直线导轨精密磨削过程的温度场建模与仿真研究毕业论文
2021-02-25 13:14:47
摘 要
在对精密直线导轨的磨削加工过程中,磨削砂轮与直线导轨的接触和相对运动会产生大量的热量,热量在局部的快速升高会在直线导轨内产生热传递。热量传递形成的温度场会引起热应力与直线导轨的热变形,从而影响精密直线导轨的加工精度,为此本文分析了精密直线导轨在磨削过程中的热传递与热变形。
在分析精密直线导轨热传递时,建立了直线导轨磨削区的热量产生模型,然后建立了导轨表面的温升模型;根据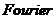 传热定律,建立了一个非齐次的抛物形微分方程热传递模型。使用MATLAB软件求解并分析了微分方程的数值解,得出结论:在直线导轨的表面磨削区温度最高,达到了401.6496℃,在直线导轨的底部温度最低,为33.0387℃。分析求解的结果,得出了热传递规律:(1)在直线导轨内部某一固定的深度(位置),随着磨削加工时间的增加,温度成递增的趋势;(2)在某一固定的时间,随着导轨内部深度的增加,导轨温度整体呈降低趋势。在深度越深的地区,越接近温度稳定时刻,温度升高得越快。
传热定律,建立了一个非齐次的抛物形微分方程热传递模型。使用MATLAB软件求解并分析了微分方程的数值解,得出结论:在直线导轨的表面磨削区温度最高,达到了401.6496℃,在直线导轨的底部温度最低,为33.0387℃。分析求解的结果,得出了热传递规律:(1)在直线导轨内部某一固定的深度(位置),随着磨削加工时间的增加,温度成递增的趋势;(2)在某一固定的时间,随着导轨内部深度的增加,导轨温度整体呈降低趋势。在深度越深的地区,越接近温度稳定时刻,温度升高得越快。
在分析精密直线导轨的热弯曲量部分,建立了直线导轨全长度范围内的热弯曲量模型。经过计算,在导轨长度为1.6m,上下表面温度差为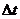 为400℃时,在直线导轨全长内的热弯曲量为3.7mm。
为400℃时,在直线导轨全长内的热弯曲量为3.7mm。
在分析精密直线导轨的内部的热应力部分,建立了直线导轨内部的应变增量模型。首先在SolidWorks软件中建立直线导轨的实体模型,然后导入Abaqus软件中进行有限元分析,最后得出结论:(1)在直线导轨的左右两端等效位移最大,导轨的底部以及中间等效位移最小;(2)直线导轨的上表面特别是靠近螺纹孔的部位剪应力最大,在导轨底部以及两端剪应力最小;(3)越靠近直线导轨的上表面和中间部位正应力越小,越靠近直线导轨的底部以及两端正应力越大;(4)直线导轨的剪应力主要分布在上表面以及四周的表面上,导轨内部剪应力较小;正应力主要分布在导轨内部,直线导轨表面和四周的正应力较小。
关键词:热传递;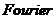 传热定律;热弯曲;热位移;热应力;
传热定律;热弯曲;热位移;热应力;
Abstract
In the grinding process of precision linear guide rail, the friction and contact between the grinding wheel and the linear guide will cause a great deal of frictional heat, and the increase in the local heat will cause heat transfer in the linear guide. The temperature field formed by heat transfer will cause the residual stress and the thermal deformation of the rail, thus affecting the machining accuracy of the linear guide rail. Therefore, the heat transfer and thermal deformation of the linear guide rail are analyzed in this article.
In the analysis of the heat transfer of the linear guide rail, a model of the heat generation in the grinding area of the linear guide rail is established, and then the temperature rise model of the rail surface is established; According to the Fourier heat transfer law, a non-homogeneous heat transfer model for parabolic differential equations is established. The numerical solution of the differential equation is solved by using MATLAB software, and the conclusions are drawn: On the surface of the linear guide rail, the temperature is the highest, reaching 401.6496℃, and the temperature at the bottom of the linear guide rail is lowest, which is 33.0387℃. The heat transfer law is obtained by analyzing and solving the results: (1) At a certain depth (position) of a linear guide, the temperature increases with time; (2) At a certain time, with the increase of the internal depth of the rail, the temperature of the rail decreases as a whole. In deeper regions, The nearer the time is to the steady temperature, the faster the temperature increases.
