振荡圆柱流数值模拟毕业论文
2020-04-10 16:56:41
摘 要
圆柱是实际生活中十分常见的物体,钝体绕流常把圆柱绕流当作重要的研究对象,其流动的现象十分复杂,圆柱绕流问题是流体与工程结构相互作用的非常常见的问题,本文主要应用建模软件建立数值计算模型,利用Fluent软件对流场中的振荡圆柱进行仿真;开展振荡圆柱的振幅和振荡频率对圆柱振荡特性的影响研究,本文的主要工作和得到主要结论如下:
将计算模型简化为二维的计算模型,圆柱的半径为1m,选取圆形计算域,并采用O型网格,对计算域进行结构化网格划分,计算了YPLUS值确定了边界层厚度为0.01mm。通过计算域无关性检验,确定计算域的大小为圆柱直径25倍的圆形计算域。
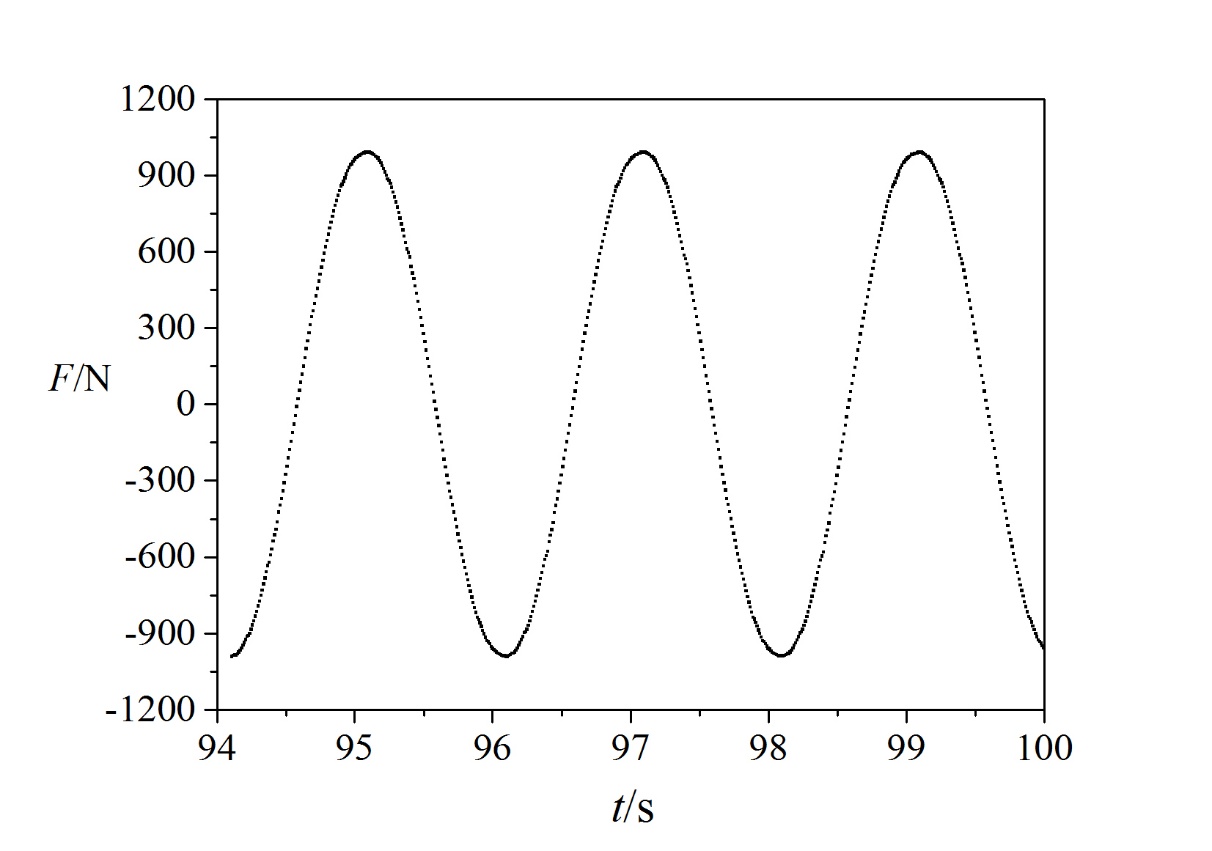
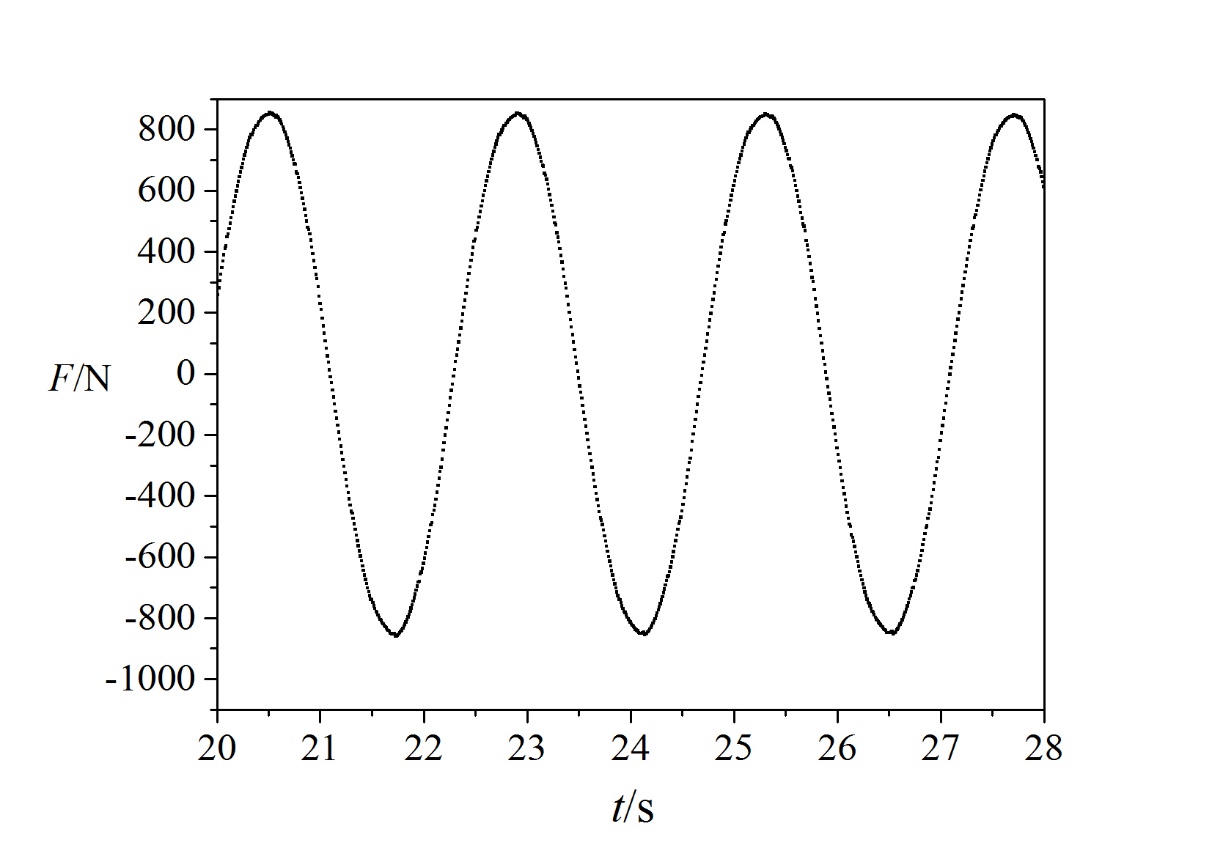
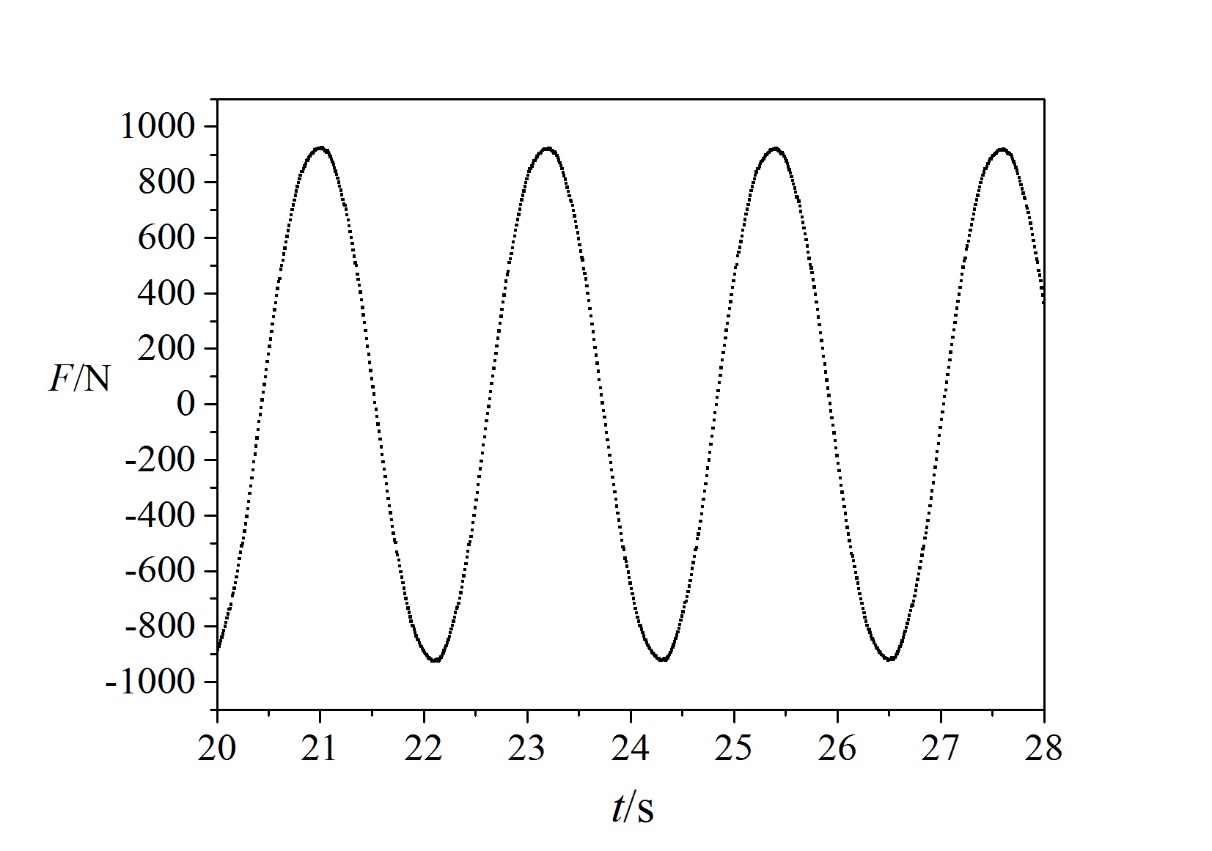
通过量纲分析,确定计算工况。运用控制变量法,通过调节频率w和速度的振幅A改变无因次数雷诺数Re、斯特劳哈尔数St中的一个,保持另一个不变,确定九个计算工况。设定圆柱的速度方程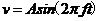 。对不同的工况条件下,进行数值模拟,计算得到结果为线性圆柱受到力的周期与圆柱运动的频率相等,且都是呈简谐趋势运动,因此将数据整理成与加速度相关的惯性力项和与速度相关的阻尼项。
。对不同的工况条件下,进行数值模拟,计算得到结果为线性圆柱受到力的周期与圆柱运动的频率相等,且都是呈简谐趋势运动,因此将数据整理成与加速度相关的惯性力项和与速度相关的阻尼项。
由于计算结果是线性的,而Morison公式是非线性的,最终将计算结果与球在静水中受迫振动的线性理论解进行对比。分析振荡球所受到力,将振荡球受到力分为惯性力和阻尼力。球的惯性力可分别提取出系数 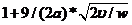 ,该系数可看作由于黏性造成的影响。粘性项可看作为匀速运动时受到的阻尼力乘以振荡修正系数
,该系数可看作由于黏性造成的影响。粘性项可看作为匀速运动时受到的阻尼力乘以振荡修正系数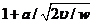 。参照振荡球公式,提取振荡圆柱惯性项和阻尼项产生的影响系数
。参照振荡球公式,提取振荡圆柱惯性项和阻尼项产生的影响系数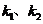 。计算表明振荡圆柱黏性影响系数
。计算表明振荡圆柱黏性影响系数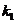 与球的黏性影响系数
与球的黏性影响系数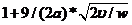 基本相同,振荡圆柱振荡修正系数
基本相同,振荡圆柱振荡修正系数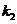 小于球的振荡修正系数。
小于球的振荡修正系数。
分析无因次数为Re和A/D对振荡圆柱的影响,通过控制变量法调节w和v使得Re和A/D其中一个改变另一个不变,计算振荡圆柱所受到力。计算表明:惯性力大小随着Re增大而增大,随着A/D增大而减小;阻尼力大小只与Re有关,随着Re增大而增大。
关键词:受迫振荡;Morison公式;球振荡公式;数值计算
Abstract
