丁醇发酵过程中细胞循环的研究毕业论文
2020-07-04 19:47:14
摘 要
丁醇作为重要的有机溶剂,在化工、医药、印染和塑料等行业具有可观的应用价值。作为燃料的生物丁醇由于环境友好、燃烧效率高等系列优点,具有良好的市场前景。
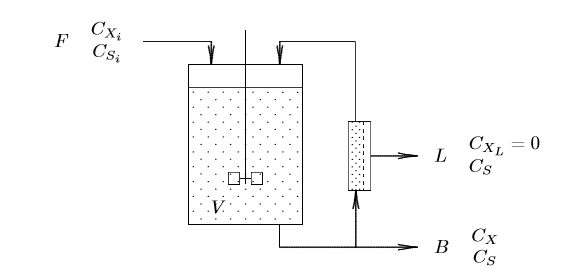
传统的丁醇发酵的碳源大多采用淀粉和糖,底物资源的短缺限制了丁醇的发展。而本实验使用的巴斯德氏梭菌菌种,能够以甘油为底物生产丁醇,在目前研究中十分稀有。生物发酵法制备丁醇一般有间歇式发酵和连续发酵等方法。对于间歇式或连续搅拌罐式发酵罐的连续操作,细胞与排出物流一起排出,这限制了发酵罐的生产力。通过将细胞从出口物流再循环到发酵罐可以提高生产率。
本课题设计并改进了细胞循环动力装置,清水测试后证明了其循环机制的可行性。之后使用了强化梭菌培养基培育发酵种子以及优化后的Biebl培养基对甘油进行发酵实验。在前人实验基础上,实验拟定最佳操作pH值为5,分别同样操作条件下进行了间歇式丁醇发酵实验和带有细胞循环装置的连续丁醇发酵。最终,间歇式发酵丁醇总体产量为3.22 g/(L∙ h),细胞循环连续发酵的丁醇总体产量为3.67 g/(L∙ h),提高了13%,具有应用价值。
关键词:丁醇 细胞循环 连续发酵 产量
Study on the Cell-recycle for Continuous Butanol Fermentation
ABSTRACT
Butanol, as an important organic solvent, is of considerable value in the chemical, pharmaceutical, printing, dyeing, and plastic industries. As a fuel, biobutanol has a good market prospect due to its advantages of environmental friendliness and high combustion efficiency.
Most of the traditional carbon sources for butanol fermentation are starch or sugar, and the shortage of substrate resources limits the development of butanol. The C. pastoris strains used in this experiment are able to produce butanol with glycerol as the substrate, which is very rare in current research. The bio-fermentation method for producing butanol generally includes batch fermentation and continuous fermentation. For continuous operation of a batch or continuous stirred tank fermenter, the cells are discharged together with the effluent stream, which limits the productivity of the fermenter. Productivity can be increased by recycling cells from the exit stream to the fermenter.
This project has designed and improved the cell-recycle unit. After the water test, it proved the feasibility of the recycle mechanism. Afterwards, the glycerol fermentation experiment was conducted using the Reinforced Clostridium Media to cultivate the fermentation seeds and the Modified Biebl Media to ferment. Based on previous experiments, the optimum pH for the experiment was set at 5, and batch butanol fermentation and continuous butanol fermentation with cell-recycle unit were performed under the same operating conditions. Finally, the overall yield of butanol in the batch fermentation was 3.22 g/(L∙ h). The overall butanol production in the cell-recycle continuous fermentation was 3.67 g/(L∙ h), an increase of 13%, which was of practical value.
