纤维素气凝胶制备及改性毕业论文
2020-07-09 20:26:45
摘 要
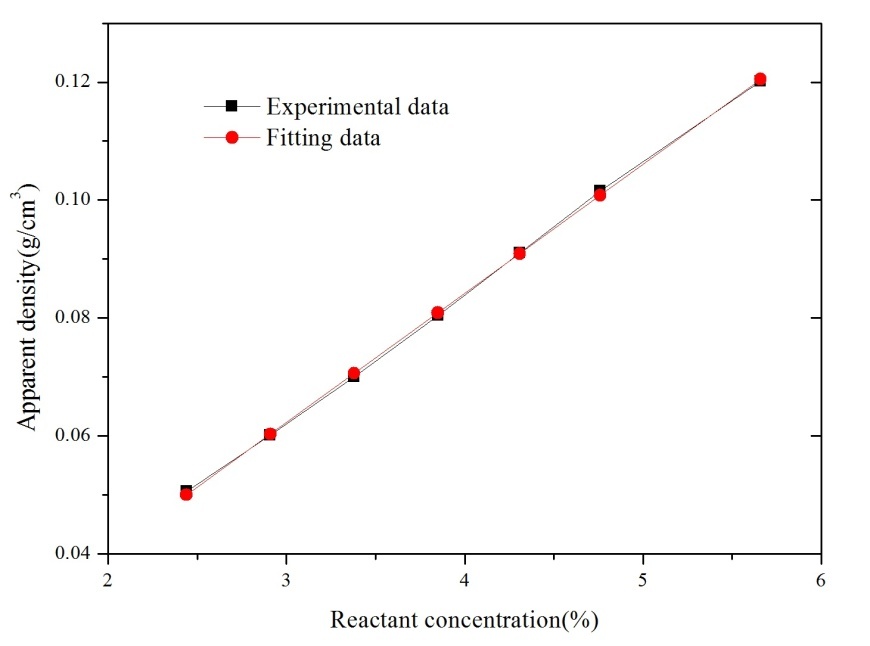
以纤维素为原料制备的气凝胶具有低密度、高比表面积、低热导率、高吸附、良好的力学性能、可再生等优异特性。本论文针对气体吸附用氨基改性纤维素气凝胶的制备开展研究。首先,采用氢氧化钠/尿素/水作为纤维素的溶解体系,通过相转化诱导溶胶-凝胶法和CO2超临界干燥工艺成功制备了纤维素气凝胶,纤维素气凝胶的密度与纤维素溶液的浓度成线性关系;其次,通过凝胶的表面化学改性制备了氨基改性纤维素气凝胶,并考察了氨基改性纤维素气凝胶的CO2气体吸附性能,其空气捕集性能可达0.31 mmol/g;最后,并对所制备样品的化学结构、热物性、晶体结构进行了测试表征,纤维素气凝胶的热导率低至0.03765 W/(m∙K),是一种潜在的优秀绝热材料。
关键词:纤维素 气凝胶 氨基改性 CO2吸附
Preparation and Modification of Cellulose Aerogels
ABSTRACT
The aerogels prepared from cellulose as raw materials have wonderful properties such as low density, high specific surface area, low thermal conductivity, high adsorption, good mechanical properties, and reproducibility. In this paper, the preparation of amino modified cellulose aerogels for gas adsorption was studied. Firstly, cellulose aerogels were successfully prepared by phase transformation induced sol-gel method and CO2 supercritical drying process using sodium hydroxide/urea/water as the solution system of cellulose. The density of cellulose aerogel is linear with the concentration of cellulose solution; secondly, the amino modified cellulose aerogels were prepared by the surface chemical modification of the gel, and the CO2 adsorption properties of the amino modified cellulose aerogels were investigated. The air trapping property of the aerogels was 0.31 mmol/g. Finally, the chemical structure, thermal properties and crystal structure of the prepared samples were tested and characterized. The thermal conductivity of cellulose aerogels was as low as 0.03765W/(mK), which was a potential excellent thermal insulation material.
