阵列缝隙作用下的壁湍流特性研究毕业论文
2020-04-08 13:26:17
摘 要
高速列车/汽车是陆运运输的重要力量,其通风系统通常安装有百叶窗结构,进而形成阵列缝隙作用下通风口的流动特点。高速气流以较小的相对运动速度通过缝隙被吸入车内,形成一种弱抽吸的流动现象。一部分气流进入箱体,剩余的气流在通风口下游形成涡旋。这种气流流动形式可以简化为气流在T-型管道中的流动,本文对该气流流动形式的壁湍流进行了相关研究:
本文选取距离换气口最近、受抽吸扰动作用最强的X=0截面处的实验数据,研究了时均速度、平均无量纲速度、湍流强度、湍流脉动强度、平坦系数、偏斜系数、湍流动能及其耗散率等平均统计特性参数并得到了一系列图像。研究发现,主流速度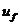 和抽吸比R是影响平均统计特性参数的两个最主要因素。其中抽吸扰动作用实质上会破坏近壁区域的层流底层,且越小的抽吸比R对层流底层造成的破坏影响越明显。层流底层被破坏后,会突显壁面对流体的粘滞作用。主流速度
和抽吸比R是影响平均统计特性参数的两个最主要因素。其中抽吸扰动作用实质上会破坏近壁区域的层流底层,且越小的抽吸比R对层流底层造成的破坏影响越明显。层流底层被破坏后,会突显壁面对流体的粘滞作用。主流速度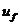 的增加会使抽吸扰动作用对平均统计特性参数的影响程度增强。因此近壁区域是大多数平均统计特性参数差异最大的地方,且都随着主流速度
的增加会使抽吸扰动作用对平均统计特性参数的影响程度增强。因此近壁区域是大多数平均统计特性参数差异最大的地方,且都随着主流速度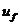 和抽吸比R的大小变化表现出了一系列有规律的特征。
和抽吸比R的大小变化表现出了一系列有规律的特征。
本文研究了抽吸扰动作用对不同位置的功率谱密度和小波谱的影响,选取了距离换气口最近、受抽吸扰动作用最强的X=0截面处的实验数据,研究了不同抽吸比R和不同主流速度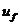 对功率谱密度和小波谱的影响。研究发现,随着无量纲距离
对功率谱密度和小波谱的影响。研究发现,随着无量纲距离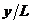 的增加,湍流流向脉动速度的功率谱密度逐渐减小,同时抽吸扰动作用对功率谱密度的影响程度也在减小。随着抽吸比R的增大,其对功率谱密度的影响程度在不断降低且低频部分受到的影响最大。随着主流速度
的增加,湍流流向脉动速度的功率谱密度逐渐减小,同时抽吸扰动作用对功率谱密度的影响程度也在减小。随着抽吸比R的增大,其对功率谱密度的影响程度在不断降低且低频部分受到的影响最大。随着主流速度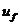 的增加,抽吸扰动作用对流向脉动速度功率谱密度的影响程度增强。通过小波谱分析发现:随着无量纲距离的增加,涡的峰值呈现下降趋势。低频涡减少比较快,低频大尺度结构减少,且小波谱能量变低。主流速度
的增加,抽吸扰动作用对流向脉动速度功率谱密度的影响程度增强。通过小波谱分析发现:随着无量纲距离的增加,涡的峰值呈现下降趋势。低频涡减少比较快,低频大尺度结构减少,且小波谱能量变低。主流速度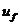 和抽吸比R对小波谱的影响主要集中在小波谱幅值、低频多尺度涡结构以及高频高能涡上。主流速度
和抽吸比R对小波谱的影响主要集中在小波谱幅值、低频多尺度涡结构以及高频高能涡上。主流速度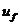 的增大会使小波谱幅值增大,低频涡减少,高频涡周期性更强并且频率更高。抽吸比R的增加会使小波谱幅值减小,且低频涡多尺度减小。
的增大会使小波谱幅值增大,低频涡减少,高频涡周期性更强并且频率更高。抽吸比R的增加会使小波谱幅值减小,且低频涡多尺度减小。
本文通过对该阵列缝隙作用下的壁湍流特性进行研究,其结果可为高速列车/汽车通风换气系统的设计提供重要的参考依据,从而减小高速列车/汽车的运行阻力和运行安全隐患,为实现陆运运输 “节能减排”和“安全高效”的发展提供技术性支持。
关键词:阵列缝隙;壁湍流;抽吸作用;平均统计特性参数;功率谱密度;小波谱
Abstract
High-speed trains/cars are backbones of land transportation. Their ventilation systems usually install window shades, causing the flow characteristics of air vent under the effect of array slots. Vehicles inhale high-speed airflow through the array slots with a smaller relative motion speed, forming a flow phenomenon of weak suction. Part of the airflow flows into the box and the remaining airflow forms vortices in the downstream of vents. This airflow form can simplify into airflow in a T-type pipe. This thesis does research on the wall turbulence of this airflow pattern:
Experimental data were selected here at the section X=0 where the ventilation port was the closest and suction disturbance was the most intensive. Those average statistical characteristic parameters such as average velocity, average dimensionless velocity, turbulence intensity, turbulence pulsation intensity, flat coefficient, deflection coefficient, turbulence kinetic energy, dissipation rate were under our study and a series of images were got. Studies have shown that mainstream speed and suction ratio are the main factors influencing average statistical parameters. In essence, suction can destroy the laminar layer of the near wall area and lower the suction ratio is, more obvious the damage will be. After the laminar layer is destroyed,the viscous effect on the fluid of wall will show up. The increase in mainstream speed makes the influences of the suction on average statistical parameters enhance. The near wall area is the most discrepant part of average statistical parameters, which show a series of regular features with the change of mainstream speed and suction ratio.
