无机纳米粒子对3D打印光敏材料的改性研究毕业论文
2020-07-03 23:47:50
摘 要
3D打印快速成形技术,是在计算机辅助技术、激光及材料等众多科学飞速发展的背景下,应运而生的一种新型制造技术。光固化快速成型是发展最久也最被看好的3D打印技术,而光敏材料一直是制约其发展的一个课题。本文旨在环氧丙烯酸酯(EA)作为预聚物的基础上,通过添加无机纳米填料,对光敏树脂进行增强增韧改性研究,制备出低粘度的、高强高韧性的光固化材料。首先,基于自由基型光固化原理的基础上,确定光敏树脂所用的光引发剂和活性稀释剂的种类和含量。对比不同光引发剂的紫外吸收光谱选择184作为本文所用的光引发剂,加入量为4%;通过比较不同含量TPGDA对体系粘度影响,确定其含量为48%时光敏树脂的粘度能够满足本研究所有实验的粘度要求。根据上述确定的各组分的占比准确称取,混合均匀后即可制得液态光敏树脂材料,然后,添加无机纳米填料对光敏材料进行增强增韧的改性。
以无机填料SiO2作为添加性改性剂对自由基型光敏材料进行增强增韧改性。不同粒径SiO2中,T-2和T-6061体系增强增韧效果更明显。当加入量为5%时,两种体系固化材料的拉伸强度分别达到了44.4MPa和44.1MPa,相比于空白实验的34.84MPa,提高了27%;与此同时,T-2体系固化材料的断裂伸长率也达到最大值11.36%,相比于空白实验的8.68%,提升了30.8%。
以无机填料TiO2作为添加性改性剂对自由基型光敏材料进行增强改性。不同粒径TiO2中,使用5-10nmTiO2改性的光敏树脂的强度最优,加入量为0.3%时达到最大值,为46.47MPa,提高了33%。
最后,对无机填料增强增韧改性后的固化材料进行金相分析。结果表明:无机纳米粒子的加入,会细化基体裂纹,扰动裂纹尖端发展,改变其传播途径,诱发基体产生大量银纹,在受到冲击或拉伸时,能吸收载荷。另外,在一定含量范围内,无机纳米粒子能相对均匀的分散,达到增强增韧的效果。
关键词:光固化成型 自由基型光敏树脂 无机纳米粒子改性 增强增韧
Study of 3D printed photosensitive materials modified by inorganic nanoparticles
Abstract
As a pioneering and pioneering new manufacturing technology, 3d printing is leading the global industry through the third industrial revolution, profoundly changing the traditional production mode and production technology. Stereo Lithography Apparatus (SLA) is one of the fastest developing 3D printing technologies, and photosensitive materials have always been a constraint to its development. This article, based on the epoxy polyacrylate, by adding inorganic nano filler, enhanced toughening modification was studied for the photosensitive resin, were suitable for the SLA, low viscosity, photosensitive material with high strength and high toughness.
In this paper, the types and contents of photoinitiators and active diluents used in photosensitive resins are determined based on the free radical photocuring system. After comparing the absorption spectrum, 184 was selected as the light initiator for subsequent experiments. By comparing the effect of different diluent TPGDA on the viscosity of the system, it was determined that the content of the system was the best at 47%. Turn the oligomer TPGDA: EA = 1:1 preparation, to join 184, 4% of the initiator was liquid photosensitive resin material, by adding inorganic filler to the photosensitive material of nanometer enhanced toughening modification research.
The free radical photosensitive materials were enhanced and toughened by using inorganic filler SiO2 as additive modifier. In SiO2 with different particle sizes, T-2 and T-6061 systems have more obvious toughening effect. When the amount of SiO2 was 5%, the tensile strength of the curing materials in the two systems reached the maximum value of 44.4MPa and 44.1MPa respectively, increasing by 129%. At the same time, the breaking elongation of the solidified material in T-2 system also reached a maximum of 11.36%, an increase of 130%.
The free radical photosensitive materials were enhanced by using inorganic filler TiO2 as additive modifier. Among the TiO2 with different particle sizes, the 5-10nm TiO2 modified resin has the best strength, reaching the maximum when the additive amount is 0.3%, increasing from 34.83MPa to 46.47MPa, and increasing by 133%.
Finally, the metallographic analysis of the solidified material after the toughening and strengthening of inorganic filler was carried out. Results show that the addition of inorganic nanoparticles, refining matrix crack, disturbing crack tip development, change the route of transmission, induced matrix to produce a large number of silver lines, in shock or stretching, can absorb the load. In addition, within a certain content range, inorganic nanoparticles can be uniformly dispersed in the matrix, so as to enhance the toughening effect.
