既有石长铁路某区段改建与增建二线选线设计毕业论文
2020-04-12 08:45:22
摘 要
既有铁路增改建是我国未来铁路建设领域面临的重点任务之一,既有线路平面重构是既有线增改建设计的基础,开展线路平面重构方法研究对提升设计效率和质量有重大意义。
既有线平面重构的目标是寻找一条光滑圆顺且尽可能逼近既有轨道中心的平面线形,由于平面线路包括直线、圆曲线与缓和曲线三种线元,而不同线元拟合方式不同,因此如何准确识别线元范围并对不同的线元进行拟合是解决该问题的关键。现有方法通常先人工识别曲率图判断测点的线元归属,然后拟合并固定直线边,最后应用各类优化方面确定最优的半径缓长。但是曲率图对于测点的偏差较为敏感,而直线固定会导致线路的拟合仅为局部优化。对此,本文建立了基于方位角变化率的初始线元分段方法,并提出了“点线一致”的新思想,即:测点的线元归属必须与最终拟合出的线元范围一致。基于该思想,构建了震荡迭代算法:(1)依据方位角变化率初步识别直线、圆曲线测点,并分别拟合相应线元;(2)根据圆曲线相对于直线的内移量计算缓和曲线,从而确定各线元的的范围;(3)依据线元范围调整原有测点归属,重新拟合直线、圆曲线;不断迭代(2)(3)过程,直到所有测点归属与线元范围一致。为进一步提升线形重构的质量,应用遗传算法对其进一步优化。
基于本文所述理论,课题组研发了既有铁路线路平面重构模块。石长线桃花江-益阳段及宜昌东-小溪塔的案例分析表明:方位角变化率图识别线元范围更为稳健可靠,该软件可自动完成既有铁路平面线形重构,且线路拟合效果较现有软件更好。
关键词:既有线重构;方位角变化率;点线一致;遗传算法
Abstract
The increase and reconstruction of existing railways is one of the key tasks facing China’s future railway construction. The re-creation of the existing railway horizontal alignment is the basis for the existing railways to be upgraded. And carrying out research on them is of great significance to improving design efficiency and quality.
Identifying the geometric elements of the line including tangents, circular curves and transition curves and fitting them to form a flat line shape that is smooth and approximates the measurement points of the existing line are the key problems of recreating the existing line. The existing method mainly uses the curvature graph to identify the geometric elements to which the measuring points belong, and uses the directional acceleration method to perform curve fitting on the basis of the fixed tangent. But the curvature diagram is more sensitive to the deviation of the measuring points, and only a locally optimized solution will be generated with the fixed tangent. In this regard, we propose that using a more stable azimuth angle rate graph to identify the geometric elements to which the measured points belong in this paper and put forward the idea of " points-alignment consistency ", that is, the attributions of all the measured points to geometric elements should be consistent with the ranges of re-created geometric elements. Based on this idea, the azimuth gradient graph is used to identify the attribution of the measured points preliminarily, and a method called swing iterations is proposed to adjust point placements dynamically、identify all the geometric elements simultaneously and re-fit them. The swing iterations is repeated until the points and lines are consistent. In order to further improve the quality of linear recreation, an improved genetic algorithm is used to further optimize the planar shape generated by swing iterations.
Based on the theories described in this paper, we have developed a software for recreation of existing railway horizontal alignments. The case studies of the Taohuajiang-Yiyang section of the Shichang line and the Yichang-xiaoxita line indicate that the azimuth rate of change graph is more stable and reliable in identifying the range of geometric elements. The software can automatically complete the recreation of the existing railway horizontal alignment and the effect is better than existing software.