The influences of suction on pulsating velocity power spectrum and wavelet spectrum in different places were researched. Experimental data were selected here at the section X=0 where the ventilation port was the closest and suction disturbance was the most intensive. The influences of different suction ratio and mainstream speed on pulsating velocity power spectrum and wavelet spectrum were under our study. Studies have shown that with the dimensionless distance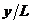 increases, the pulsating velocity power of turbulent fluctuation velocity cuts down and the influence of the suction on the pulsating velocity power spectrum is also in reducing. With the increase of suction ratio, the influence of it on pulsating velocity power spectrum is on the decline and the part of lower frequencies is the most affected. With the increase of mainstream speed, the influence of suction on pulsating velocity power spectrum is gradually increasing. Throuth the wavelet filters spectral analysis ,the research shows that with the dimensionless distance
increases, the pulsating velocity power of turbulent fluctuation velocity cuts down and the influence of the suction on the pulsating velocity power spectrum is also in reducing. With the increase of suction ratio, the influence of it on pulsating velocity power spectrum is on the decline and the part of lower frequencies is the most affected. With the increase of mainstream speed, the influence of suction on pulsating velocity power spectrum is gradually increasing. Throuth the wavelet filters spectral analysis ,the research shows that with the dimensionless distance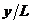 increases, the peak of the vortex shows a downward trend, the low frequency vortex decreases quickly, the low frequency large scale structure decreases, and the small wave spectrum energy is lower. The influences of suction ratio and mainstream speed on the wavelet spectrum are focused on small spectral amplitude, low frequency multiscale vortex structure and high frequency energy vortex. With the increase of mainstream speed, small spectral amplitude increases and low frequency vortex reduces and the periodic of the high frequency vortex is stronger as well as the frequency is higher. The increase of suction ratio can make amplitude of the wavelet decrease and low frequency vortexes reduce .
increases, the peak of the vortex shows a downward trend, the low frequency vortex decreases quickly, the low frequency large scale structure decreases, and the small wave spectrum energy is lower. The influences of suction ratio and mainstream speed on the wavelet spectrum are focused on small spectral amplitude, low frequency multiscale vortex structure and high frequency energy vortex. With the increase of mainstream speed, small spectral amplitude increases and low frequency vortex reduces and the periodic of the high frequency vortex is stronger as well as the frequency is higher. The increase of suction ratio can make amplitude of the wavelet decrease and low frequency vortexes reduce .
Characteristics of wall turbulence under the effect of array slots were under our research, providing important reference to the design of ventilation systems of high-speed trains/cars, which can reduce running resistance and safety hazards as well as provide technical support to realize energy saving, emission reduction, safety and efficiency development of land transportation.
