含石膏质集料水泥基材料的变形特性研究毕业论文
2020-07-07 21:57:51
摘 要
硫酸盐侵蚀一直是导致混凝土强度下降、影响混凝土耐久性的问题之一。根据硫酸盐的来源不同,硫酸盐侵蚀可以分为内部硫酸盐侵蚀和外部硫酸盐侵蚀。内部硫酸盐侵蚀,硫酸盐的来主要源包括水泥中的石膏,矿物掺和料中的硫酸盐,集料中的硫酸盐等。我国中西部地区存在着大量的石膏质岩层,在实际工程中,出现了由于集料引入过量的硫酸盐造成混凝土内部硫酸盐侵蚀破坏的事例。
本文通过成型含有石膏质集料的净浆和砂浆试件,研究了石膏掺入量、水灰比对含石膏质集料净浆试件膨胀性能的影响,对比研究了石膏掺入量、水灰比和养护温度对含石膏质集料砂浆试件膨胀率、强度性能的影响。并采用了XRD和SEM分析了内部硫酸盐侵蚀过程中,砂浆试件内部矿物组成和微观结构的演化过程。经研究表明:
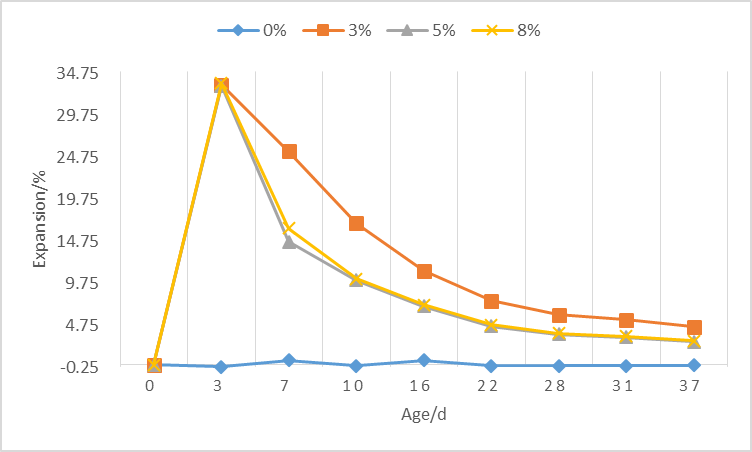
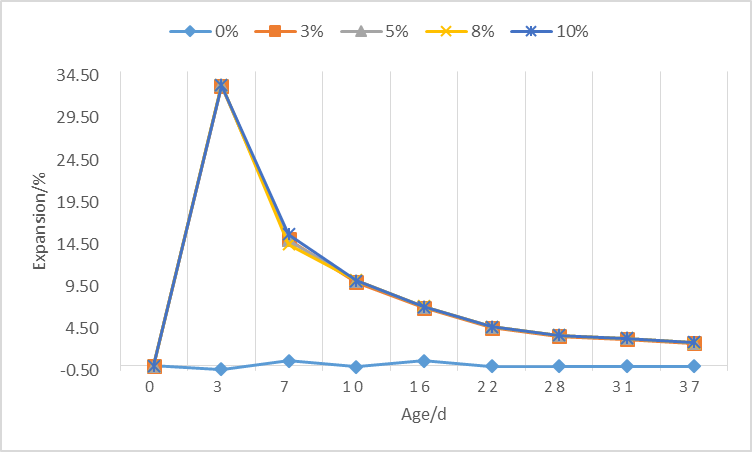
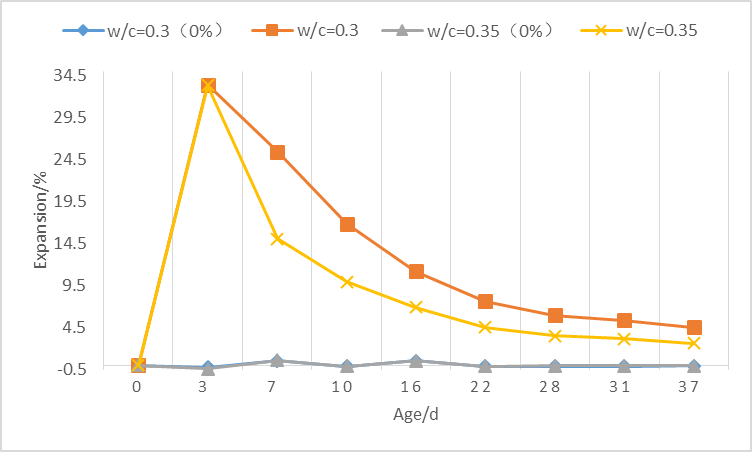
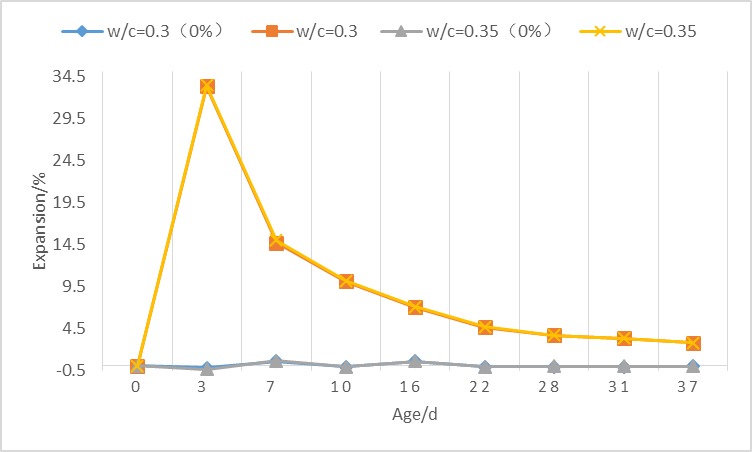
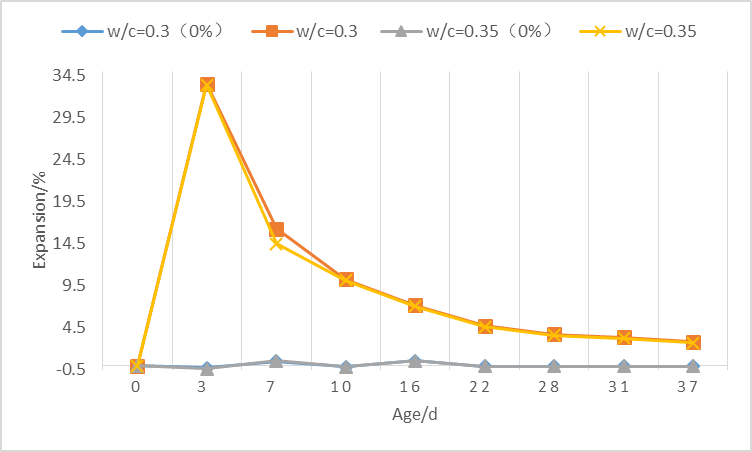
1)对于净浆试件,石膏掺量越高,试件的膨胀率越大,在早期3d、7d时掺有石膏的试件,膨胀率会迅速增大,而后膨胀率逐渐减小,但均大于未掺石膏样品。相同石膏掺量下,水灰比对试验的膨胀性能影响不大。
2)石膏质集料的掺入会明显降低试件的强度,随着石膏质集料掺量的增加,砂浆试件的膨胀率逐步增加。养护温度越高,砂浆试件的膨胀率并不一定大,养护温度为40℃,砂浆试件的膨胀率最大。相同石膏掺量下,水灰比对砂浆试件的膨胀性能影响不大。
3)通过XRD和SEM分析表明,180d内含石膏质集料砂浆试件内部生成了大量的钙矾石,在砂浆试件内部出现了一些裂纹分布在石膏集料周围,但都是一些细小的裂纹分布在石膏集料在周围,没有出现贯穿性裂纹,石膏集料与浆体没有出现明显的脱空。
关键词:硫酸盐侵蚀 石膏集料 微观结构变化
Study on Deformation Characteristics of Cement-based Materials Containing Gypsum Aggregates
ABSTRACT
Sulfate attack has always been one of the problems that caused the concrete strength to decrease and affect the durability of the concrete. According to the source of sulfate, sulfate attack can be divided into internal sulfate attack and external sulfate attack. Internal sulfate attack, the main sources of sulfate include gypsum in cement, sulfate in mineral admixtures, sulfate in aggregates, etc. In China's central and western regions, there are a large number of gypsum rock formations. In actual projects, there have been cases where the sulfate inside the concrete has been damaged due to the excessive sulfate introduced by the aggregate.
