活性炭基水合氧化铁纳米复合材料深度净化水中磷的实验研究毕业论文
2020-07-04 19:51:59
摘 要
磷含量过高是造成水体富营养化的深层原因。在各种除磷的方法中吸附法以其易操作、高效快速、无二次污染、可回收利用、价格低廉的优点得到了广泛的应用。金属氧化物吸附剂吸附速率快、吸附容量高,具有很高的吸附潜能,但金属氧化物微纳的尺寸限制了其在工程当中的应用。本实验利用活性炭负载水合氧化铁,制备出载铁活性炭复合材料,并对其除磷性能进行试验研究。结果表明,复合吸附剂对磷的吸附效果与温度成正比,但是温度对于吸附量的影响效果不显著。pH越高吸附效果越差,吸附量在pH为2-3时最高。随着时间的推移,吸附剂的吸附效果提高,当达到13h时,吸附剂的吸附效果趋于平缓,吸附量接近饱和。溶液中共存的SO4-、Cl-、NO3-三种竞争离子都不会对磷的吸附效果造成显著地影响,表明复合材料具有优异的吸附选择性。利用NaOH溶液作为脱附剂溶液进行脱附试验,结果表明,10%NaOH溶液用于脱附最佳。脱附过后,进行吸附剂的再吸附实验,表面该载铁吸附剂的再生性能很好。
关键词:载铁活性炭 除磷 吸附 再生
Experimental study on enhanced purification of phosphorus from water by activated carbon based hydrated iron oxide nanocomposite
Abstract
High phosphorus content is the deep cause of eutrophication.The adsorption method has been widely used in various phosphorus removal methods due to its advantages of easy operation, high efficiency, no secondary pollution, recyclable utilization and low price.Metal oxide adsorbent has high adsorption potential due to its fast adsorption rate and high adsorption capacity, but the size of metal oxide nanometer limits its application in engineering.In this experiment, ferrogen-loaded