玻璃粘结用高强度碱催化胶水的配方与老化研究毕业论文
2020-07-05 17:39:22
摘 要
目前,对于高光洁度玻璃的粘结正在研发一种新的粘结技术。在国际上,这种技术被应用在各种引力波探测器中。探测器中有些部位的安装和固定,如硅光学元件,可以使用这种特殊的胶粘方法,即氢氧化物催化粘结技术,简称HCB。简单来说,如果在表面之间可以形成硅酸盐网络,换言之,任何含有二氧化硅的材料,则该技术可实现多种材料之间的粘结。
本文重点研究在碱胶水中加入不同吸水高分子的不同质量含量对粘结强度的影响。并采用冷热循环和室外自然太阳光紫外线照射进行老化试验,测老化对粘结强度的影响。对粘结的样品分别进行4小时和8小时后的移动测其对粘结性能的影响。实验中使用万能测试机测量剪切强度,数据越大,则证明碱胶水的粘结能力越强。
实验结果表明,吸水高分子的加入会大幅度的影响碱胶水的粘结性。自然状态下紫外线的老化对其几乎没有影响。4小时和8小时后的移动实验会影响胶水的剪切强度。无尘空间下粘结的玻璃片强度比自然状态下的大一些。冷热循环对粘结强度破坏力非常大。
关键词:HCB 玻璃 吸水高分子 剪切强度 老化
Study on the Formulation and Aging of High Strength Alkali-catalyzed Glue for Glass Bonding
Abstract
At present, a new bonding technology is being developed for the bonding of high gloss finish glass. Internationally, this technique is used in various gravitational wave detectors. The mounting and fixing of some parts of the detector, such as silicon optical elements, can use this special adhesive method, namely the hydroxide