Keywords: array slots; wall turbulence; suction; average statistical parameters; pulsating velocity power spectrum; wavelet spectrum
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第1章 绪论 1
1.1背景和意义 1
1.2 壁湍流的基本理论概述 2
1.2.1概念与基本结构 2
1.2.2 壁湍流的特征与壁面类型 3
1.2.3 研究方法与特性参数 5
1.3 壁湍流的研究现状 6
1.4本文的主要内容 7
1.5本章小结 8
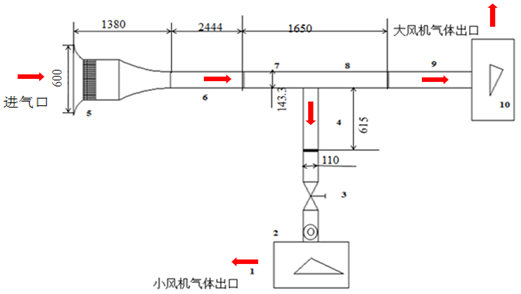
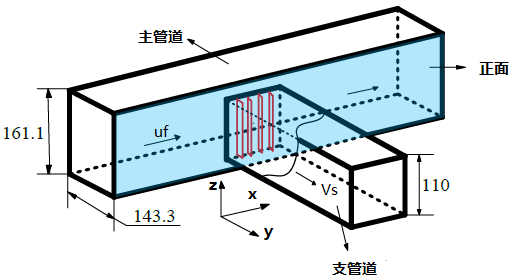
第2章 本研究的实验设计与重点仪器概述 9
2.1 实验测量装置介绍 9
2.2 实验工况的设定 10
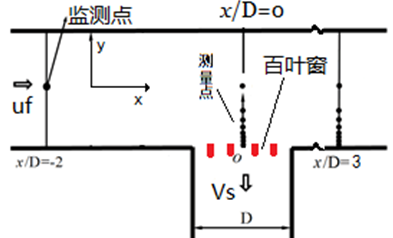
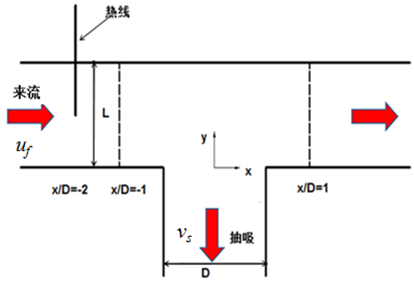
2.3 实验测量位置的选择 11
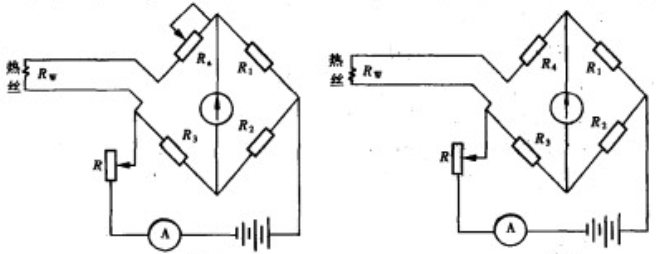
2.4 重点实验仪器热线风速仪的概述 13
2.4.1热线风速仪的结构与分类 13
2.4.2热线风速仪的测量原理 14
2.4.3热线风速仪的误差 15
2.4.3.1热线风速仪的空间分辨率 15
2.4.3.2热线风速仪的时间分辨率 16
2.4.3.3温度对热线风速仪的影响 16
2.4.4热线风速仪的校准标定 16
2.4.5 热线风速仪的其他应用 17
2.4.5.1湍流参数的测量 17
2.4.5.2雷诺数的测量 18
2.4.6测速方法的最新研究进展综述 18
2.5 本章小结 20
第3章 湍流流场的平均统计特性分析 21
3.1主流速度的检测采集与选取 21
3.2主流速度的时均分布与平均无量纲分布 21
3.2.1 主流速度的时均分布 22
3.2.2 主流速度的平均无量纲分布 24
3.3湍流脉动强度与湍流强度 25
3.3.1 主流速度的湍流脉动强度 25
3.3.2 主流速度的湍流强度 27
3.4 平坦系数与偏斜系数 29
3.4.1 平坦系数 29
3.4.2 偏斜系数 31
3.5 湍流动能及其耗散率 32
3.5.1 湍流动能 32
3.5.2 湍流动能的耗散率 34
3.6本章小结 37
第4章 湍流流场的脉动特性分析 38
4.1 湍流流场的功率谱分析 38
4.1.1抽吸作用对不同位置功率谱密度的影响 38
4.1.2不同抽吸比对功率谱密度的影响 43
4.1.3不同主流速度对功率谱密度的影响 45
4.2 湍流脉动流场的小波谱分析 47
4.2.1 不同位置处的小波谱分析 52
4.2.2 不同主流速度对小波谱的影响 54
4.2.3 不同抽吸比对小波谱的影响 56
4.3 本章小结 58
第5章 结论与展望 59
5.1 结论 59
5.2 展望 60
参考文献 62
附录Ⅰ 本研究的湍流流场平均统计特性参数 66
附录Ⅱ 本研究的功率谱和小波谱计算程序 69
致谢 72
第1章 绪论
1.1背景和意义