Cylindrical is a very common object in the daily life. The flow around the bluff body often regards the flow around the cylinder as an important research object, and its flow phenomenon is very complicated. The problem of the flow around the cylinder is a very common problem in the interaction between the fluid and the engineering structure. This paper mainly uses the modeling software to establish the numerical calculation model. Using the Fluent to simulate the oscillating cylinder in the flow field, and carries out the study of the influence of the motion amplitude and oscillation frequency of the oscillating cylinder. The main work and conclusions of this paper are as follows:
The computational model is reduced to a two-dimensional computational model. The radius of the cylinder is 1m. The circular calculation domain is selected. Computational domain is divided into structured grids by using O-grid. The YPLUS value is calculated to determine the thickness of the boundary layer. 0.01mm. Through the calculation of the domain-independence test, the calculation domain is determined to be a circular computation domain 25 times the diameter of the cylinder.
Through dimensional analysis, determine the calculation conditions. Using the control variable method, one of the Reynolds number Re and the Strouhal number St is changed by adjusting the frequency 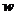 and the amplitude A of the speed, and the other is held constant, and nine calculation conditions are determined. Set the speed equation
and the amplitude A of the speed, and the other is held constant, and nine calculation conditions are determined. Set the speed equation 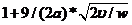 of the cylinder. Under different working conditions, numerical simulations are performed. The results show that the cycle of the force acting on the linear cylinder is equal to the frequency of the cylinder movement, and both are in a simple harmonic trend. Therefore, the data is organized into acceleration-related inertial terms. And speed-related damping terms.
of the cylinder. Under different working conditions, numerical simulations are performed. The results show that the cycle of the force acting on the linear cylinder is equal to the frequency of the cylinder movement, and both are in a simple harmonic trend. Therefore, the data is organized into acceleration-related inertial terms. And speed-related damping terms.
Because the calculation result is linear and the Morison formula is nonlinear, the calculation result is finally compared with the linear theoretical solution of the ball in forced vibration in the still water. Analyze the force exerted by the oscillating ball, and divide the oscillating ball into force and damping force. The inertial force of the ball can be used to extract the coefficient 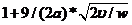 , which can be regarded as the effect due to viscosity. The viscous term can be seen as the damping force experienced by a uniform motion multiplied by the oscillation correction coefficient
, which can be regarded as the effect due to viscosity. The viscous term can be seen as the damping force experienced by a uniform motion multiplied by the oscillation correction coefficient 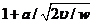 . Refer to the oscillating sphere formula to extract the influence coefficient
. Refer to the oscillating sphere formula to extract the influence coefficient 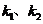 generated by the inertia term and the damping term of the oscillating cylinder. The calculation shows that the viscosity coefficient
generated by the inertia term and the damping term of the oscillating cylinder. The calculation shows that the viscosity coefficient 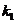 of the oscillating cylinder and the viscosity coefficient
of the oscillating cylinder and the viscosity coefficient 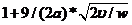 of the ball are basically the same, and the oscillating cylinder oscillation correction coefficient is smaller than the ball oscillation correction coefficient
of the ball are basically the same, and the oscillating cylinder oscillation correction coefficient is smaller than the ball oscillation correction coefficient 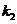 .
.
Analysis of the number of non-causal factors for Re and A/D affects the oscillating cylinder. Using the control variable method to adjust w and v such that one of Re and A/D changes is the same, the force exerted by the oscillating cylinder is calculated. The calculation shows that the magnitude of the inertial force increases with the increase of Re, and decreases with the increase of A/D. The magnitude of the damping force is only related to Re and increases with the increase of Re.
