高分散Ru@ZrO2催化剂的制备及其催化氧化1,2-二氯乙烷的研究毕业论文
2020-07-02 22:40:59
摘 要
含氯挥发性有机物(CVOCs)拥有良好的稳定性和溶解性,因此大量应用于化工生产过程,这类污染物不但严重污染环境,也对人体健康造成严重危害。催化氧化法能耗小,在比较低的温度下便可燃烧,并且可以较为有效的避免二次污染,因此在销毁CVOCs的方法中,催化氧化是一种经济节能且环保的方法。钌作为工业化的HCl氧化制Cl2催化剂,在CVOCs催化氧化反应中表现出很强的抗氯中毒能力,以此得到广泛关注,而贵金属成本较高,限制了其进一步发展。因此提高其在载体上的分散性、减小其颗粒尺寸,使得每个金属原子都作为活性位是目前研究发展的趋势。
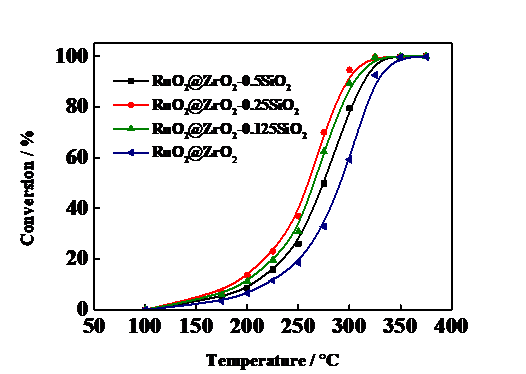
本文采用自发沉积策略制备RuO2@ZrO2催化剂,为了减少焙烧时催化剂表面Ru的烧结,导致部分活性组分失活,采用保护壳策略在催化剂表面进行二氧化硅修饰,提高贵金属Ru在催化剂表面的分散性。考察了不同浓度的正硅酸四乙酯溶液对RuO2@ZrO2-xSiO2催化剂催化氧化1,2-二氯乙烷活性的影响,通过XRD,H2-TPD,N2-吸脱附以及H2-TPR等表征方法测试催化剂的物理和化学性质。从结果可以得出,经过SiO2修饰后的催化剂能够有效提高RuO2在催化剂表面的分散性,提高催化剂的活性,随着硅浓度的增加,活性呈现先增加后降低的趋势,RuO2@ZrO2-0.25SiO2表现出最优的催化活性,其中RuO2@ZrO2催化剂90%转化率温度大约为328℃,经过硅修饰后明显下降,在RuO2@ZrO2-0.25SiO2时达到最低温度,为297℃。说明随着正硅酸四乙酯浓度的增加,对催化剂表面的RuO2颗粒的保护作用越明显,但是过多的氧化硅在催化剂表面会覆盖部分活性组分导致活性下降。
关键词:含氯挥发性有机物 催化氧化 高分散 贵金属 保护壳
The preparation and catalytic oxidation of 1, 2-dichloroethane with high dispersion RuO2@ZrO2 catalyst.
Abstract
Chlorine volatile organic compounds (CVOCs) had very good stability and solubility, so the were widely used in chemical production processes. Such pollutants not only seriously pollute the environment, but also cause serious harm to human health. Catalytic oxidation technology had low energy consumption, could be combusted at relatively low temperatures, and it was difficult to cause secondary pollution to the environment. Therefore, in the method of destroying CVOCs, catalytic oxidation was an economical, energy-saving and environmentally friendly method. As an industrialized HCl catalyst for the oxidation of HCl to Cl2, CVOCs exhibit a strong resistance to chlorine poisoning in the catalytic oxidation reaction. This had attracted widespread attention, and the high cost of precious metals had limited its further development. Therefore, to improve its dispersibility on the support and reduce its particle size, making each metal atom as an active site was the current research and development trend.
The RuO2@ZrO2 catalyst was prepared by a spontaneous deposition method. In order to reduce the Ru sintering on the catalyst surface during roasting, some active components were deactivated, and the silica surface was modified on the surface of the catalyst by a protective shell strategy to improve the dispersion of Ru on the catalyst surface. The effects of different concentrations of tetraethyl orthosilicate on the catalytic activity of RuO2@ZrO2-xSiO2 catalysts for 1,2-dichloroethane oxidation were investigated. The effects of XRD, H2-TPD, N2-absorption desorption and H2-TPR were investigated. Such characterization methods test the physical and chemical properties of the catalyst. It could be concluded from the results that the catalyst modified with SiO2 could effectively improve the dispersibility of RuO2 on the catalyst surface and increase the activity of the catalyst. As the concentration of silicon increases, the activity shows a trend of increasing first and then decreasing, RuO2@ZrO2-0.25SiO2 The optimum catalytic activity was exhibited. The 90% conversion temperature of RuO2 @ZrO2 catalyst was about 328℃. After being modified by silicon, the RuO2 @ZrO2 catalyst decreased obviously. When RuO2 @ZrO2 -0.25SiO2 reached the lowest temperature, it was 297℃. It showed that the protective effect of RuO2 particles on the surface of the catalyst was more obvious with the increase of tetraethyl orthosilicate concentration, but too much silica will cover part of the active components on the surface of the catalyst, resulting in decreased activity.