党的十八大以来,我国交通运输事业的发展进入了现代化综合运输体系建设的新阶段。作为普及度最高、发展规模最大的陆运运输,也取得了长足的发展与进步。首先,以高速铁路为骨架、以城际铁路为补充的多层次快速客运网络初步建成。全国铁路营业总里程达12.4万公里,规模居世界第二[1];其中高速铁路近五年来新增1.6万公里,总里程达2.2万公里,位居世界第一,占世界高速铁路运营总里程60%以上[1]。“四纵四横”高铁网基本成型,成为世界上唯一高铁成网运行的国家。其次,广覆盖的公路运输网络体系更加成熟。全国公路通车总里程达470万公里,高速公路通车里程达13.1万公里,位居世界第一[1]。国省干线网络的建设也不断完善,连接了全国所有县级及以上行政区,等级公路里程占全国公路总里程的90%[1]。
放眼我国未来陆运运输事业的发展,要全面建成安全、便捷、高效、绿色的现代陆运运输体系。铁路运输方面,我国高速铁路将构建横贯东西、纵贯南北、更加密集的“八纵八横”高铁主通道[2-3]。到2025年,我国铁路网规模将达17.5万公里左右,其中高铁3.8万公里左右[1-3]。到2030年,基本实现内外互联互通、区际多路畅通、省会高铁连通、地市快速通达、县域基本覆盖[2-3]。公路运输方面,将加快完善高速公路建设的步伐,有序发展地方高速公路,加强高速公路与口岸的衔接,使公路运输为国民经济的发展贡献更多力量。
“节能减排”和“安全高效”是我国各类交通运输发展规划必备的原则和指导思想。当今世界能源形势危急,化石燃料的储量满足不了经济全球化快速发展的需要。能源需求的日益增多与能源短缺之间的矛盾成为人类所面临的共同挑战。与此同时全球污染问题日益严重,如何减少道路污染物的排放及其危害也成为人们所关注的焦点。基于以上实情,交通运输部出台多项文件倡导节能低碳发展,推动资源节约集约利用[4]。由于陆运运输消耗的能源总量巨大,因此如何挖掘陆运运输的技术节能潜力,提升技术性节能减排也成为多方研究的焦点。此外“安全高效”的要求也不容忽视。快捷的陆运运输在带给我们便捷的同时,也给我们的生活埋下了潜在的安全隐患。近年来发生的几起高铁技术性事故触目惊心,公路运输的技术性事故也应引起我们的重视。及时发现和解决潜在的技术性安全问题,保障陆运运输安全高效地运行,也成为相关研究的热点。
高速列车/汽车是陆运运输的重要力量,其通风系统在高速列车/汽车运行时一方面保证了车内空气的流通,提高了乘客的舒适性。另一方面可以对动力装置进行散热,确保其运行的安全性。为了阻挡外部杂物的进入,高速列车/汽车的通风系统通常安装有百叶窗结构,进而形成阵列缝隙作用下的通风口的流动特点。高速气流以较小的相对运动速度通过缝隙被吸入车内,进而形成一种弱抽吸的流动现象。一部分气流进入箱体,剩余的气流在通风口下游形成涡旋,增加了高速列车/汽车表面的运行阻力,对高速列车/汽车的安全运行也有着重要的影响。
高速列车/汽车通风系统中的气流流动形式可以简化为气流在T-型管道中的流动。对该阵列缝隙作用下的壁湍流特性进行研究,研究结果可为高速列车/汽车通风换气系统的设计提供重要的参考依据,从而减小高速列车/汽车的运行阻力和运行安全隐患,为实现陆运运输 “节能减排”和“安全高效”的发展提供技术性支持。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示:
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