Keywords: the existing railway horizontal alignment re-creation; azimuth angle rate graph; points-alignment consistency;genetic algorithm
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景 1
1.1.1既有线改建重要性 1
1.1.2既有线重构重要性 2
1.1.3既有线重构关键问题 2
1.2国内外研究现状 3
1.2.1既有线重构测量方法 3
1.2.2既有线重构直曲线元识别方法 3
1.2.3直曲线元拟合方法 4
1.2.4线路自动重构方法 5
1.3本文研究内容 6
第2章 既有线线元识别方法研究 7
2.1曲率图识别线元 7
2.1.1计算测点曲率 7
2.1.2绘制曲率图 8
2.1.3人工识别几何元素范围 9
2.1.4总结与启发 11
2.2方位角图识别线元 11
2.2.1计算方位角 11
2.2.2绘制方位角图 12
2.2.3人工识别几何元素范围 12
2.2.4总结与启发 14
2.3方位角变化率识别线元 14
2.3.1计算方位角变化率。 14
2.3.2绘制方位角变化率图 15
2.3.3识别直曲分段 15
2.4阈值取值探索 15
2.4.1阈值变化影响 15
2.4.2阈值取值方法 16
第3章 既有线线元拟合方法研究 18
3.1手工拟合直曲线元 18
3.1.1直线拟合 18
3.1.2曲线拟合 19
3.1.3计算拨量 21
3.2现有软件拟合直曲线元 23
3.2.1拟合思路 23
3.2.2单曲线拟合 23
3.2.3线路整体恢复与拨量计算 25
3.2.4结果对比与分析 26
3.2.5现有软件存在问题 27
3.3基于点线协同思想拟合直曲线元 27
3.3.1单曲线点线协同 27
3.3.2线路整体优化 30
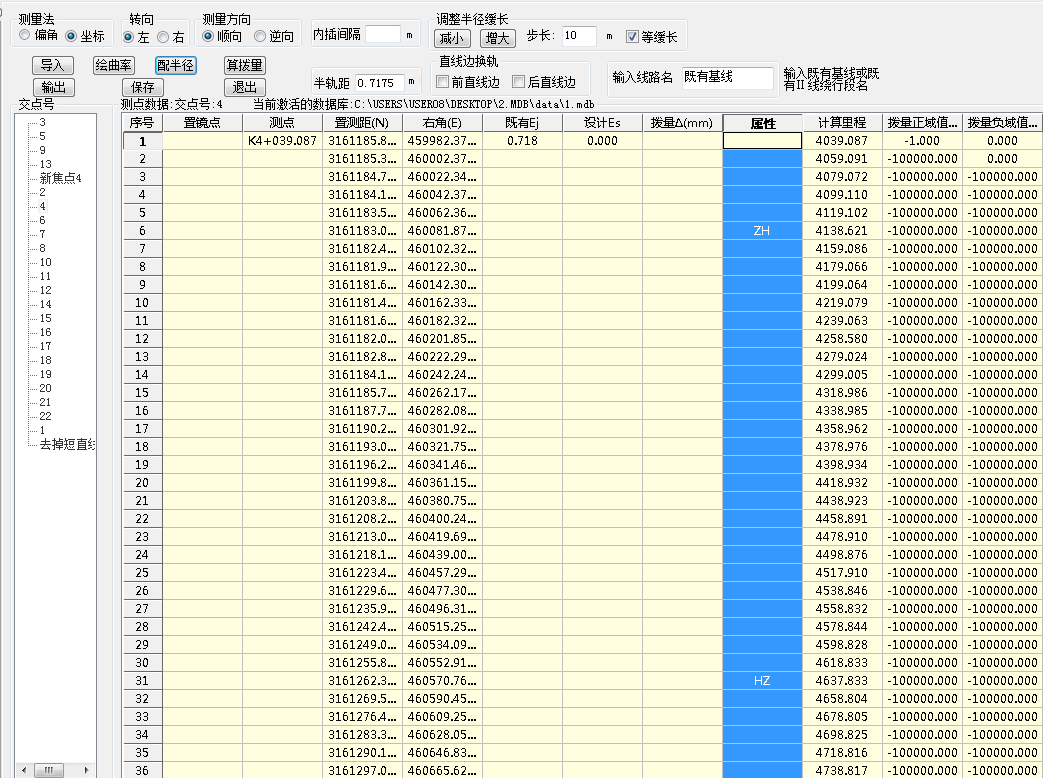
第4章 程序开发与案例分析 32
4.1程序开发 32
4.2结果对比与分析 32
4.3案例分析与验证 33
4.3.1案例简介 33
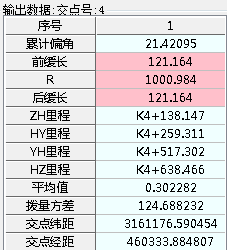
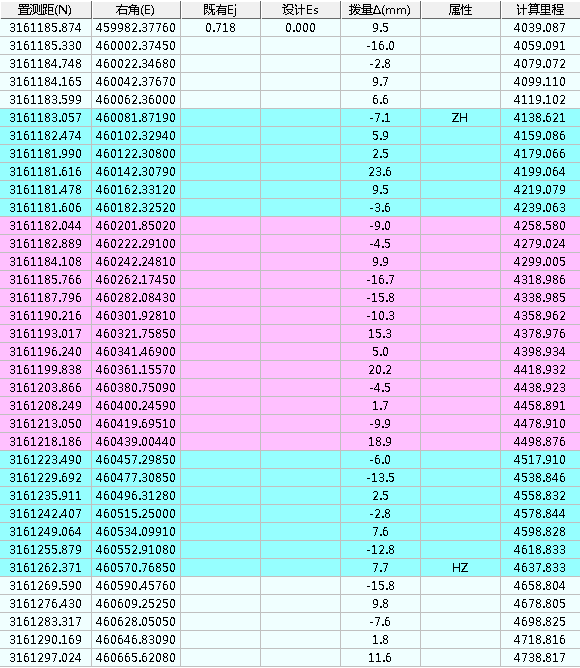
4.3.2线路重建过程与结果 34
4.3.3优势对比与分析 37
第5章 结论与展望 39
5.1结论 39
5.2展望 39
参考文献 40
致 谢 42
第1章 绪论
1.1 研究背景
1.1.1既有线改建重要性
