕变实验研究 蠕变曲线图 显微结构研究
Abstract
20Cr32Ni1Nb centrifugal casting alloy is widely used in high temperature metal materials . The initial microstructure of the 20Cr32Ni1Nb centrifugal casting alloy was found to be a dendritic network of carbides on the austenitic matrix. Because dendrites contain large amounts of carbides, barriers to dislocation are formed, and the presence of niobium promotes the refinement of primary carbides and reduces creep crack growth In this paper, the creep behavior of 20Cr32Ni1Nb steel was observed after 890 ℃ and 950 ℃ respectively. The creep curves of 20Cr32Ni1Nb were observed, and the creep curve was drawn after collecting the data. It was observed that the creep rate curve was mainly composed of the first Creep stage and creep third creep stage, the second creep stage is difficult to observe, the minimum creep rate and the relationship between fracture time and stress follow the power law. Analysis of creep data available, steel has obvious high stress state and low stress state, combined with microscopic observation of the microstructure, the third creep stage in the high stress state of the formation of the reasons for the cross section and necking loss As well as the growth of the pores, while in the low stress state is the degradation of the microstructure. At the same time with the 25Cr35Ni0.4C steel creep performance expansion, to determine 20Cr32Ni1Nb steel is more suitable as a high temperature material.
Keywords: 20Cr32Ni1Nb steel ;creep experimental study;creep curve; microstructure study
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1前言 1
1.2蠕变定义 2
1.3蠕变机理 2
1.3.1位错滑移蠕变 2
1.3.2扩散蠕变 3
1.3.3晶间滑动蠕变 3
1.4蠕变曲线阶段 3
1.5研究方法 3
第二章 实验过程 4
2.1应力实验 4
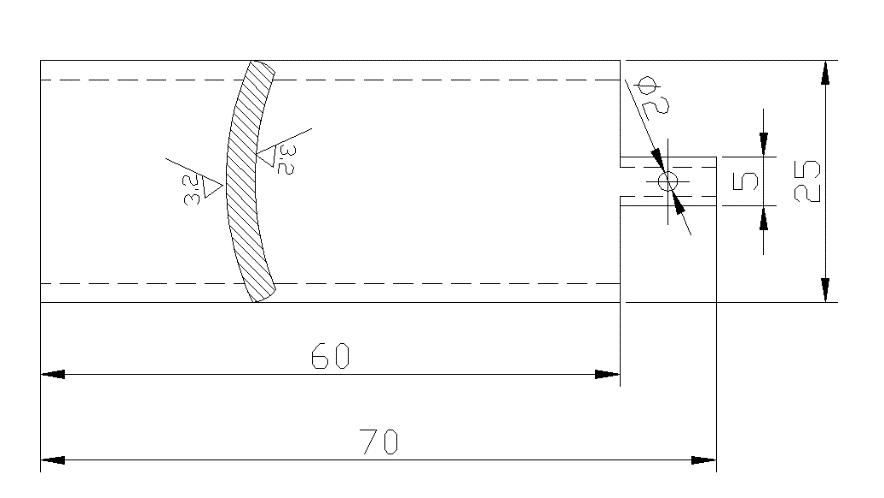
2.1.1试样制备及试验参数 4
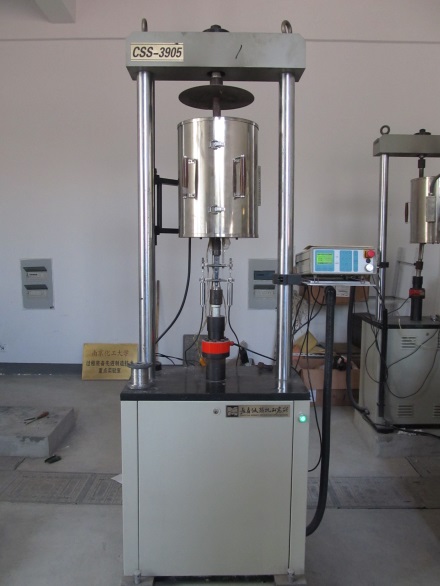
2.1.2 蠕变试验设备及方法 6
2.1.3 蠕变试验步骤及过程 7
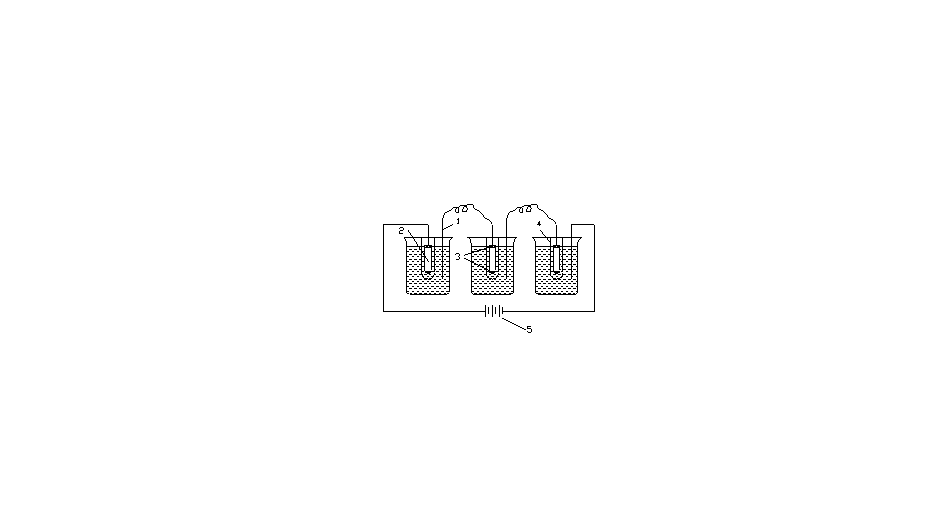
2.2电解萃取试验 7
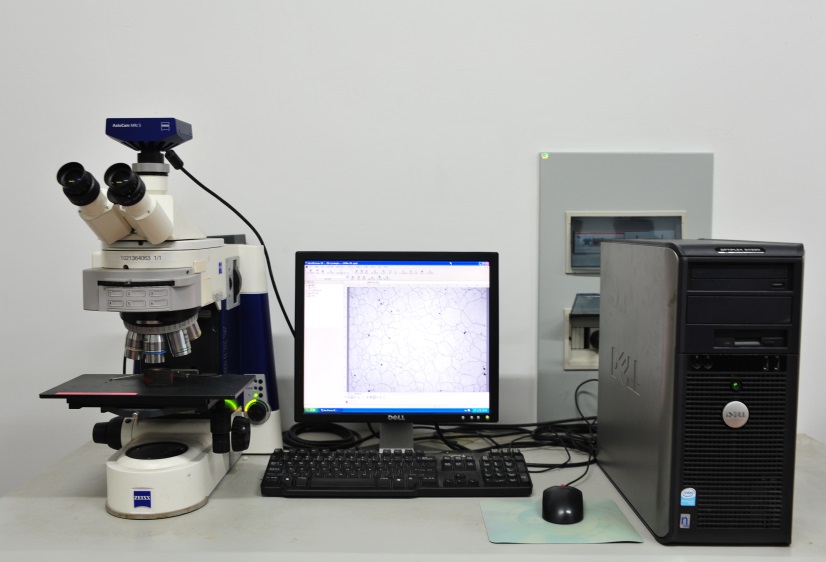
2.3显微结构的观察和分析 9
第三章 实验结果 11
3.1 20Cr32Ni1Nb钢的蠕变变形行为 11
3.2蠕变性能应力和温度的依赖关系 11
3.3 Monkman-Grant 和修正 Monkman–Grant的关系 13
3.4蠕变损伤容限值 14
3.5 20Cr32Ni1Nb钢的蠕变强度 15
3.6断口特征 16
第四章 结论 27
参考文献 28
第一章 绪论
1.1前言
金属在工业上适用范围非常广泛。但许多的金属,因为自身性能的所限制,导致不适合在高温下工作[1]。但是在众多领域里诸如化工,冶金,石油,能源等,大量的金属构件又必须在高温高压条件中长期运转,这就需要材料具有很好的高温抗蠕变性能。因此选择合适的高温金属材料以避免因为构件在高温下蠕变失效引起的安全问题就显得尤为重要。
与其他具有高碳的奥氏体不锈钢(如HU40,HK40和HP40钢)相比,含有低碳的20Cr32Ni1Nb钢经过热处理后表现出的结构是带有枝晶间一次碳化物网络的过饱和奥氏体基体。 这些显微结构特征有助于材料的蠕变强度。 众所周知,钢主要依赖于基体的固溶强化和基体和晶界的颗粒硬化,以在高温下获得良好的蠕变性能[2-4]。 由于良好的机械性能,抗蠕变性和耐腐蚀性,出口歧管组件中使用的20Cr32Ni1Nb钢被认为是合金800或其衍生物[5-6]更经济的替代品。故20Cr32Ni1Nb离心铸造合金这个广泛使用的高温金属材料进行研究。
1.2蠕变定义
当温度T大于等于(0.3~0.5)熔点t并远远低于屈服强度的应力下,材料伴随加载时间的延长慢慢地产生了塑性变形这种情况称为高温蠕变[7]。
按照施加应力方式区分,高温下的蠕变变形有高温压缩蠕变、高温拉伸蠕变、高温弯曲蠕变和高温扭转蠕变这四种蠕变方式。高温蠕变取决于材料的结构和材质,对材料在高温情况下的应变趋势和断裂寿命有着重要影响。
相关图片展示:





课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



