地埋管地源热泵传热特性分析毕业论文
2020-07-11 18:20:11
摘 要
能源对人类的影响十分重大,没有能源的支撑,人类就无法继续发展下去。然而随着社会的发展,能源变得越来越短缺,此时人们发现地热能是一个解决能源危机的好办法。而地埋管地源热泵则是利用地热能的重要方式。地埋管地源热泵工作中,地埋管的传热特性起着非常大的作用。因此本文对地埋管地源热泵的传热特性进行分析。
首先,本文阐述了地埋管地源热泵研究的背景,及国内外学者研究的现状。然后根据地埋管的两种不同埋管方式(水平埋管和竖直埋管)进行比较。根据现有条件对水平埋管进行设计。在前人的基础上根据已知的地埋管管径,间距等条件,对地埋管排布方式进行设计。并计算管路排布的能量损失,从而选出了最优的管路排布方法,最后通过计算土壤蓄热量来验证设计是否成功。设计完成后,对水平埋管及竖直埋管分别进行模拟分析,通过设置不同的边界条件如地埋管管径,管子入口流速,土壤的导热系数等模拟地埋管温度云图及曲线图以分析这些因素对管子传热的影响。通过模拟可以得出以下结论:
水平埋管中,由于管子直径与土壤尺寸相差得不大,所以传热较快,但也不太稳定。管子流速对地脉管换热特性影响较大。具体表现在,随着流速的增加。传热变得更均匀。管径对管子传热基本没有什么影响。竖直埋管中钻孔间距取为4m是合理的,不会产生热干扰。随着管径的增大,换热面增大,导热热阻减小,所以流量变化较小.由于本身的管径很小限制速度相差不大,所以流速对管子和土壤之间的换热影响不大。土壤的热物性本身对管子换热特性影响大,但由于土壤的导热系数本身不大,且不同的土壤的导热系数相差也不大,因此土壤导热系数对地埋管传热特性影响不大。非稳态模拟中,可以发现经过一段时间变化后,土壤的温度逐渐降低。最终趋于稳定。
关键词: 地源热泵 地埋管 传热特性
Analysis of heat transfer characteristics of ground source heat pump.
Abstract
The impact of energy on mankind is very significant. Without the support of energy, mankind cannot continue to develop. However, with the development of society and the shortage of energy, it is found that geothermal energy is a good way to solve the energy crisis. The ground source heat pump is an important way to utilize geothermal energy. The heat transfer characteristics of buried pipe are very important in the work of ground source heat pump. Therefore, the heat transfer characteristics of buried pipe ground source heat pump are analyzed.
Firstly, this paper describes the background of the research of ground source heat pump and the current situation of domestic and foreign scholars. Then the comparison between two buried pipes (horizontal buried pipe and vertical buried pipe) was conducted. The horizontal buried pipe was designed according to the existing conditions. On the basis of the predecessors, the layout of buried pipe is designed according to the known conditions of buried pipe diameter and spacing. The energy loss of pipeline arrangement is calculated and the optimal pipeline arrangement method is selected. Finally, the calculation of soil heat storage capacity is calculated to verify the success of the design. Design is completed, the horizontal buried pipe and vertical buried tube respectively simulated analysis, by setting the different boundary conditions such as buried pipe diameter, pipe inlet velocity, the coefficient of thermal conductivity of the soil and exchanger simulation temperature contours and curves to analyze the impact of these factors on the heat transfer pipe. The following conclusions can be drawn from the simulation:
In the horizontal pipe, because the diameter of the pipe is not so different from the soil size, the heat transfer is faster, but it is also unstable. The velocity of the tube has great influence on the heat transfer characteristics of the earth. Specifically, as the flow rate increases. Heat transfer becomes more uniform. Tube diameter has little effect on pipe heat transfer. It is reasonable to take the hole spacing in the vertical buried pipe as 4m, without thermal interference. With the increase of pipe diameter, the heat transfer surface increases, and the thermal resistance decreases, so the flow rate changes less. Because the diameter of the pipe is very small, the velocity is not very small, so the flow rate has little effect on the heat transfer between the pipe and the soil. The thermal
physical properties of the soil itself influence on heat transfer characteristics of the pipe, but due to the coefficient of thermal conductivity of the soil itself is not big, and different soil coefficient of thermal conductivity are also is not big, so the soil coefficient of thermal conductivity of buried pipe has a little influence on heat transfer characteristics. In unsteady state simulation, the temperature of soil decreases gradually after a period of change. Eventually it tends to be stable.