既有线增改建在我国铁路建设中占有十分重要的地位。随着社会经济发展,铁路的客货运量也大幅增长,为了使既有铁路运输能力适应运输需求,需要对其进行改扩建[1]。此外,随着城市规模扩大,一些既有铁路尤其是枢纽内的一些支线、专线被城市包围,逐渐被闲置,将其改建为市郊铁路参与城市交通是对资源的合理利用[2]。可见,改建既有铁路有利于提高运输能力,构建高效便捷、安全经济的现代铁路网络。
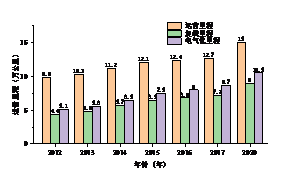
我国十三五规划[3]提出要加强既有铁路电气化改造、单线铁路改建为双线铁路,要求复线率和电气化率分别达到60%和70%左右。截止2017年末,中国铁路营业里程达到12.7万公里,复线里程7.2万公里,比上年增长5.4%,复线率56.5%,比上年提高1.6个百分点;电气化里程8.7万公里,比上年增长7.8%,电化率68.2%,比上年提高3.4个百分点。同时,我国中长期铁路网规划[4]中提出要加强既有路网技术改造和枢纽建设,提高路网既有通道能力,推进周边互联互通;规划2016到2025年,普速铁路网规模达到13.1万公里左右,既有线增建二线2万公里左右,既有线电气化2.5万公里。可见,在相当长的一段时间内,我国面临着繁重的既有线增改建设计任务。
图1.1 全国铁路运营里程 |
1.1.2既有线重构重要性
当列车在轨道上行驶时,车轮撞击轨道,使轨道中心线偏离原先设计的线位,变得不光滑。特别是在曲线上,因为列车的特性和速度是不同的,而轨道在曲线上的超高是固定的。因此,对于一个速度而言,最佳的特定超高不能平衡在其他速度下在该水平曲线上移动的列车的离心力,轨道受到列车横向压力,偏离原先设计的路线。