In this paper, the effect of gypsum incorporation and w/c on the expansion performance of gypsum-aggregate pulp paste specimens was investigated by molding the specimens of paste and mortar containing gypsum aggregates. The gypsum-incorporation and water were comparatively studied. Effect of Ash Ratio and Curing Temperature on the Swelling Rate and Strength Properties of Plaster Cast Mortars. XRD and SEM were used to analyze the evolution process of the mineral composition and microstructure of the mortar specimen during the internal sulfate attack. Research shows that:
(1) For paste specimens, the higher the gypsum content, the greater the expansion rate of the specimens. In the early 3d and 7d gypsum test specimens, the expansion rate will increase rapidly, and the post-expansion rate will gradually decrease, but both are greater than No gypsum sample was added. At the same gypsum dosage, the w/c has little effect on the expansion performance of the test.
(2)The incorporation of gypsum aggregates will significantly reduce the strength of the specimens. As the gypsum aggregate content increases, the expansion rate of mortar specimens gradually increases. The higher the curing temperature, the expansion rate of the mortar specimen is not necessarily large, the curing temperature is 40°C, and the expansion rate of the mortar specimen is the largest. With the same amount of gypsum, the w/c has little effect on the expansion performance of the mortar specimen.
(3)XRD and SEM analysis showed that a large amount of ettringite was formed inside the 180day gypsum-aggregate mortar specimen. Some cracks appeared inside the mortar specimen around the gypsum aggregate, but all were small crack distributions. There is no penetrating crack in the gypsum aggregate around, and there is no obvious voiding of gypsum aggregate and paste.
.
KEY WORDS:Sulfate attack; Gypsum aggregate; Deformation
目录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT II
目录 1
第一章 绪论 3
1.1背景介绍 3
1.2混凝土硫酸盐侵蚀 4
1.3硫酸盐侵蚀机理 5
第二章 实验材料与方法 7
2.1 实验材料及设备 7
2.1.1试验材料 7
2.1.1.1水泥 7
2.1.1.2石膏 8
2.1.1.3骨料 8
2.1.2实验设备 8
2.2研究方法 10
2.2.1样品制备 10
2.2.1.1砂浆 10
2.2.1.2净浆 11
2.2.2测量方法 12
2.2.2.1抗压强度 12
2.2.2.2测长 12
2.2.2.3矿物相组成 13
第三章 实验结果 15
3.1净浆试件劣化过程 15
3.1.1石膏掺量的影响 15
3.1.2水灰比的影响 17
3.2 砂浆试件劣化过程 20
3.2.1 膨胀性能 20
3.2.1.1 石膏掺量的影响 20
3.2.1.2水灰比的影响 21
3.2.1.3 养护温度的影响 21
3.2.2 强度性能 22
3.2.2.1 抗压强度 22
3.2.2.2 抗折强度 23
3.2.3 矿物组成 24
第四章 结论与展望 27
4.1结论 27
4.2展望 27
参考文献 29
致谢 32
第一章 绪论
1.1 背景介绍
随着人们进入21世纪,科技发展日新月异,人们的需求也越来越多,越来越广泛。作为世界上最大的发展中国家,我国自然也不甘落后,在世界舞台上展示着中国令人震惊的发展速度和力量。在中国共产党第十九次全国代表大会上,习近平总书记首次提出“新时代中国特色社会主义思想”,在总书记的带领下,我们正在大踏步向全面建成小康社会的宏伟蓝图进发。然而,我国国土辽阔,地形复杂,在追求经济快速发展的大潮流中,交通条件依然是重中之重。就像一句老话说的那样:要想富,先修路。这句话即便是放到如今也丝毫不过时。
只有路通了,经济才能发展,文化才有交流,社会才能进步。中国人口数量众多,资源分布不均匀,公路和铁路便以其经济、便捷的优势成为我国广泛使用的大众化交通工具,且在我国的综合交通运输体系中处于骨干地位。
交通强国,铁路先行。我国铁路有八纵八横,在一份分析报告中可以看到,中国电气化铁路总里程在五十多年里突破了五万多公里,超越了俄罗斯,攀升为世界第一位。但由于许多历史和经济原因,我国铁路发展曾长期落后于他人,并且与世界上许多的国家和地区相比,我国铁路网的密度和质量还不够理想。
特别是在我国的中西部地区,随着铁路和公路建设逐渐延伸到偏远山区[12],一些复杂的地形和特殊的地质条件给设计师和施工人员都造成了不小的困扰,成为一项棘手的挑战。比如我国贵州省地区“天无三日晴,地无三尺平”。其岩层中的碳酸盐类岩石容易溶蚀,常常产生溶洞、漏斗、暗河及溶蚀裂隙,而岩层中的粘土岩类岩石则容易风化、雨水天气会引起软化,以至于造成泥石流等灾害。
相关图片展示:


课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