Keywords: ground source heat pump; buried pipe; heat transfer characteristics
目录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1引言 1
1.2课题研究现状 1
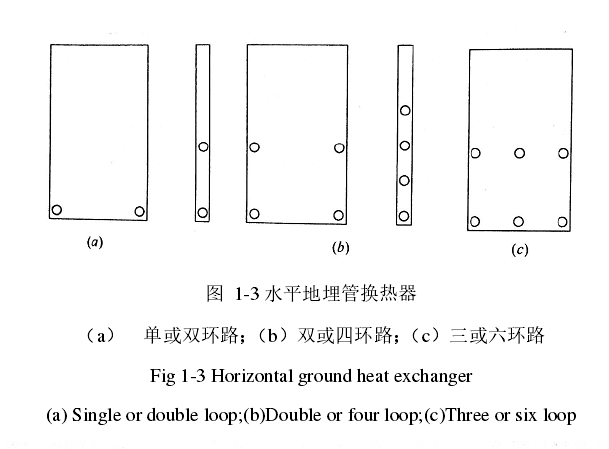
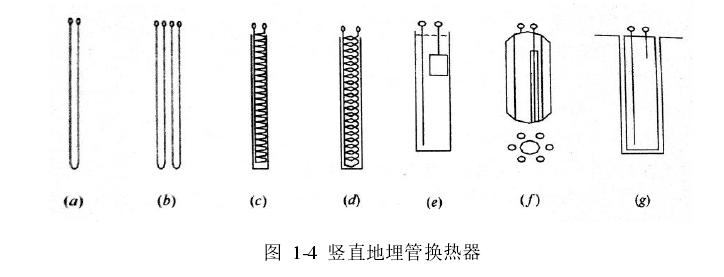
1.3埋管方式分类 2
1.4影响地埋管地源热泵传热特性因素 3
1.4.1 地质条件的影响 3
1.4.2 回填材料的影响 3
1.4.3埋管材料的影响 4
1.4.4地层初始温度对传热特性的影响 4
1.4.5介质流量及埋管深度的影响 4
1.5小结 4
第二章 Ansys软件的介绍 5
2.1 ansys介绍 5
2.2 fluent软件的介绍 5
2.3小结 5
第三章 传热理论及模型理论硏究 6
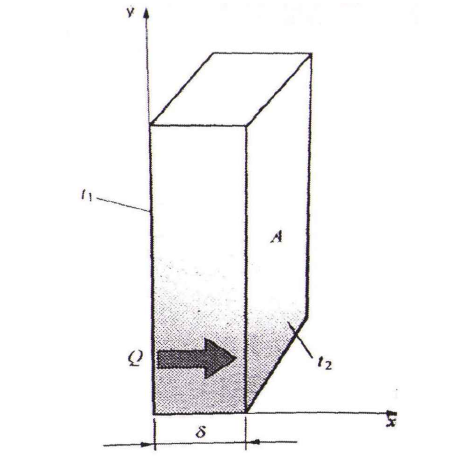
3.1导热 6
3.2热对流 7
3.3热辐射 8
3.4小结 9
第四章 地埋管地源热泵系统的设计 10
4.1地埋管埋管间距设计 10
4.2管道的能量损失分析 13
4.3土壤蓄热量 16
4.3.1理论分析 16
4.3.2验证 18
4.4小结 18
第五章 地埋管模型建立与模拟 19
5.1控制方程 19
5.2网格划分 20
5.3边界条件设置 21
5.4对地埋管传热特性影响因素分析 22
5.4.1钻孔间距对管群传热的影响 22
5.4.2地埋管管径对地埋管传热效果影响 24
5.4.3 流体进口流速对地埋管换热性能的影响 26
5.4.4土壤导热系数对地埋管换热性能的影响 27
5.4.5非稳态下地埋管模拟情况 28
5.5小结 29
第六章 水平埋管模拟 30
6.1建模及网格划分 30
6.2水平埋管模拟分析 31
6.3小结 36
第七章 结果与展望 37
7.1结果 37
7.2未来展望 37
参考文献 38
致谢 40
第一章 绪论
1.1引言
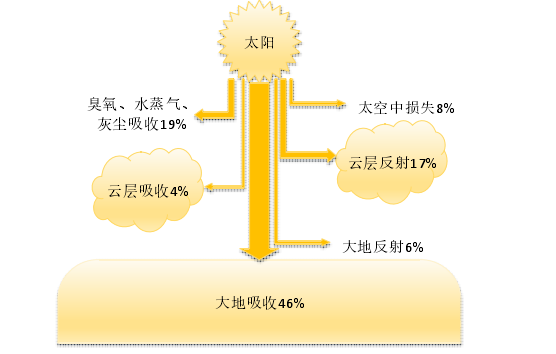
能源对人类的影响十分重大,是人们生存发展的重要物质基础,在整个人类文明发展历程中扮演着不可或缺的角色[1]。而随着社会的发展,能源变得越来越少,因此发展可再生能源显得非常紧迫和有必要。而地热能就是其中的佼佼者。它无穷无尽且能量巨大。地热能的来源有三部分1.太阳辐射2.地球内部的熔融岩浆3.放射性物质的衰变。大多太阳能被土壤所吸收,如图1-1所示。据有关资料,全球地热能的总量大约为1.45×1026 J,是全球煤炭总量的17000万倍[2]热泵是利用地热能的一种机器,它的产生可以更好的发展地热能,因此研究地源热泵的传热特性有着很好的意义[3]。
相关图片展示:
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。