activated carbon composite materials were prepared by using activated carbon loaded with hydrated iron oxide, and its phosphorus removal performance was studied experimentally.The results showed that the adsorption effect of the composite adsorbent was proportional to the temperature, but the effect of temperature on the adsorption was not significant.The higher the pH, the worse the adsorption effect,and the adsorption is highest at a pH of 2-3.As time goes on, the adsorbent adsorption effect increases. When it reaches 13h, the adsorbent adsorption effect tends to be flat and the adsorption amount is close to saturation.The co-existence of three competing ions in solution will not significantly affect the adsorption effect of phosphorus, indicating that the composite has excellent adsorption selectivity.The results show that 10% NaOH solution is the best for desorption.After desorption, the resorption experiment of adsorbent was carried out.
Keywords: Iron load activated carbon; phosphorus removal; adsorption; regenerate
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第一章 前言 1
1.1 研究背景 1
1.2 常用的污水除磷工艺 1
1.2.1化学凝聚法 1
1.2.2结晶法 2
1.2.3 吸附法 2
1.2.4生物法 2
1.2.5人工湿地法 2
1.3 吸附除磷的研究进展 3
1.3.1 常见的除磷吸附剂 3
1.3.2 吸附法除磷技术的展望 4
1.4 铁氧化物吸附剂 5
1.5 本论文的意义 5
第二章 实验部分 6
2.1 实验试剂及仪器 6
2.2 实验方法 7
2.2.1 载铁活性炭的制备 7
2.2.2 磷溶液的配制 7
2.2.3 显色剂的配制 7
2.2.4温度对吸附的影响实验 8
2.2.5 pH对吸附的影响实验 8
2.2.6 动力学对吸附的影响实验 8
2.2.7 竞争离子对吸附的影响实验 9
2.2.8 脱以及再吸附实验 9
2.3 分析及计算 10
2.3.1 磷溶液标准曲线 10
2.3.2 吸附量的计算 11
第三章 实验结果与讨论 12
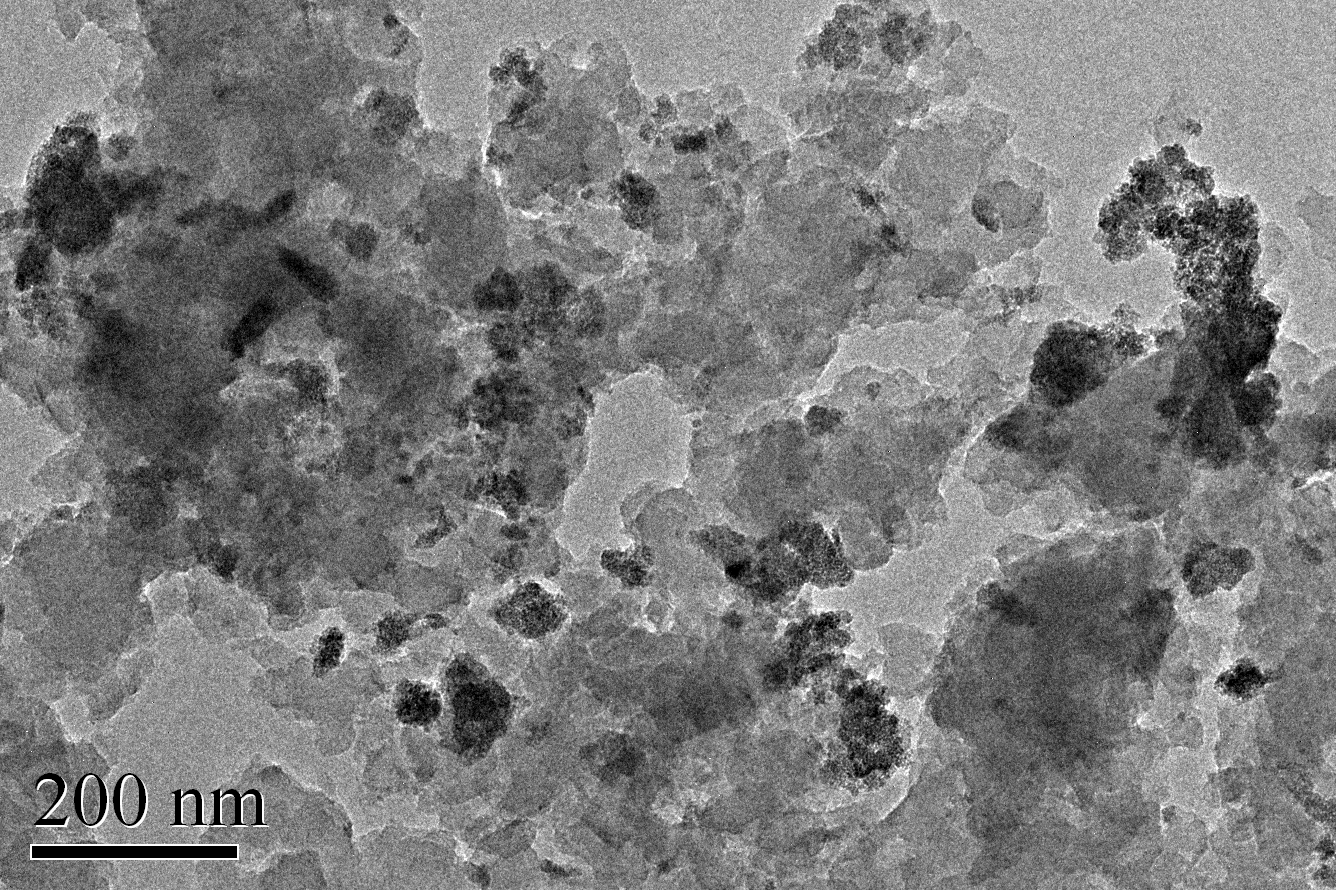
3.1 吸附剂的表征 12
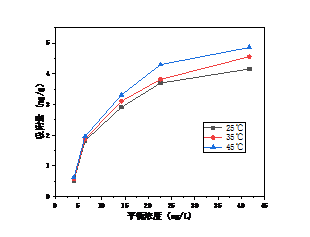
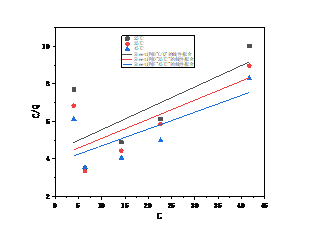
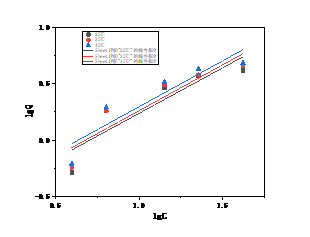
3.2 温度对吸附的影响 12
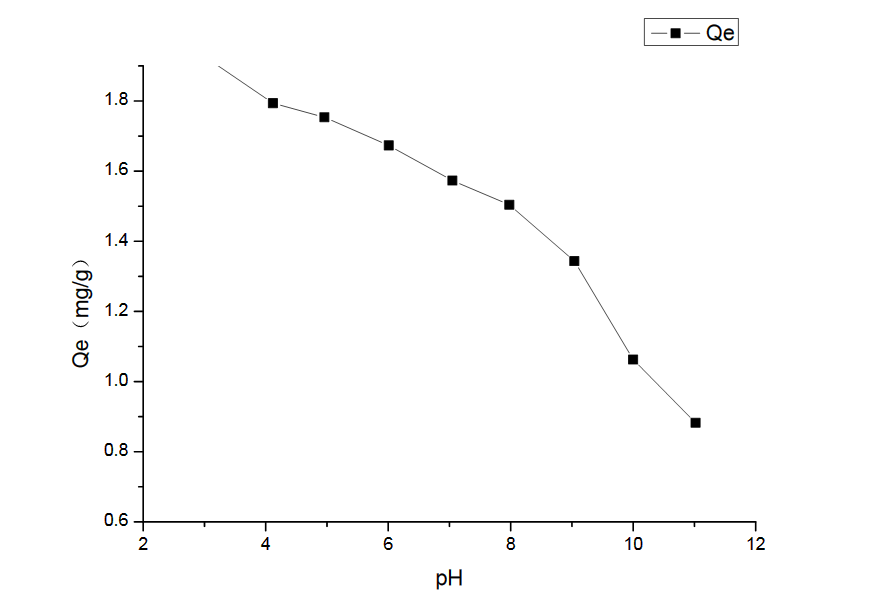
3.2 pH对吸附的影响 15
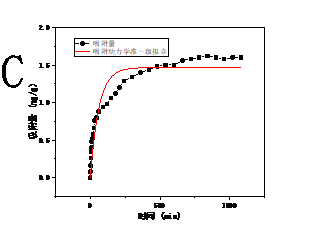
3.3 吸附动力学 16
3.4 竞争离子对吸附的影响 17
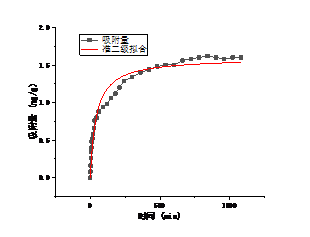
3.5 吸附剂的脱附以及再吸附实验 17
第四章 结论与展望 20
4.1 结论 20
4.2 展望 21
参考文献 22
致谢 25
第一章 前言
1.1 研究背景
由于营养物质的增加而引起的水体富营养化会导致水生环境退化或者是物种组成发生变化,例如藻类激增导致的藻华现象甚至是海底缺氧的现象。不论是何种用途的水体,水体富营养化的现象都是一个严重的问题。
氮和磷是导致水生植物生长养分过量激增的两个关键因素。虽然藻类的产生是水生生态系统食物链的第一个环节,但是富营养化条件下藻类会过度生长,最终导致水体环境的严重退化。因此,水体富营养化速度加快的首要因素就是营养物质的进入。
相关图片展示:
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