Keywords: forced oscillation Morison formula spherical oscillation formula numerical calculation
Keywords: Forced oscillation;Morison formulation;Oscillating ball;Numerical calculation
目 录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 课题研究背景和意义 1
1.2 国内外研究现状 1
1.3 本文研究内容 3
第2章 计算模型 5
2.1 计算流体力学 5
2.2 控制方程与湍流模型 5
2.3 计算网格划分 6
2.4 本章小结 8
第3章 振荡圆柱数值模拟研究 9
3.1 振荡圆柱的基本模型 9
3.1.1 模型假设和符号说明 9
3.1.2 计算工况 10
3.2 数值计算参数设置 11
3.3 计算域无关性检验 11
3.4 圆柱计算结果处理 12
3.5 本章小结 19
第4章 计算结果与其它公式对比 20
4.1 计算结果与Morison公式对比 20
4.2 计算结果与球的理论解对比 21
4.2.1 作用在振荡球上的力 21
4.2.2 惯性项的对比 22
4.2.1 阻尼力的对比 24
第5章 运动幅值和频率对振荡圆柱的影响 29
5.1 雷诺数对振荡圆柱的影响 29
5.2 振幅直径比对振荡圆柱的影响 30
第6章 结论与展望 32
参考文献 33
致 谢 35
绪论
课题研究背景和意义
随着我国的经济实力快速提高,以及自然资源的需求增加,对于海洋资源的需求越来越多,国家提出了海洋强国的战略目标,成为在开发海洋、利用海洋、保护海洋、管控海洋方面拥有强大综合实力的国家。海洋平台作为重要的海洋装备,一直是各国研究的热点,人类在勘采石油资源的时候,开发了各式的新型海洋平台:浮式生产储油系统、浮式生产钻井储油装置、张力腿平台、半潜式平台以及立柱式平台。由于海洋环境的随机性和复杂性,产生了众多的复杂的工程问题,如何理解和解决相关问题是十分急需的[1]。其中圆柱绕流问题是流体与工程结构相互作用的非常常见的问题。由于流体的作用,流体和圆柱是相互耦合的作用。流体的流动使得圆柱发生变形和振动,因此研究圆柱在流场中振荡非常有现实意义[2]。
圆柱是实际生活中十分常见的物体,钝体绕流常把圆柱绕流当作重要的研究对象,其流动的现象也是十分的复杂,它包含了流体的分离、漩涡的形成和脱落等等复杂的非线性问题。粘性不可压缩流体绕圆柱的流动会产生各种不同的流动状态,随着雷诺数的增加,会产生越来越复杂的流动图案表明了系统有越来越复杂的组织结构[3]。
国内外研究现状
相比于方柱等具有明显棱角的钝体形状,圆柱绕流的分离点是不固定的,这给圆柱绕流的研究带来了更大的困难[4]。有众多的学者在相关领域进行研究。刘松,符松用有限体积法对平行于均匀来流方向受迫振荡的圆柱绕流问题进行了二维数值模拟,验证了试验中的同步脱落现象,计算结果为研究实际流动中圆柱振荡与涡脱落的相互耦合作用打下了基础[2]。李明用OpenFOAM软件对零均值和单向正弦振荡流作用下的圆柱绕流进行了数值模拟,探究了来流中振荡流成分所占比重对圆柱的动力响应的影响[4]。龚帅,郭照立利用了Boltzman方法对不可压横向振荡圆柱绕流问题进行了数值研究,提高了计算的效率并分析了实验现象[5]。梁亮文利用Fluent软件在低雷诺数下对横向受迫振荡圆柱和弹性支撑圆柱涡激运动问题进行数值计算分析。得出三维圆柱以一定频率振荡时会抑制流场中漩涡三维特性的出现[6]。顾罡用CFD方法求解了二维非定常单圆柱和双圆柱流问题,分析漩涡的运动和脱落,与吴国雄教授给出的结果作对比,给出了可靠的分析结果,验证了数值解的正确性[7]。张宇飞,肖志祥,符松采用Arbitrary Lagrange-Euler方法求解运动坐标系Navier-Stokes方程组,分析均匀来流下雷诺数为150的静止和流向振荡的圆柱绕流[8]。