The thermal bending model of the linear guide rail is established in the analysis of the thermal bending amount of the linear guide rail. When the rail length is 1.6m, and the temperature gradient of the upper and lower surfaces is 400℃, the thermal bending amount of the linear guide rail is 3.7mm.
When analyzing the thermal stress of the linear guide rail, the temperature and strain increment model of the linear guide rail is established. In the SolidWorks software, the entity model of the linear guideway is established, and then the finite element analysis is carried out in the Abaqus software. Finally, the conclusions are drawn: (1) the equivalent displacement is the biggest at the left and right ends of the linear guide rail, and the displacement is the least at the bottom and middle of the rail; (2) the top surface of the linear guide, especially near the threaded hole, has the largest shear stress, and the minimum shear stress is at the bottom and the left and right ends of the linear guide rail; (3) the normal stress is very small near the upper and middle of the linear guide, and is very large near the bottom and both ends of the linear guide; (4) the shear stress of the linear guide rail is mainly distributed on the upper surface and around the surface, and the shear stress in the guide rail is very small; The normal stress is mainly distributed inside the guide rail, and the normal stress on the surface and the circumference of the guide rail is very small.
Keywords: heat transfer; Fourier heat transfer law; thermal bending; Thermal displacement; Thermal stress;
目录
摘要 3
Abstract 4
第一章 绪 论 1
1.1研究背景 1
1.2研究目的与研究意义 1
1.3国内外研究现状 2
1.4研究的基本内容 3
1.5研究的目标 3
第二章 直线导轨磨削热模型 4
第三章 精密直线导轨的热传递模型 6
3.1热传递方程 6
3.2初始条件和边界条件 8
第四章 热传递方程的求解 9
4.1精密直线导轨磨削温度场的计算 9
4.2热传递方程的差分方法求解 10
4.3 直线导轨热传递方程求解结果分析 10
第五章 直线导轨的热弯曲量计算 14
第六章 直线导轨的有限元分析 15
6.1有限元分析原理 15
6.2有限元分析步骤 17
6.3 Abaqus有限元结果分析 20
第七章 结论 23
第八章 论文的改进方向 24
致谢 27
参考文献 25
第一章 绪 论
1.1研究背景
随着人们生活水平的不断提高,对机械加工产品和零件的质量以及精度也提出了更高的要求。在工业产品的机械加工过程中,加工设备(如机床)的高速化、高精化是一个必然的发展趋势。经过研究发现,加工过程中工件精度不足的问题主要是由加工过程中的机械振动特性和热特性引起的[1]。很多专家和学者在他们的研究中发现,加工过程中的热传递导致的热变形和残余应力是造成机床加工误差的主要因素。英国伯明翰大学J.P教授的研究告诉我们,加工过程中40%-70%的误差来源于温度场的不均匀和结构热变形[2]。而切削加工作为机床最重要的加工方式之一,在加工零件的过程中产生了大量的切削热,被加工工件的内部因此产生不均匀的温度分布场,这导致被加工工件内部产生结构热变形和残余应力分布,直接地影响了被加工工件的加工精度。随着数控机床加工的高精度、高刚度、高速度的不断发展,机床加工过程中工件的热态性能以及残余应力的研究越来越受到人们的重视。
精密机床直线导轨是精密机床的一个非常重要的构件,在加工工件的工序中主要起到了支撑和导向的作用,保证机床部件在加工过程中的各种外力作用下能精确地沿着指定的方向运动。在精密直线导轨的磨削加工过程中,磨削砂轮与精密直线导轨的接触及相对运动会消耗大量的能量,从而产生大量的热量,会在导轨内产生热量的传递。不均匀的热量传递过程中形成的温度场则会引起残余应力与直线导轨的变形,影响直线导轨的加工精度,最终导致精密机床在加工零件的过程中被加工工件精度的降低。由此表明,如何通过建立直线导轨磨削加工过程的温度场、分析导轨热特性、减少导轨加工过程的残余应力和提高直线导轨的加工精度将是非常重要的一部分。
1.2研究目的与研究意义
对高精度机床直线导轨的热态性能研究是研究制造高精度、高性能的数控机床的关键部分,为我国高精度加工的产业化应用提供技术支撑,是我国在“高精尖”数控装备方面突破技术封锁的必由之路,是机械加工数控技术领域创新性发展的重要任务之一。直线导轨精密磨削过程的温度场研究有助于分析精密机床直线导轨在磨削加工过程中的热应变,进而提高直线导轨的导向精度。
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



