大脑视觉皮层信号分离方法研究毕业论文
2020-07-07 21:37:04
摘 要
用电极在头皮和大脑皮层记录电位随时间变化波形的曲线为脑电信号,是测量并反映大脑活动的重要标志。能够帮助人们积极探索大脑活动世界。但是,我们所测量获取的脑电信号,往往很微弱。在极其微弱的脑电信号中还充斥着大量的干扰信号(背景噪声),是一种典型的非线性非平稳的随机信号。传统的信号处理分析方法都用于线形平稳的理想信号。而对于非线性非平稳的随机信号而言,不能够有效的降噪和提取有用的信号用于研究。
经验模态分解(Empirical Model Decomposition,EMD)是信号处理领域一种新型的方法,对于非线性非平稳信号十分适用。对于复杂的信号源,经验模态分解方法能够将其自适应的分解为一系列不同频率尺度的信号分量,即本征模函数(Intrinsic Mode Function,IMF)。而所测量的脑电信号中的干扰信号,可以经过EMD分解为IMF参量后滤除。
序参量(Order Parameter)是协同学里的一种重要物理参量。是用于判断系统的是否稳定的一种衡量系数。同样也是非线性同步耦合的重要参量。对于所测得的随机信号,通过寻找序参量方程,对脑电信号的波谱具有重要的研究意义。
主成分分析(Principal Component Analysis,PCA)是一种信号分离的重要研究算法。该方法从能量的角度出发,对随机信号的分离有独特的优势,可以为分离视觉刺激信号的波谱提供了有效途径。
本文深入研究了EMD、Order Parameter以及PCA的基本原理和在脑电信号中的处理,主要包括以下三个方面:(1)基于EMD方法对小鼠脑电信号的分离;(2)序参量在研究小鼠脑电信号非线性同步的意义。(3)PCA算法在弱信号提取中的应用。我们对小鼠的脑电信号分别采用上述方法,试图寻找视觉刺激部分的对应频率成分。考虑到小鼠脑电信号的复杂特点,我们首先引入了三种数学方法。针对三种方法的特征,进行了分别讨论。其次通过对基础信号的研究与分析,找到与脑电信号的相同点。最后将小鼠的脑电信号作为研究对象,将三种方法结合起来实施信号的分离与提取,找到其视觉刺激部分响应。
关键词 :经验模态分解 序参量 非线性同步 希尔伯特黄变换 主成分分析
Study on Signal Separation Methods of Cerebral Visual Cortex
Abstract
The curve which records the waveform of the potential change with time in the scalp and cerebral cortex is an electroencephalogram signal, which is an important marker for measuring and reflecting brain activity. Can help people actively explore the world of brain activity. However, the EEG signals we measure are often very weak. The extremely weak EEG signal is also filled with a large number of interference signals (background noise), which is a typical non-stationary, non-stationary random signal. Traditional signal processing analysis methods are used for ideal linear smooth signals. For nonlinear non-stationary random signals, effective noise reduction and extraction of useful signals cannot be used for research.
Empirical Model Decomposition (EMD) is a new method in the field of signal processing. It is suitable for nonlinear non-stationary signals. For complex signal sources, the empirical mode decomposition method can be adaptively decomposed into a series of signal components at different frequency scales, namely Intrinsic Mode Function (IMF). The interference signals in the measured EEG signals can be filtered out after the EMD decomposes into IMF parameters.
Order parameter is an important physical parameter in synergy. It is a measure of the stability of the system. It is also an important parameter of nonlinear synchronous coupling. For the measured random signal, by looking for the order parameter equation, it has important research significance for the spectrum of the EEG signal.
Principal component analysis (PCA) is an important research algorithm for signal separation. This method has unique advantages for the separation of random signals from the perspective of energy, and can provide an effective way to separate the spectrum of visual stimulation signals.
This paper deeply studies the basic principles of EMD, Order Parameter, and PCA and the processing in EEG signals, including the following three aspects: (1) Separation of mouse brain electrical signals based on EMD method; (2) Order parameters To study the significance of nonlinear synchronization of mouse brain electrical signals. (3) The application of PCA algorithm in weak signal extraction. We used the above methods for the brain's electrical signals in mice, trying to find the corresponding frequency components of the visual stimulation part. Taking into account the complex characteristics of mouse brain signals, we first introduced three mathematical methods. The characteristics of the three methods were discussed separately. Second, through the research and analysis of the basic signals, find the same point with the EEG signal. Finally, the mouse EEG signal was used as the research object, and the three methods were combined to perform signal separation and extraction, and find the visual stimulus part of the response.
