圆柱形三元镍钴铝动力电池的电化学-热耦合行为研究毕业论文
2020-07-07 22:10:06
摘 要
锂离子动力电池作为当今非常理想的储能装置,仍然存在着在放电和放热过程中的不均匀或是过度化情况。锂离子电池是个复杂的能源体系,采用计算机数值仿真技术可以建立电池模型,准确全面迅速地观察到电池内部的动态变化。本文借助多物理场仿真软件COMSOL,对镍钴铝动力电池建立了一个电池内多种行为耦合的电化学-热耦合模型,综合了电池制造商提供的和实验室测量的电池参数,最终确定了所建立模型的各项参数,经过各项实验验证了模型的合理性。
电化学模型表明:电极-集流体界面或电极-隔膜界面电流密度最大,电化学反应最剧烈。热模型表明:电池放电倍率越大,温度升高越快。引起电池温度升高的主要热量包括负极的可逆热和正极的不可逆热。当放电倍率大于5C时,容易引发安全事故。
为了研究不同风冷条件下的温度情况,本文改变电池对流换热系数以模拟整个过程。结果表明:过低或过高的换热系数都会带来负面影响,因此应当选择合适的对流换热环境。
关键词:锂离子电池;有限元;COMSOL;耦合模型
Study on electrochemical and thermo-coupling behavior of cylindrical tri-nickel-cobalt aluminium power cells.
Abstract
As a very ideal energy storage device, lithium ion power battery still exists in the process of discharge and exothermic process. The lithium ion battery is a complex energy system, and the computer numerical simulation technology can be used to establish the battery model, and the dynamic changes of the battery can be observed accurately and comprehensively. In this paper, with the help of many physical field simulation software COMSOL, an electrochemical-thermal coupled model has been set up to investigate electrochemical and thermal behaviour during constant current discharging process, a combination of battery manufacturers and laboratory measurement of battery parameters, eventually determine the parameters of the established model, through the experiments to verify the rationality of the model.
Electrochemical models show that the electrode-separator fluid interface or electrode-current collector interface has the largest current density, and the electrochemical reaction is the most intense. The thermal model shows that the higher discharging current, the faster the temperature rise. The main heat that causes the increase of battery temperature includes the irreversible heat of the negative electrode and the irreversible heat of the positive pole. When discharge current rate is greater than 5C, it is easy to cause safety accidents.
In order to study the temperature under different air conditions, the heat transfer coefficient of the cell was changed to simulate the whole process. The results show that the heat transfer coefficient of too low or too high will have a negative effect, so the suitable convective heat transfer environment should be selected.
Key Words: Li-ion battery; finite element; COMSOL; coupling model.
目 录
摘要…………………………………………………………………………………I