此外,列车的制动力以及牵引力也会导致轨道变形。随着运营时间的增加,变形不断积累,线路与原有设计线路会发生较大的偏差。因此,无论是铁路养护维修还是在既有线改建设计,都需要首先进行既有线的重构。
在铁路养护维修中,为了尽可能减少对铁路运营的中断,主要基于绳正法判断线路平顺度,即沿现有铁路轨道中心线等间距设置测点,定期用道尺测量,直线地段首先目测线路方向,必要时采用10m弦沿轨头内侧边测量正矢;曲线地段采用20m弦沿外轨轨头内测边逐点测量正矢,并与计划正矢进行比较,判断曲线是否需要整正。然后对偏差较大的部分进行拨道整正并沿着路线重新检查和校正轨距[5]。因此,长期的养护维修会将轨道中心线调整为重新创建的路线。这种路线可能与最初设计的路线大不相同,特别是对于现有的有碴轨道的铁路,其偏差通常很大。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
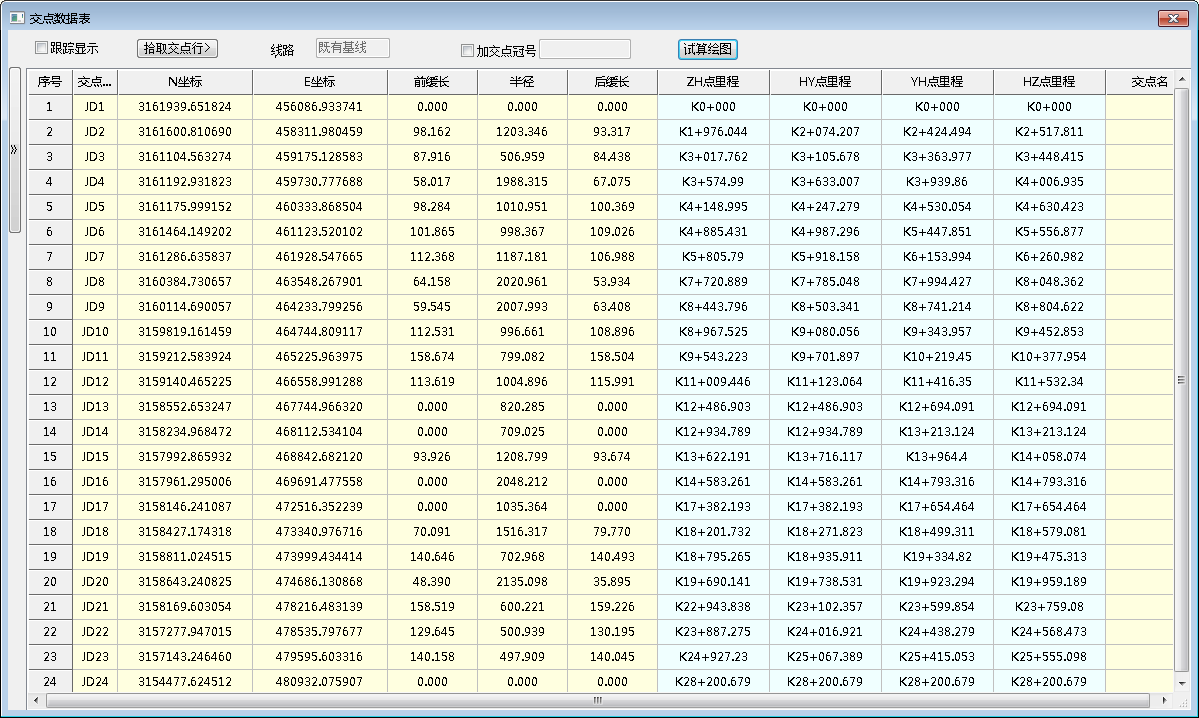
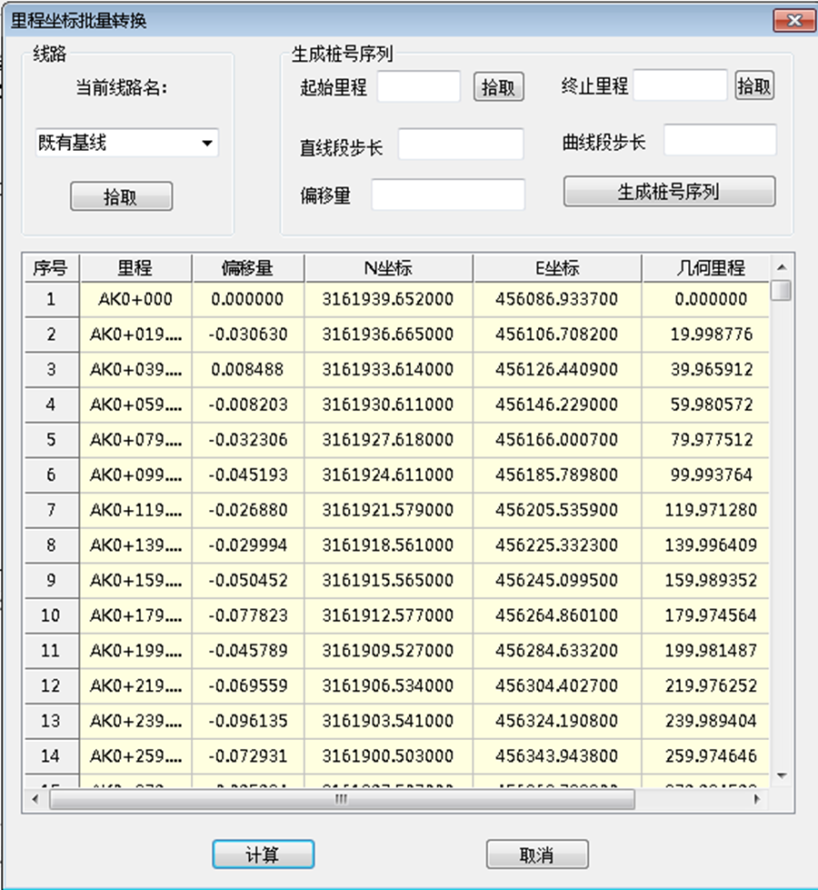
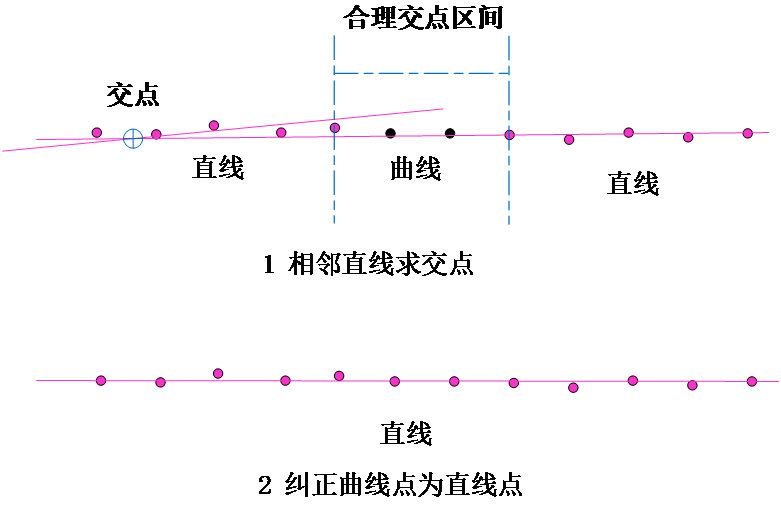
相关图片展示:
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。