Key words: butanol; cell recycle; continuous fermentation; productivity
目 录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 文 献 综 述 1
1.1 丁醇的性质 1
1.2 丁醇的价值 1
1.2.1丁醇的应用领域 1
1.2.2丁醇的国内外市场 2
1.3 丁醇的生物合成 2
1.3.1 ABE发酵 2
1.3.2 PBE发酵 3
1.4 丁醇发酵理想模型 5
1.4.1 连续搅拌罐式发酵罐 5
1.4.2 细胞循环连续发酵 6
第二章 实验材料与方法 8
2.1 实验材料 8
2.1.1 菌种 8
2.1.2 膜 8
2.1.3 化学药品以及器材 8
2.2 强化梭菌培养基(Reinforced Clostridium Media)的制备 9
2.3 微量元素溶液 SL7 的制备 11
2.4 改进Biebl培养基的制备 11
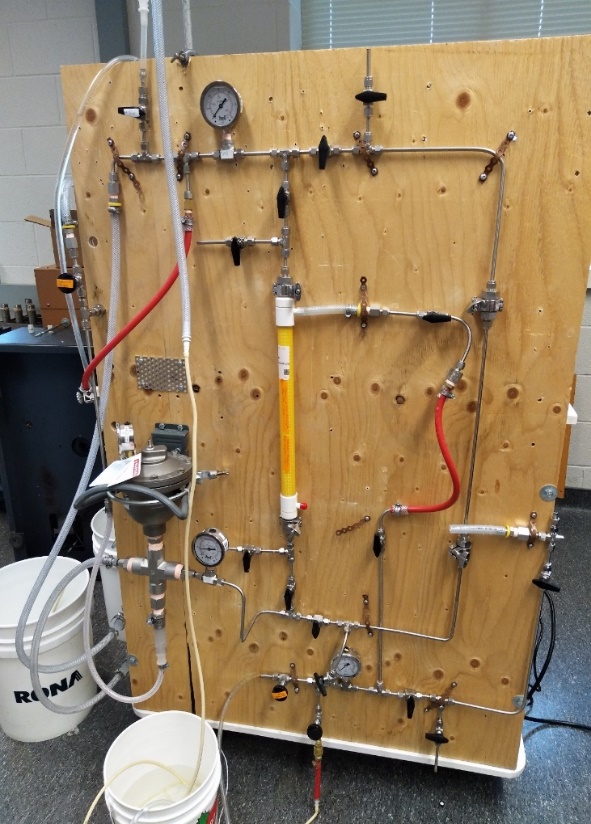
2.5 生物反应器(7.5L)操作步骤 12
2.6取样,样品处理的操作步骤 14
