交通转盘中的污染物传播特性数值模拟毕业论文
2020-04-12 09:00:57
摘 要
随着城市化的飞速发展,城市规模不断扩张,人们的生活半径也在不断扩大,不少家庭都拥有一辆甚至多辆私家车。目前,机动车已经成为城市居民日常出行的主要交通工具。据统计,截止 2017年年底,我国机动车保有量已突破3.10亿辆。随着居民出行频率的不断增长,汽车尾气污染逐渐成为我国大中型城市空气污染的重要来源之一,并且这种情况仍在不断恶化。城市街谷中由于机动车排放而形成的污染物聚集,对行人和附近居民的身体健康产生了巨大的危害,了解其中污染物扩散机制对于控制污染物至关重要。
本文借助CFD计算软件Ansys Fluent,以武汉城区内某处交通转盘为物理模型,以CO标记污染物,采用标准k-ε模型,进行数值模拟。通过模拟不同风速下的污染物扩散情况来进行对比,得出结论。本文的主要工作如下:
首先对于国内外对于街谷污染物扩散机制研究的现状进行梳理和分析,讨论各种方法的进展和成果。着重关注了城市道路污染物分布,街谷中机动车尾气排放污染扩散模拟以及风向风速对于街谷内污染物扩散的影响等方面的研究成果,借鉴前人的研究方法,利用CFD技术,通过对非对称的交通转盘模型进行数值模拟,分析不同因素对污染物扩散的影响和作用。
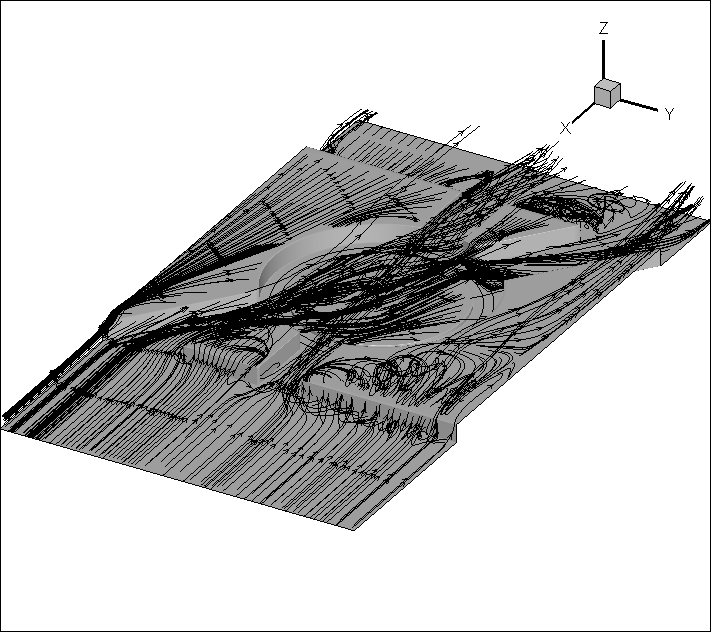
结果显示,建筑物对于流场有阻碍作用,在靠近壁面处会形成涡流,造成污染物聚集;风速对于污染物清除有积极作用,风速越大,在进出口处的污染物浓度越低,污染物聚集越少;在转盘和建筑物之间污染物并不会因为风速大而降低浓度,反而会造成更严重的聚集情况。
本文不同于以往的交通转盘数值模拟研究,采用非对称的交通转盘模型,更为接近真实情况,模拟结果也更具有参考意义。
关键词:交通转盘;数值模拟;CFD;污染物扩散
ABSRACT
With the rapid development of urbanization, the scale of the city has continued to expand, and people’s lives have continued to expand. Many families have one or more private cars. At present, motor vehicles have become the main mode of transport for city residents to travel daily. According to statistics, as of the end of 2017, the number of motor vehicles in China has exceeded 310 million. With the increasing frequency of residents' travel, automobile exhaust pollution has gradually become one of the important sources of air pollution in large and medium-sized cities in China, and this situation is still worsening. The accumulation of pollutants due to the emission of motor vehicles in urban streets and valleys has caused great harm to the health of pedestrians and nearby residents. Understanding the mechanism of pollutant diffusion among them is crucial for the control of pollutants.
In this thesis, the CFD simulation tool Ansys Fluent is used to simulate the transport carousel somewhere in the urban area of Wuhan. The pollutant is marked by CO and the standard k-ε model is used for numerical simulation. The results were compared by simulating the diffusion of pollutants at different wind speeds and conclusions were reached. The main work of this article is as follows:
First of all, the current situation of research on the diffusion mechanism of street-level pollutants at home and abroad are analyzed, and discusses the progress and results of various methods. Emphasis was placed on the distribution of pollutants on urban roads, the diffusion simulation of pollution from exhaust emissions of motor vehicles in the street valley, and the influence of wind speed on the diffusion of pollutants in the street valley. The results of previous research methods were used, and CFD technology was adopted to achieve asymmetry. The traffic wheel model was used for numerical simulation to analyze the influence of different factors on the diffusion of pollutants.