Keywords: Chlorine-containing; Volatile organics; Catalytic oxidation; High dispersion; Precious metal; Coating
目 录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 文献综述 1
1.1课题背景 1
1.2催化氧化处理CVOCs的基本原理 2
1.3贵金属催化剂研究进展 2
1.3.1钌基催化剂 3
1.3.2其他贵金属催化剂 4
1.4主要研究内容及关键技术 5
第二章 实验部分 6
2.1实验原料及仪器 6
2.1.1 实验气体及试剂 6
2.1.2 实验仪器 6
2.2催化剂制备 7
2.3催化剂表征 7
2.3.1 X-射线衍射(XRD) 7
2.3.2 N2吸附-脱附(N2-Sorption) 7
2.3.3 H2程序升温脱附(H2-TPD) 8
2.3.4 H2程序升温还原(H2-TPR) 8
2.4催化剂的活性评价 8
2.4.1实验装置 8
2.4.2分析方法 9
第三章 RuO2@ZrO2-xSiO2催化氧化DCE性能研究 11
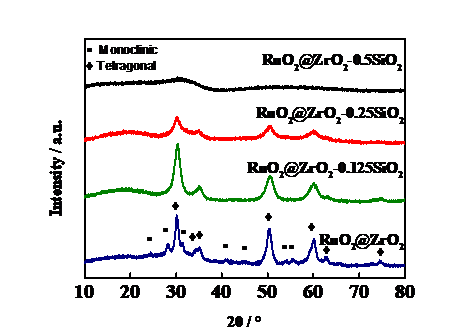
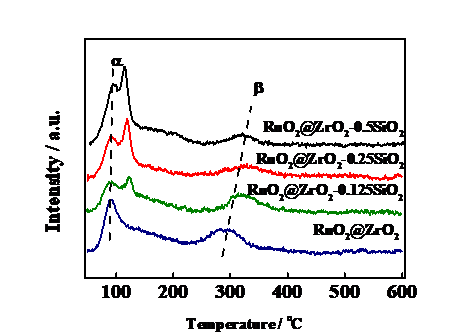
3.1 XRD分析 11
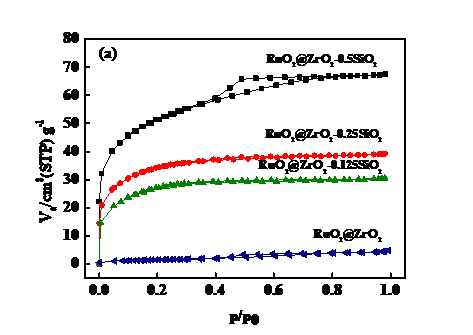
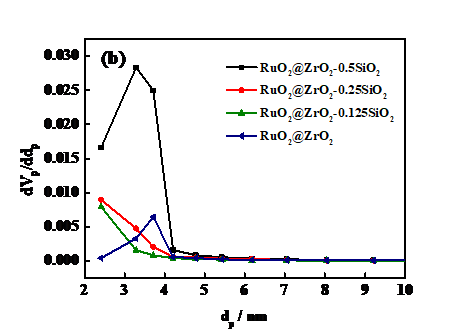
3.2 N2-Sorption分析 12
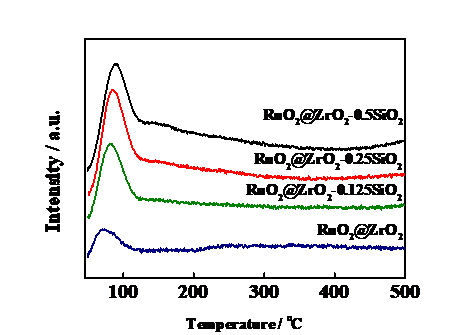
3.3 H2-TPD分析 13
3.4 H2-TPR分析 14
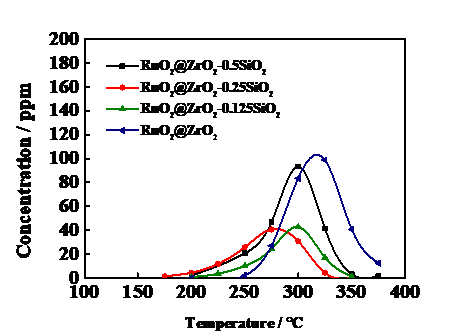
3.5催化剂反应活性测试 15
3.6催化剂的稳定性测试 18
第四章 结论 21
参考文献 22
致谢 25
第一章 文献综述
1.1课题背景
挥发性有机化合物,简称为VOCs,WHO将其定义为常温下饱和蒸气压大于133.32 Pa,且沸点在50 ℃ ~ 260 ℃的有机化合物。[1]其中,含氯挥发性有机化合物,又简称为CVOCs,是挥发性的有机化合物里毒性大,并且污染环境相对比较持久的化合物。常见的CVOCs主要有以下三种类型:(1)脂肪烃类,例如二氯甲烷,二氯乙烷,三氯乙烯等;(2)芳香烃类,例如氯苯,多氯苯等;(3)聚合类,例如多氯联苯,多氯二苯并二呋喃,多氯二苯并二噁英等。[2]
因为CVOCs拥有比较好的溶解性以及反应惰性,所以它们在制药,石油,涂料等工业生产中被广泛的使用,它们主要来源于工业生产中的热导液,有机溶剂,化工产品的中间体等。通常以工业废气废水的形式排放到环境中去,对人类健康以及环境的影响,表现为以下两方面:(1)大部分CVOCs因为其毒性与恶臭,会严重影响人的呼吸系统,心血管系统以及神经系统,并且许多CVOCs还拥有致畸致癌致突变的作用,易在人体内富集,严重影响人类生命健康。(2)臭氧层空洞以及光化学烟雾等环境污染会因为CVOCs的排放而加剧,这些污染将长期在环境中存在,严重危害人的生命健康并且会对生态环境产生持久的破坏与污染。[3]因此,关于如何净化CVOCs废气的研究,对于大气环境的保护,与促进世界经济的发展具有非常重要的意义。
相关图片展示:
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