Key Words: Photocuring;Free radical photosensitive materials;Modification of inorganic nanoparticles;Enhanced toughening
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 3D打印的简介 1
1.2 光敏树脂的概述 3
1.2.1 光敏树脂的组成 3
1.3.2 光固化成形对光敏树脂的要求 4
1. 3 光敏树脂的改性 5
1.3.1 无机纳米粒子改性光敏树脂的制备 5
1.3.2 光敏树脂改性用无机纳米粒子 6
1.4 研究目的和内容 9
1.4.1研究目的 9
1.4.2研究内容 9
第二章 实验材料和方法 11
2.1 实验材料 11
2.2 实验主要仪器 11
2.3 改性树脂的制备 11
2.4 性能表征方法 12
第三章 结果与讨论 15
3.1 光引发剂的选择 15
3.2 稀释剂的选择 16
3.3 SiO2改性光敏树脂的研究 16
3.1.1 不同粒径SiO2及含量对粘度的影响 16
3.1.2 不同粒径SiO2及含量对力学性能的影响 17
3.1.3 不同粒径SiO2及含量对体积收缩率的影响 19
3.1.4 金相分析 20
3.4 TiO2改性光敏树脂 21
3.2.1 固化时间 21
3.2.2 不同粒径TiO2及含量对粘度的影响 24
3.2.3 不同粒径TiO2及含量对力学性能的影响 25
3.2.4 不同粒径TiO2对收缩率的影响 27
3.2.1 金相分析 27
第四章 总结与展望 29
4.1 总结 29
4.2 展望 30
参考文献 31
致 谢 34
第一章 绪论
1.1 3D打印的简介
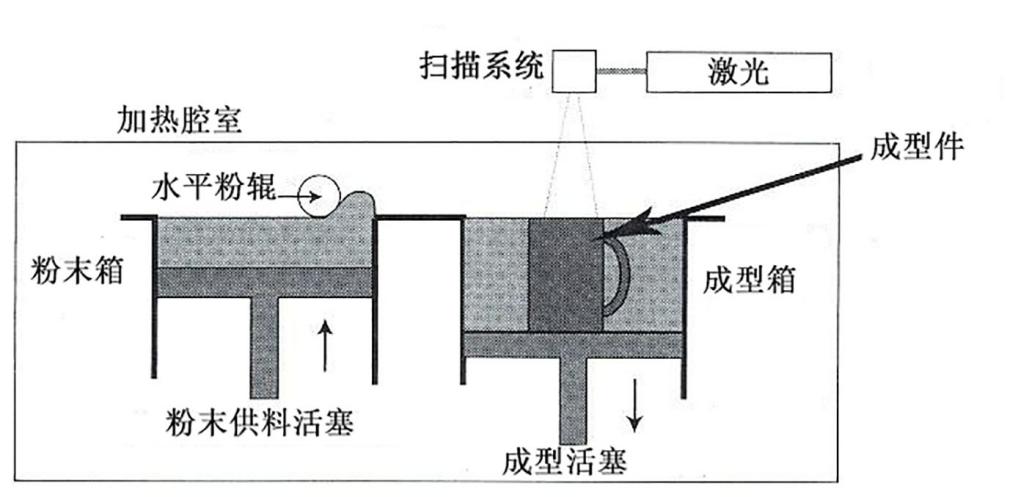
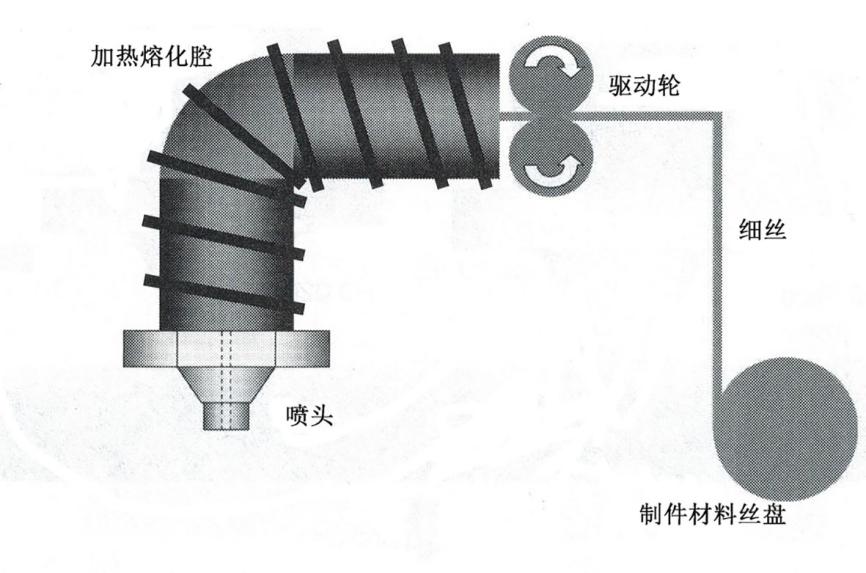
3D打印技术,是在计算机辅助技术、激光及材料等众多科学飞速发展的背景下,应运而生的一种新型制造技术。与传统的“去除”加工方法和“变形”的处理方法不同,快速成形技术选用逐层叠加的制造法,属于材料堆积型制造技术,也称为增长型制造(incremental manufacturing)或分层制造成形技术[1]。快速成型技术表现了“降维”制造的思维:在制造过程当中,一些复杂的物理实体的立体结构被分割成无数的二维形状以达到加工处理的要求,从而使实体的复杂的三维结构的制作变得简单。3DP技术类似于在纸张上逐行画线条,使这些线条堆叠时能够形成图像。在3DP中,首先在一个平台上制造对应于零件横截面的材料薄层,然后使下一层堆叠在它的顶部形成零件,如图1-1所示[11]。
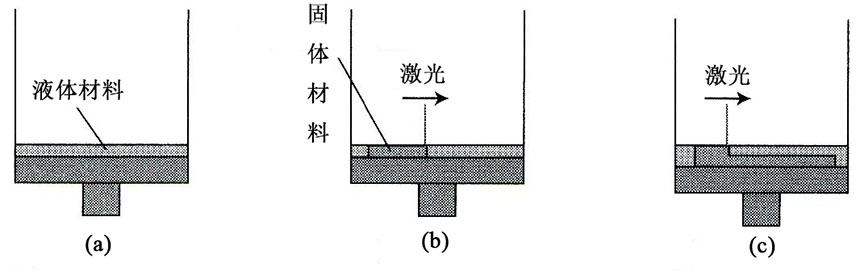
相关图片展示:


课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