Keywords: Empirical mode decomposition Order Parameter Non-Linear Synchronization Hilbert-Huang Transform Principal Component Analysis
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 EMD研究背景与发展趋势 1
1.2 非线性同步 2
1.3 PCA技术的研究背景及意义 2
1.4 Hilbert-Huang Transform 2
1.5 Order Parameter 3
1.6 本文主要研究内容及结构安排 3
第二章 PCA算法在脑电弱信号中的提取 5
2.1 引言 5
2.2 PCA算法基本原理 5
2.3 PCA算法的基本性质 6
2.4 PCA算法的使用 7
2.5 基于PCA算法小鼠视觉刺激信号提取 8
2.6 本章小结 9
第三章 基于经验模态分解的脑电信号数据预处理方法 10
3.1 引言 10
3.2 EMD基本原理 10
3.3.1 Hilbert变换 10
3.3.2 瞬时频率 11
3.3.3 本征模函数 12
3.3 EMD实现方法 14
3.4 脑电信号的相关特点 17
3.5 基于小鼠脑电信号的EMD处理 18
3.6 本章小结 20
第四章 基于序参量对于脑电信号的拟合 21
4.1 引言 21
4.2 序参量基本原理 21
4.3 基于序参量的随机信号分解 23
4.4 基于小鼠脑电信号的序参量拟合 23
4.5 本章小结 24
第五章 总结 26
5.1 本文主要工作 26
5.2不足与展望 26
参考文献 27
致谢 29
第一章 绪论
人类脑计划(Human Brain Project,HBP)是继人类基因组计划之后,又一国际性科研计划,其核心是神经信息学(Neuroinformatics),该研究旨在努力探究数十亿个神经元的信息,以期对知觉、行动以及意识等有更进一步的了解[1]。科学家们预期这是一条开发新技术的好途径,由此可能进一步认识像老年痴呆和帕金森综合症等疾病,有望为各种精神疾病研究出新的治疗方法,此外,该计划还可以更好地为人工智能服务[2]。
脑电波(Electroencephalography,EEG)是大脑在活动时,脑皮质细胞群之间形成电位差,从而在大脑皮质的细胞外产生电流[3]。人在主动思维或受到不同的感觉刺激时,能够产生特定模式的脑电信号[4]。因此,脑电波信号的采集、噪声的消除以及特征提取技术就成为脑电波信号处理系统设计的关键环节[5]。
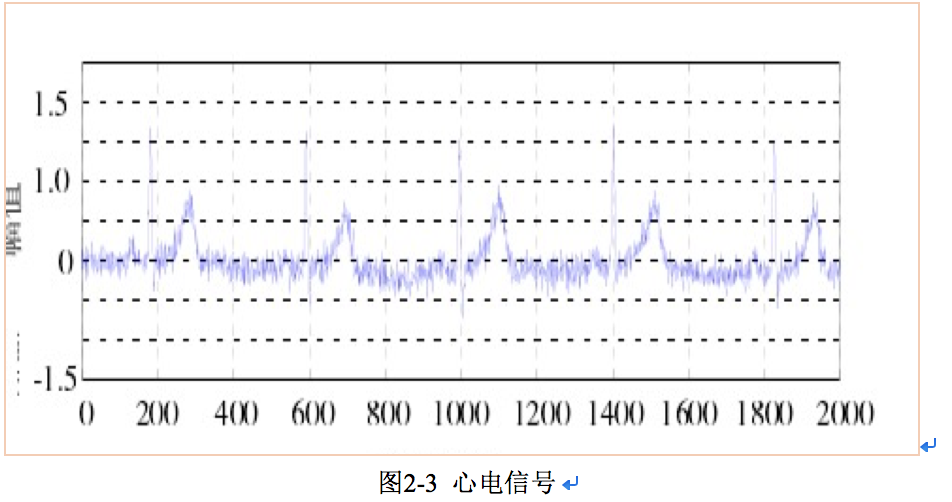
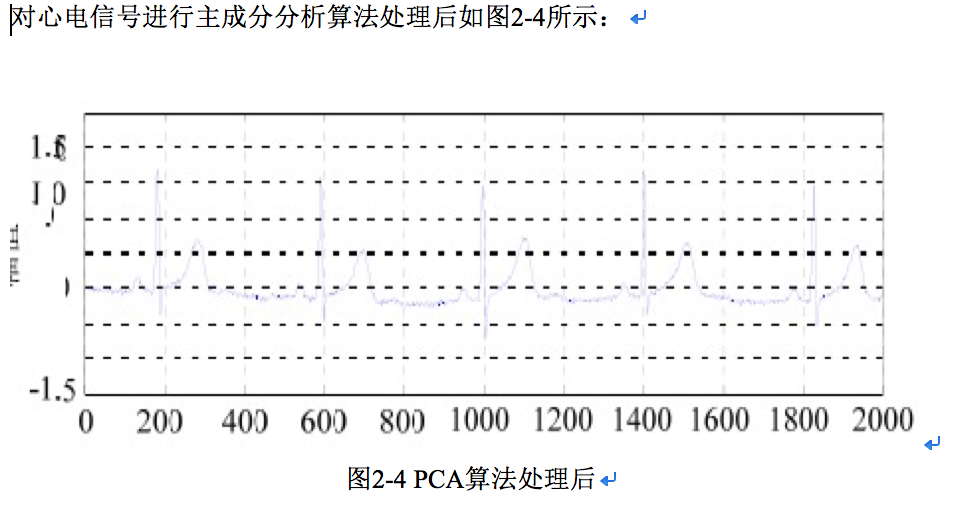
相关图片展示:
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