ABSTRACT………………………………………………………………………II
第一章 绪论 ………………………………………………………………………1
1.1 引言 …………………………………………………………………………1
1.2 锂离子动力电池 ……………………………………………………………1
1.2.1锂离子动力电池的结构……………………………………………1
1.2.2锂离子电池的工作原理……………………………………………1
1.2.3电化学-热耦合效应 ………………………………………………2
1.3 锂离子电池模型的研究现状 ………………………………………………2
1.3.1电化学模型的数学处理方法………………………………………2
1.3.2国外电化学热耦合模型的研究进展………………………………2
1.3.3国内电化学热耦合模型的研究进展………………………………3
1.3.4国内外电化学热耦合模型研究方向………………………………4
第二章 COMSOL与有限元法…………………………………………………5
2.1 COMSOL简介 ………………………………………………………………5
2.2有限元法及应用………………………………………………………………5
2.2.1有限差分法…………………………………………………………5
2.2.2有限元法……………………………………………………………7
2.3有限元方法的应用和趋势 …………………………………………………8
第三章 数理模型 ………………………………………………………………9
3.1 模型介绍 ……………………………………………………………………9
3.1.1一维电化学模型………………………………………………………9
3.1.2二维产热模型…………………………………………………………9
3.1.3建模假设 ……………………………………………………………10
3.2 建模思路……………………………………………………………………11
3.3 控制方程……………………………………………………………………11
3.4 模型参数确定………………………………………………………………12
第四章 模型验证及结果讨论…………………………………………………15
4.1 NCR18650B简介……………………………………………………………15
4.2实验系统搭建 ………………………………………………………………15
4.3数值方法 ……………………………………………………………………16
4.4实验验证 ……………………………………………………………………17
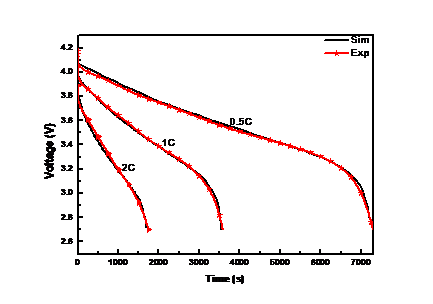
4.4.1电化学验证……………………………………………………………17
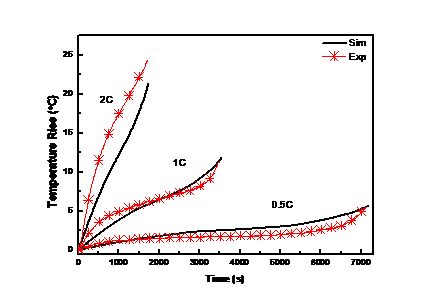
4.4.2热力学验证……………………………………………………………18
4.5脉冲测试 ……………………………………………………………………18
4.6本章小结 ……………………………………………………………………19
第五章 结果与讨论 ……………………………………………………………21
5.1 放电过程中的电化学行为特性……………………………………………21
5.2 热分析与产热表征…………………………………………………………23
5.3 在热管理系统中应用………………………………………………………25
第六章 结论………………………………………………………………………28
致谢…………………………………………………………………………………29
参考文献 …………………………………………………………………………31
附录…………………………………………………………………………………32
第一章 绪论
1.1 引言
人类社会自筚路蓝缕到现代社会,能源问题始终是关乎人类社会发展的重大问题,经济社会的飞速发展往往都伴随着能源的重大突破。而经过了数百年的开采挖掘,传统能源如石油、天然气等,已经有了逐渐枯竭的趋势。传统能源所带来的副作用在日益严峻的环境问题、生态问题中显露无疑。除了加大传统能源使用限制之外,人们的目光,转移到新兴的绿色节能技术和清洁能源开发上来。一大批新能源相关的战略性新兴产业涌现出来。与之相应,科学研究领域,新能源也再度成为关注焦点。新能源汽车产业也是一大炙手可热的研究热点,而电池技术在其中起到了核心作用。锂离子电池的工作电压很高,同时具有较大的能量密度,在长时间的循环利用上表现也很突出[1]。锂离子电池还具有无工作记忆、绿色清洁等优点[2],能一定程度上满足汽车对动力电池的要求。
1.2 锂离子动力电池
1.2.1锂离子动力电池的结构
锂离子动力电池是由电芯、外壳及正负极接线端组成。圆柱形电池的电芯是螺旋卷绕式的,其基本结构[3]包括:正极集流体、正极活性材料层、隔膜、负极活性材料层、负极集流体、极耳。
1.2.2 锂离子电池的工作原理
1980年M.Armand[4]提出摇椅式锂二次电池的构想,形象地描述了锂离子电池的工作原理。在充电时,正极Li 脱嵌,Li 通过电迁移的方式穿过隔膜到达负极,在负极得到电子发生还原反应,并且锂离子嵌入到负极石墨活性次材料中。放电过程与此相反,负极活性锂失去电子变为Li ,同样因为电迁移作用迁移至正极,在正极发生还原反应得到电子并嵌入到正极活性材料中。简而言之,Li 在正负极的材料中来回穿梭,完成了电能和化学能之间的互换。
电池的放电反应:
相关图片展示:




课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