catalytic bonding technique, abbreviated as HCB. In simple terms, if a silicate network can be formed between the surfaces, or in other words, any material containing silicon dioxide, this technique can achieve adhesion between a variety of materials.
This article focuses on the effect of different mass content of different water-absorbing polymers added to the alkali-catalyzed glue on the bond strength. The aging test was performed using the thermal cycle and the outdoor natural sunlight ultraviolet radiation, and the effect of aging on the bond strength was measured. The adhesion of the bonded samples was measured after 4 hours and 8 hours, respectively, to determine their effect on the bonding performance. The shear strength of the test sample was measured with a tensile machine. The greater the shear strength, the stronger the binding ability of the alkaline glue.
The experimental results show that the addition of water-absorbing polymer will greatly affect the adhesion of the alkaline glue. Ultraviolet aging has little effect on the natural state. Moving experiments after 4 hours and 8 hours will affect the shear strength of the glue. Bonded glass sheet in dust-free space is stronger than in natural state.Cold and hot cycles are very damaging to bond strength.
Keywords: HCB ; Glass; Water-absorbing polymer; Shear strength; Aging
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 前言 1
第二章 理论部分 3
2.1国内进展 3
2.2国外进展 3
2.2.1 Gravity Probe B 4
2.2.2天基GW探测器 4
2.2.3 LISA Pathfinder 5
2.2.4高新LIGO 5
2.2.5蓝宝石悬浮液 7
2.3HBC研究现状 8
2.3.1粘结厚度 8
2.3.2机械损失 9
2.3.3弹性模量 10
2.3.4尺寸稳定性 10
2.3.5光学性能 10
2.3.6热传导 11
2.3.7当前研究热点 11
2.4高吸水树脂(SPA) 11
2.4.1特性 12
2.4.3吸水原理 13
2.4.4 结构特征 13
2.4.5应用 13
第三章 实验部分 14
3.1实验原料 14
3.2实验仪器 14
3.3研究目标 14
3.4剪切强度测试 14
3.5预期成果 14
3.6实验流程 14
第四章 结果与讨论 16
4.1单一溶质 16
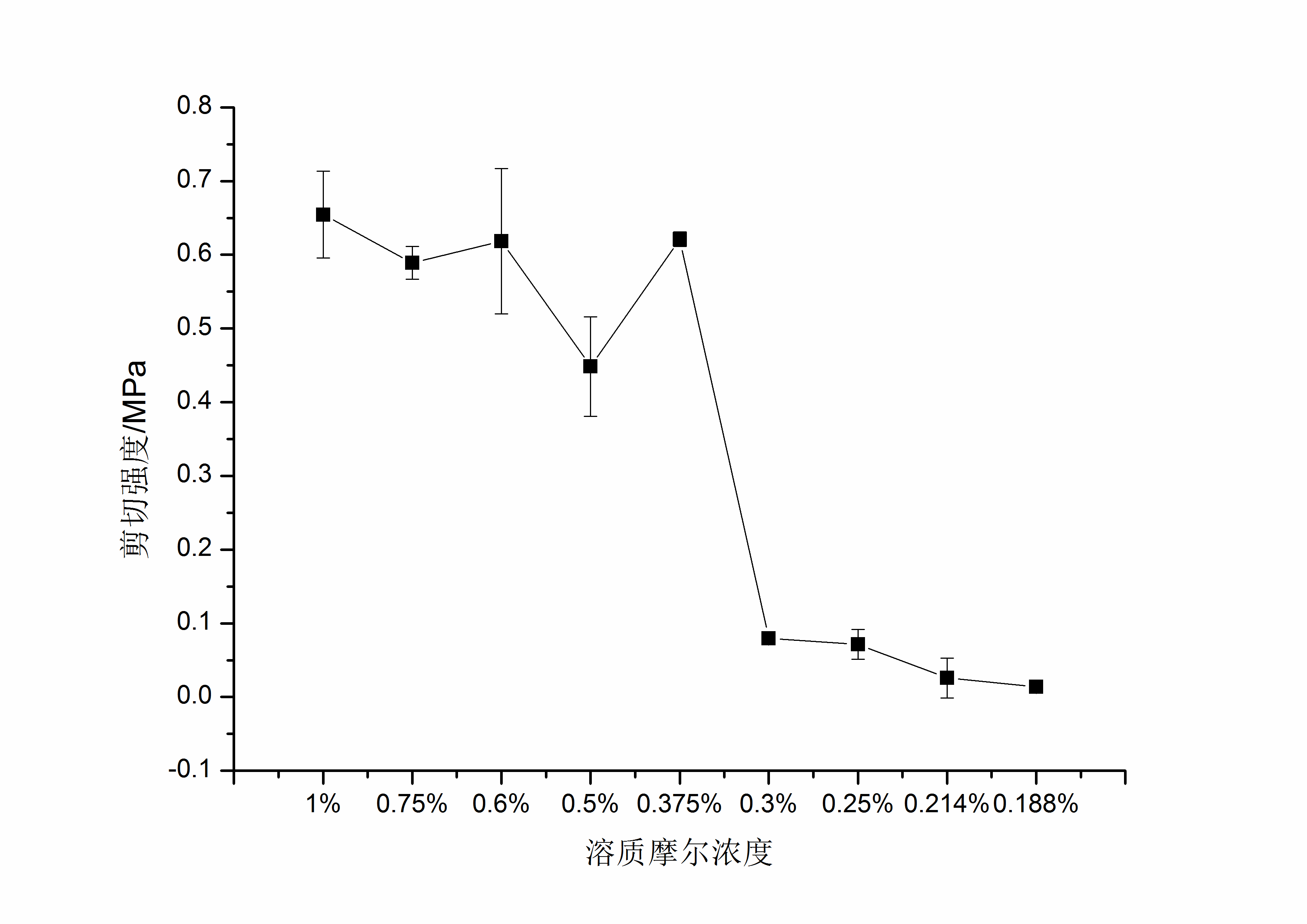