2.7高效液相色谱操作 15
2.8 间歇式发酵的操作步骤 15
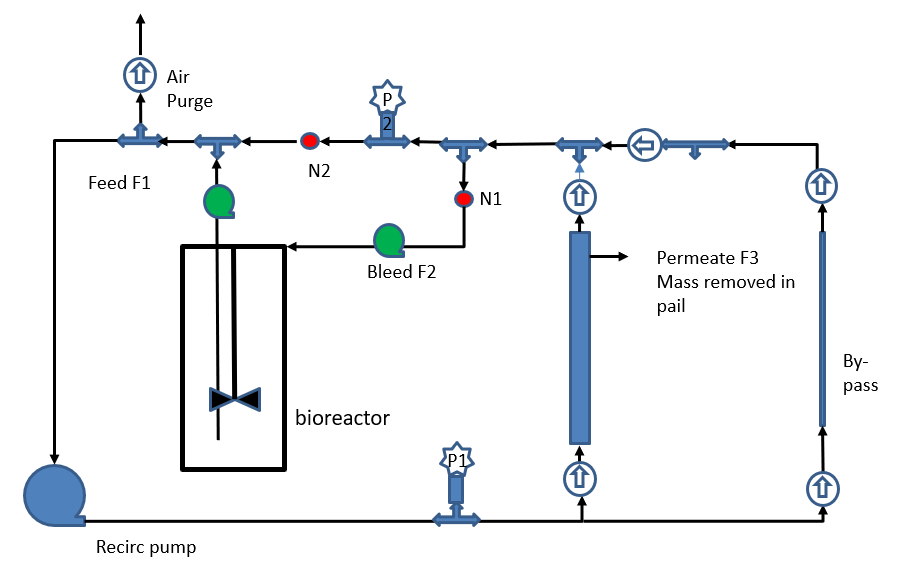
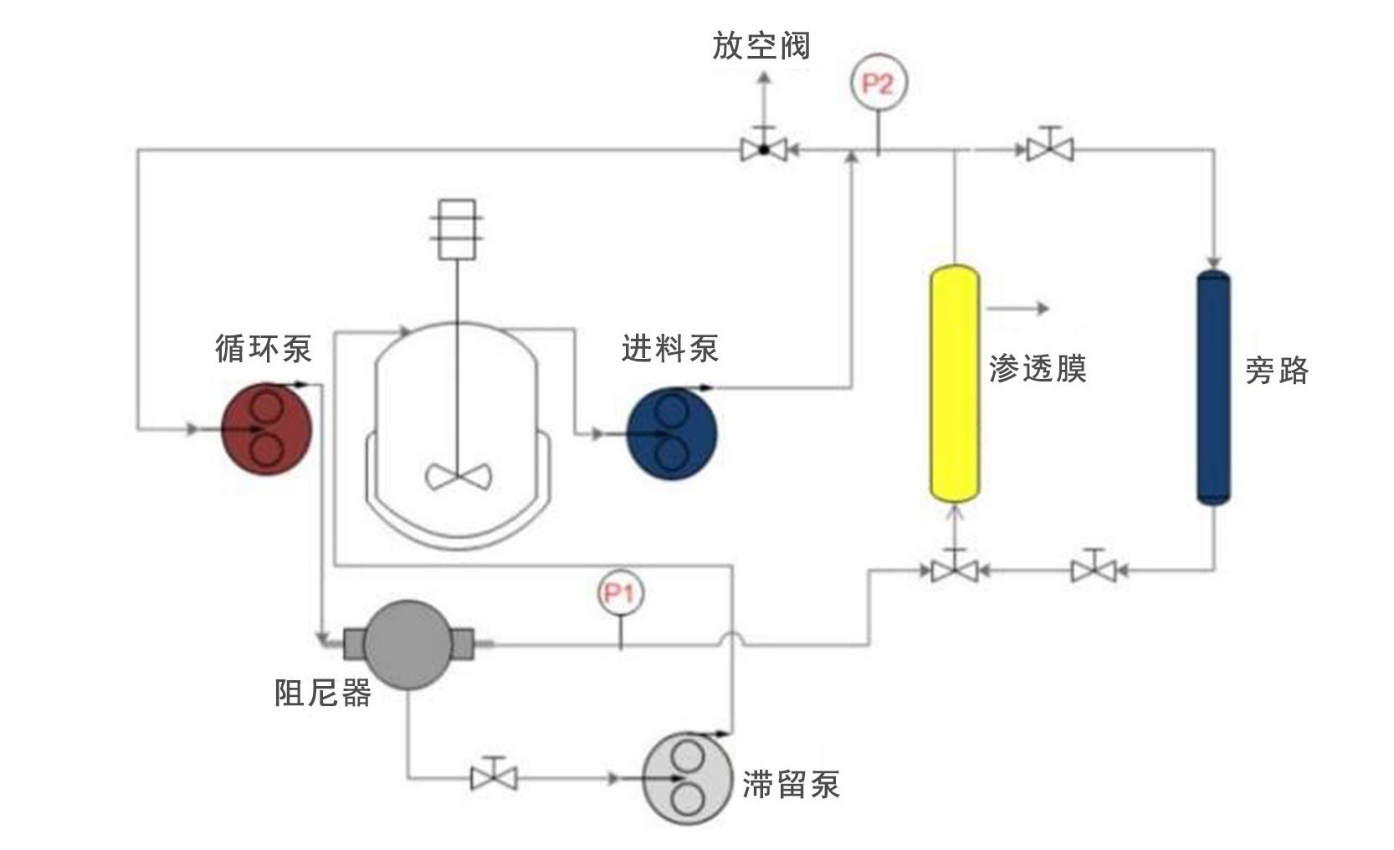
2.9 细胞循环连续丁醇发酵 16
2.9.1 细胞循环单元操作步骤 19
2.9.2 清洁系统的操作步骤 19
2.9.3 膜的保存 20
第三章 结果与讨论 21
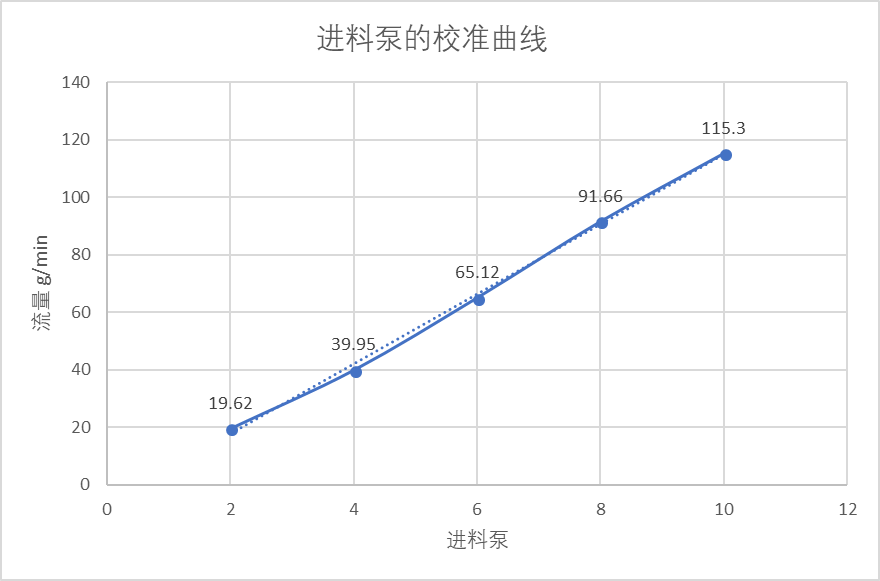
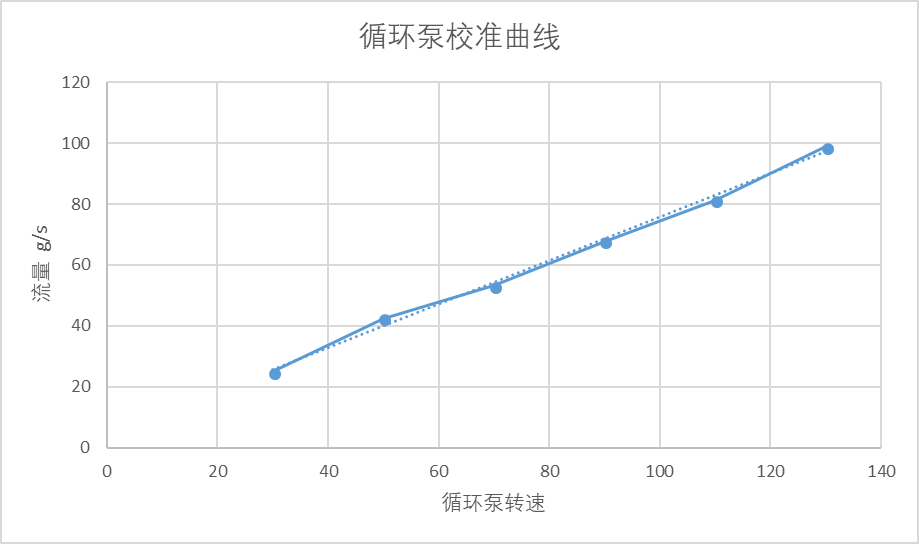
3.1 泵的流量校准 21
3.2 间歇式发酵 23
3.3 细胞循环用于连续丁醇发酵 26
第四章 结论与展望 28
4.1 实验结论 28
4.2 动力结构的改进设想 28
4.3 能源结构的改进设想 29
参考文献 30
致谢 33
第一章 文 献 综 述
1.1 丁醇的性质
丁醇(butanol),化学式为C4H9OH,醇类,沸点为117.6℃。20°C时,丁醇在水中的溶解度为7.7%。丁醇可与乙醇等多种有机溶剂混溶。 [1-2]。
表1-1 醇类和汽柴油的物化特性
名称 | 密度/(g·ml-1) | 沸点/℃ | 闪点/℃ | 辛烷值(RON) | 十六烷值 |
甲醇 | 0.7920 | 64.5 | 11~12 | 106~115 | 3~5 |
乙醇 | 0.7893 | 78.4 | 13~14 | 100~112 | 8 |
丁醇 | 0.8109 | 117.7 | 35~37 | 95~100 | 25 |
汽油 | 0.72~0.78 | 40~210 | -45~-38 | 80~98 | 5~25 |
柴油 | 0.82~0.86 | 180~370 | 65~88 | 约20 | 45~65 |
1.2 丁醇的价值
1.2.1丁醇的应用领域
丁醇作为重要的有机溶剂,在化工、医药、印染和塑料等行业具有可观的应用价值。
在化工方面,丁醇主要可作制作正丁酯类增塑剂的原料,包含邻苯二甲酸酯、磷酸酯等,此类增塑剂宽泛应用于橡胶以及塑料制品。除此丁醇还是合成丁醛、丁酸和丁胺等物质的原料,也用作有机染料和脱蜡剂等[3]。
相关图片展示:
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