Keywords: Cellulose; Aerogel; Amino modification; CO2 adsorption
目 录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT II
目 录 III
第一章 绪论 1
1.1引言 1
1.2纤维素气凝胶的制备 2
1.2.1纤维素气凝胶制备:直接溶解 2
1.2.2纤维素气凝胶制备:水相分散 3
1.3纤维素气凝胶改性 3
1.3.1引入电学、磁学性能 3
1.3.2负载活性物质 3
1.3.3提高力学性能 4
1.3.4氨基改性 4
1.4纤维素气凝胶的干燥 5
1.5研究目的及主要内容 5
第二章 实验方法 6
2.1原料及仪器 6
2.1.1 纤维素气凝胶及氨基改性纤维素气凝胶制备原料及仪器 6
2.2 实验内容 6
2.2.1 纤维素气凝胶的制备 6
2.2.2 氨基改性的纤维素气凝胶的制备 7
2.3 测试表征方法 7
第三章 结果讨论 9
3.1 纤维素气凝胶制备及表征 9
3.1.1 纤维素气凝胶形貌分析 9
3.1.2 前驱体浓度对纤维素气凝胶的影响 9
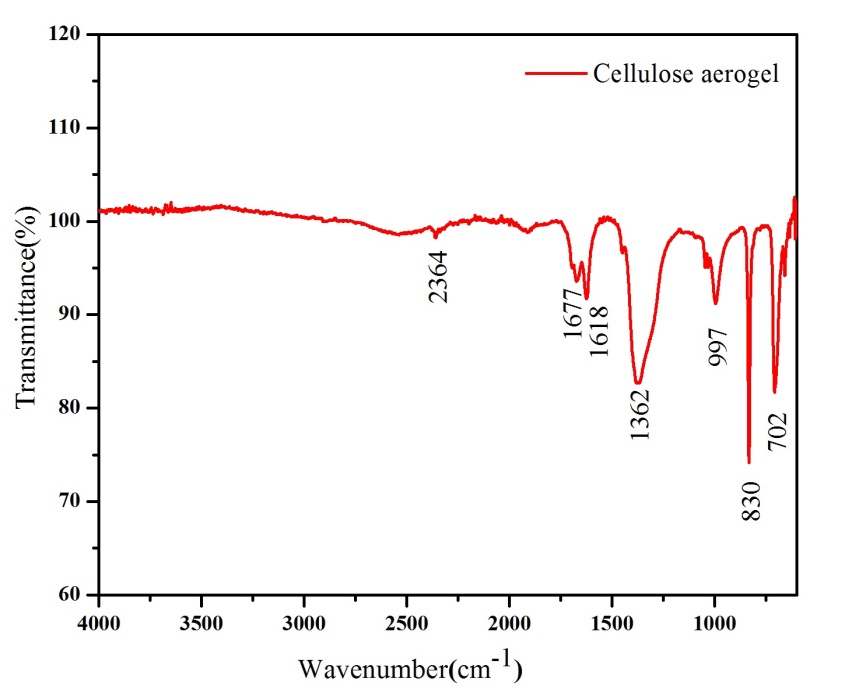
3.1.3 红外光谱分析 10
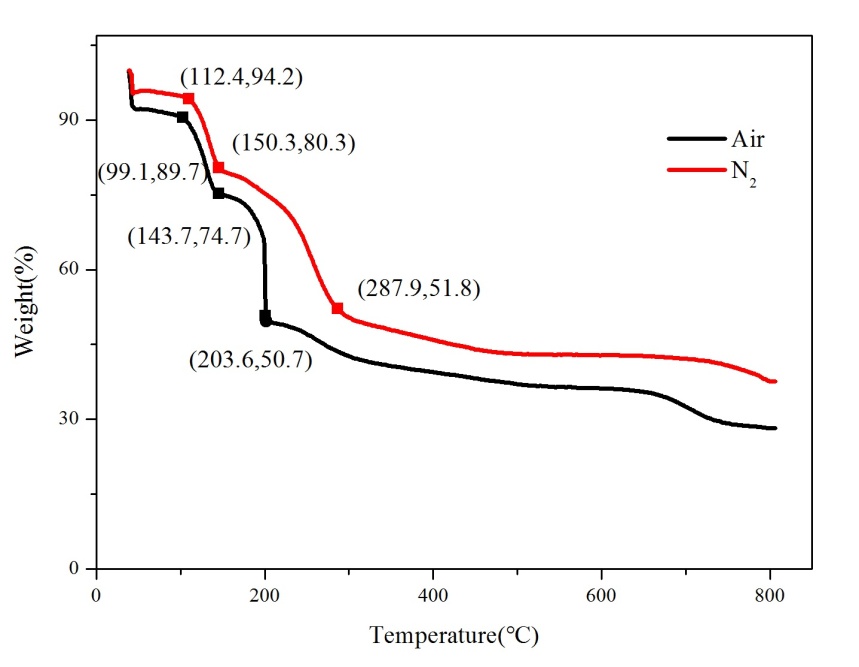
3.1.4热重分析 11
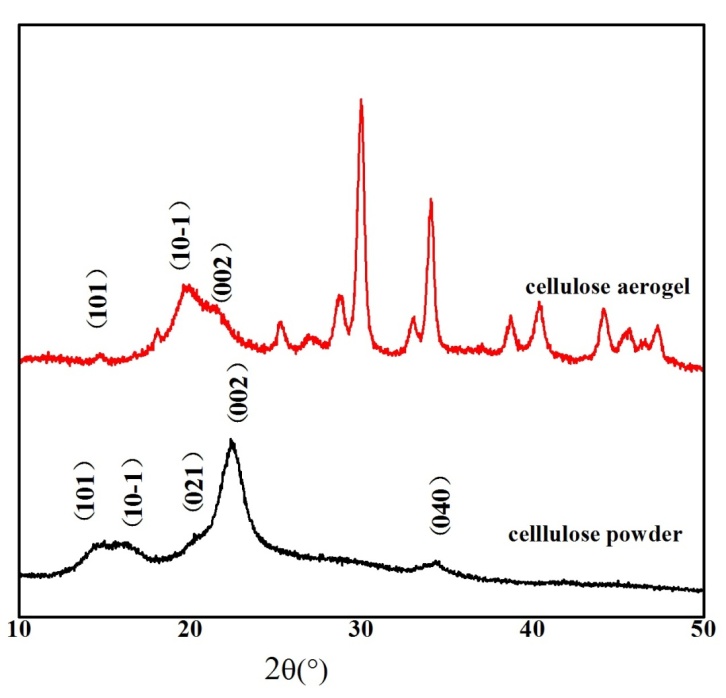
3.1.5 X-射线衍射分析 11
3.2 氨基改性的纤维素气凝胶制备表征及CO2吸附性能研究 12