王志东,周林慧采用SIMPLE算法求解N-S方程,采用动网格技术模拟网格的运动边界,对振荡圆柱进行模拟[9]。杨烁,吴宝山采用多种流动模型在高雷诺数下对定常和非定常状态的圆柱绕流进行了数值模拟,计算了圆柱的升阻力系数、分离点位置、Strouhal数等结果[10]。 Obasaju, E. D, Bearman等人做了关于圆柱绕流的试验测定[11]。 Guilmineau E, Queutey P等在低雷诺数下对振荡圆柱绕流进行了数值模拟,给出了振荡圆柱涡脱落图,涡线和等压力线图[12]。 J. Decuyper, T. De Troyer, M.C. Runacres, K. Tiels, J. Schoulcens等人运用非线性系统辨识技术,建立了非线性空间模型来分析振荡圆柱,并与CFD软件计算结果进行对比[13]。 Zhida Yuan, Zhenhua Huang等人通过试验测的高频流对振荡圆柱的力,并通过与Morison公式对比,得到新的无量纲系数[14]。得出对于大多数KC数和振荡频率,圆柱振荡频率为其受到主要力频率的两倍[15]。贲安庆采用了大涡模拟的方法计算了低雷诺数下的圆柱绕流。最终用能量梯度理论来解释了上述的结果,对结果进行了分析,验证了关于压力驱动流动的稳定性判定准则[16]。王亚玲、刘应中,缪国平等人利用计算流体力学软件 CFX- 4模拟计算了三维圆柱绕流,最终的结果显示计算的结果有明显的三维特性,并对比了二维的计算结果和三维计算结果的异同[17]。段志强等人研究了圆柱绕流中的“夹带”作用形成的卡门涡街的现象,提出了一种沿对称的流动方向上,带分隔板的减阻抗振结构。并且结果表明,圆柱后加分隔板能限制旋涡脱落,板长的不同会产生不同的效果[18]。陈蓥, 付世晓, 许玉旺等人对均匀流中近壁面垂直流向振荡圆柱水动力特性进行了研究,探究了振荡频率和振幅等一系列因素对阻力的影响。并且在拖曳水池中进行了一系列的试验。最终得到近壁面的会对振荡圆柱能量传递有影响[19]。赵宇, 王薇, 鄂学等人求解了不可压二维 N- S方程 ,对在均匀来流中旋转振荡圆柱进行了数值模拟,利用频谱分析的方法。得到了圆柱涡脱落频率与强迫振荡频率之间的作用。得到了涡的形成和脱落的规律[20]。 付英男探讨了流向强迫振荡柱体的水动力特性,通过CIP计算了流体的控制方程,将计算结果与他人的计算结果进行对比,并分析了圆柱和方柱绕流的差异,分析不同的振幅和频率的振荡柱体,绕流的水动力参数[21]。戴光清采用了数字粒子成像测速仪对振动圆柱体在静水中产生的振荡流场进行了研究。试验数据表明,在KC数为12时圆柱振荡尾流中将存在一个斜向涡街,当KC =6.2 8时,而无涡街产生。斜涡街稳定时 ,圆柱受力基本一样,在涡街方向转变时 ,柱体沿运动方向的力小于斜向的受力[22]。Peppa S, Triantafyllou G S.等人研究流向微振幅简谐扰动的圆柱体的敏感性。圆柱体遵循八字形轨迹,其可以逆时针或顺时针方向运行,结果表明运动的顺序不同,其中所受的力也不同[23]。胡克, 林哲等人模拟了亚临界雷诺数10000情况时,振动圆柱的涡街形成过程,求解锁定范围内不同振荡频率下升力和阻力系数。分析了计算结果与试验的误差[24]。樊洪明, 王小华, 何钟怡等人,采用时间推进和张量分析的方法推导了对流扩散通用微分方程,对低雷诺数的粘性流体圆柱绕流进行了模拟。表明了三阶部分展开的Taylor-Galerkin有限元法稳定性好[25]。
圆柱振荡问题是一个十分复杂的问题,其中圆柱所受到的力与很多参数相关,并且这些参数之间也有许多的关联。根据相似理论可知自然界和工程中各相似现象相似原理的学说,并且提供了如何整理数据,如何设计计算的工况,以及如何将结果进行换算的理论基础,了解影响振荡圆柱的无因次数是十分有必要的,因此本文给出了影响圆柱振荡的主要影响因素:
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示:
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