4.2溶质摩尔浓度的影响 17
4.3Na2SiO3·9H2O用量的影响 18
4.4吸水树脂粘结 19
4.5吸水树脂的影响 20
4.7移动的影响 24
4.8冷热循环的影响 25
4.9紫外线老化 26
4.10傅里叶变换红外光谱分析 27
第五章 结论与展望 28
5.1结论 28
5.2展望 28
参考文献 29
致谢 32
第一章 前言
2016年,美国LIGO探测到引力波,在世界各地掀起了很大的反响。近几个世纪,国际上主要靠测量电磁波来发现天文学。引力波有望推进研究引力量子化的进展,开辟了一条研究宇宙的新方向,促使人类步入天文学新的时代[2]。如下图1-1。
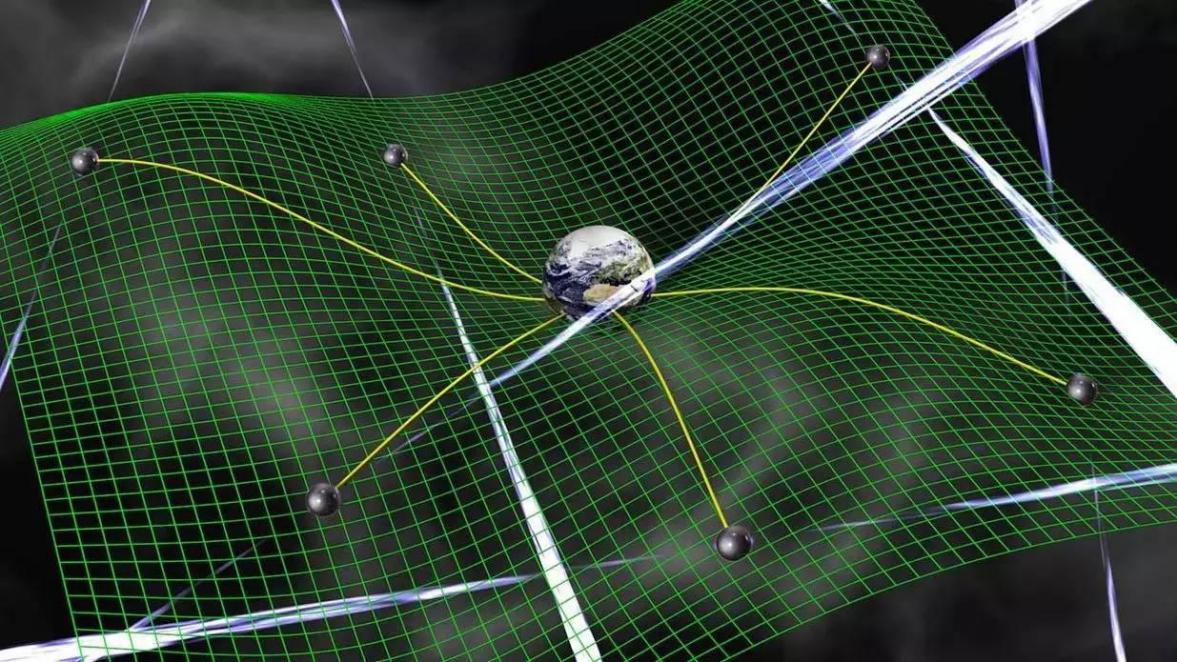
图1-1 引力波
引力波探测器的光学系统必须由轻质材料制成,能够承受先显著的加速度和温度化,诸如ZERODUR,ULE(超低膨胀材料)和二氧化硅等材料都可能是合适的。根据光学系统的具体要求以及光学布局的透射和反射特性,这些材料可以单独使用或一起使用来制造光学平台。这些光学系统的几何布局往往非常复杂,对机械稳定性要求非常严格,因此连接部件是一个很大的挑战。有很多粘结措施,众所周知的有,如:光学接触[3-5],扩散粘结[4,6,7],玻璃料粘结[3]、粘合剂粘结[3,8]和机械紧固[9],这种传统的粘结方法的代替物是HCB。
因为该技术粘结过程可以在室温下进行,并且产生非常强的粘结力,可以在低至2.5 k的低温系统中应用,可以实现高对准精度,且粘结厚度非常薄,因此产生非常低的机械损失和噪声水平。最初是在斯坦福大学发明的[10,11],用于为Gravity Probe B任务的光学望远镜粘结二氧化硅部分[12],此过程利用氢氧化物催化作用将光学元件连接到光学固定件上,以获得高稳定性,同时满足精确对准的要求。它的固化原理分为三个步骤:
相关图片展示:

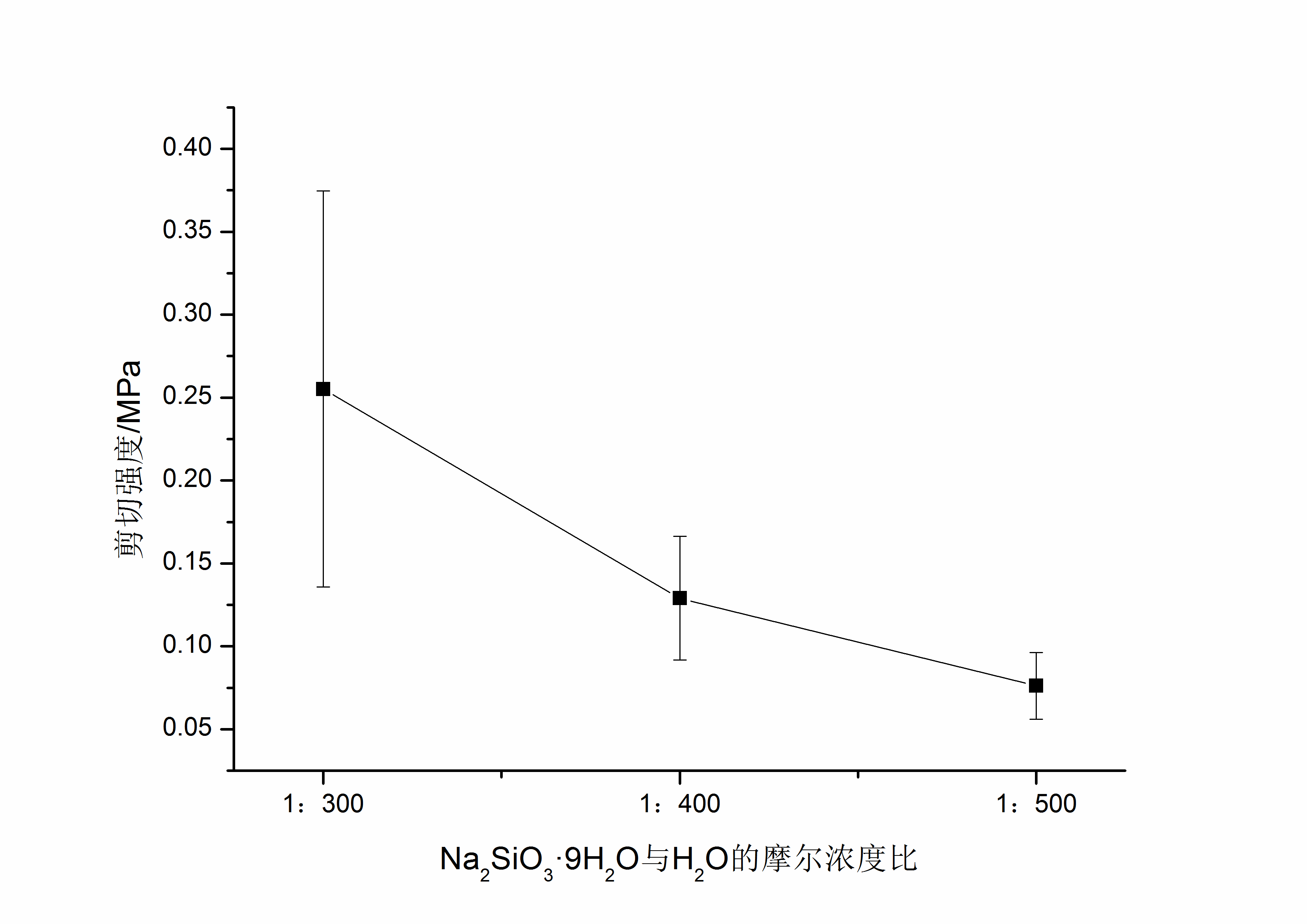
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