3.2.1 氨基改性的纤维素气凝胶形貌分析 12
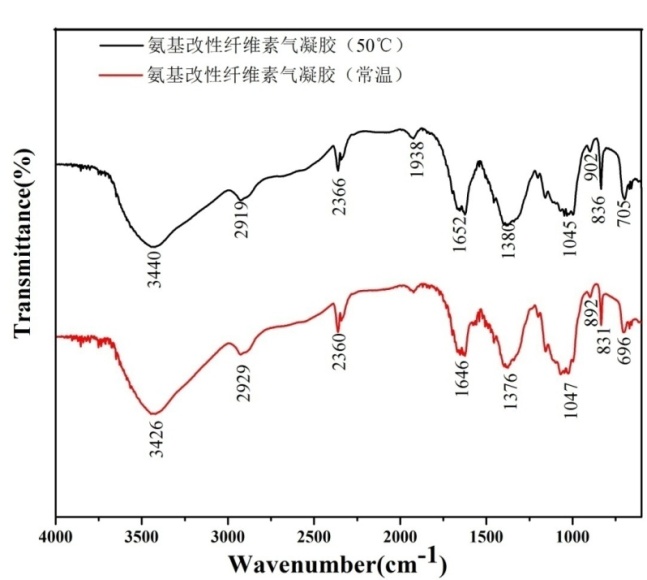
3.2.2 红外图谱分析 13
3.2.3 热重分析 14
3.2.4 CO2吸附性能 15
第四章 结论和展望 17
4.1结论 17
4.2展望 17
参考文献 18
致 谢 21
第一章 绪论
1.1引言
气凝胶是一种具有特殊性质的凝胶,它是把湿凝胶网络结构中的液体置换成气体而不改变凝胶本身的三维网络结构得到的[1],是湿凝胶干燥处理后得到的产物。现在普遍将气凝胶定义为一种气体和固体的混合物质。
1931年,Kistler[2]教授首先以硅酸钠为原料制备出二氧化硅气凝胶。但是由于制备过程繁复、制备成本较高、样品机械性能较差,没有引起人们的重视。随着溶胶-凝胶(sol-gel)术的发展,无机气凝胶和聚合物气凝胶开始大量出现[3]。例如间苯二酚/甲醛缩聚物气凝胶和二氧化硅气凝胶得到了快速发展[4]。有机气凝胶机械性能优良。但是有机气凝胶有着不可避免的缺点就是热稳定性较差,在高温条件下易分解。
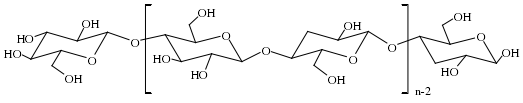
纤维素是自然界的天然高分子,分子式是(C6H10O5)n,它具有分布广,储量大等特点,并且具有良好的生物可再生性、生物相容性和生物可降解性等独特的特点[5]。2001年,Tan Chibing等人[6]以纤维素衍生物作为原料,通过常压干燥的技术,得到了纤维素气凝胶。纤维素的化学结构如图一所示。
相关图片展示:
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。