The results show that buildings have an obstructing effect on the flow field, and turbulences are formed near the wall surface, causing the accumulation of pollutants; the wind speed has a positive effect on the removal of pollutants. The higher the wind speed, the lower the pollutant concentration at the entrance and exit, and the pollution. The less aggregates there are; the pollutants between the turntable and the building will not reduce the concentration due to the large wind speed, but will cause more serious accumulation.
This thesis is different from the previous research on the numerical simulation of traffic turntables. The asymmetric traffic turntable model is more close to the real situation and the simulation results are more referential.
Key words: traffic roundabout; numerical simulation; CFD; pollutant diffusion
目录
摘要 3
ABSRACT 4
1绪论 6
1.1研究背景及意义 6
1.1.1研究背景 6
1.1.2 研究意义 7
1.2国内外研究现状 7
1.2.1 研究方法 7
1.2.2 影响因素 8
1.3本文的主要工作 9
2街谷污染物传播的基础理论 10
2.1 CFD数值模拟原理 10
2.1.1 网格技术基础 11
2.1.2 网格自适应 11
2.1.3 湍流模型选择 12
2.1.4 数值离散方法 12
2.2污染物扩散方程的选择 13
3交通转盘污染物扩散数值模拟 14
3.2边界条件设定 16
3.3污染源设定 16
3.4网格独立性验证 16
4数值模拟结果分析 17
4.1模型的几何结构对流场及污染物分布的影响 19
4.2风速对流场及污染物浓度场的影响 19
5总结与展望 24
5.1 总结 24
5.2 展望 24
参考文献 26
致谢 28
1绪论
1.1研究背景及意义
1.1.1研究背景
目前,机动车已经成为城市居民日常出行的主要交通工具。据统计,截止 2017年年底,我国机动车保有量已突破3.10亿辆[1]。随着居民采用机动车出行的频率不断增长,汽车尾气逐渐成为我国城市空气污染的重要来源之一,并且这种状况仍在恶化。
交叉路口的建筑物会阻碍机动车过往排放的废气的扩散,容易引起机动车交通污染物的堆积。机动车尾气的逸散性排放导致污染物进入地面呼吸区而没有完全扩散和稀释。危害路人和楼内居民健康。城市道路和建筑物的复杂性对道路的微观环境造成严重影响,导致空气污染物的扩散方式变得十分复杂。由2015年的环境监测结果显示[2],中国机动车尾气中仅有颗粒物达到57.4万吨。大量的颗粒物质悬浮在我们所依赖的城市环境中,这不仅会降低道路的可见度,还会严重危害人体健康。根据环境组织的初步估计,自2013年以来,中国有20多个省市经历了霾。过去五年,大气污染对公共卫生造成的公共卫生超过9000亿元。持续的阴霾天气对居民的精神,心理和情绪影响有着隐蔽的影响,这是不容忽视的。
目前,中国许多大中城市的空气污染以烟尘和机动车尾气的综合污染为特征。机动车辆健康最严重的危害是固体颗粒物[3]。颗粒通常具有大比表面积并具有强吸附能力。它在空气中传播,生长携带大量有毒有害物质,如铜,锌等重金属和多环芳烃等有机物。典型粒径小于2.5微米的颗粒会随着人体呼吸而累积在呼吸道,气管,支气管和肺部。他们携带的细菌会导致一系列呼吸系统疾病[4]。国内外学者进行的大量病理学研究表明[5],颗粒物浓度与人体的发病率和死亡率呈正相关,对人体呼吸系统的负面影响最为严重。颗粒物粒径越小,携带的毒性和有害物质就越多,可以长期悬浮在大气中,对大气环境和人体健康造成更大的危害。我们将液体和固体颗粒状物体称为“颗粒”[6],其颗粒大小分布范围广泛,在大气中的物理和化学性质也是如此。当汽车发动机中的燃料没有完全燃烧时,排出的废气将含有大量细小颗粒。根据颗粒的粒径大小,可分为TSP,PM10,PM2.5,可以将超细颗粒和纳米颗粒引入肺中;大气中的总悬浮颗粒物是粒径小于100μm的颗粒物质。纳米颗粒分别对应于小于0.1μm和0.05μm的颗粒。在数值模拟和实验研究中,颗粒质量浓度通常用于量化总悬浮颗粒物PM10和PM2.5对环境和人体健康的影响。定量浓度被用作超细颗粒和纳米颗粒的评价指标[7]。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
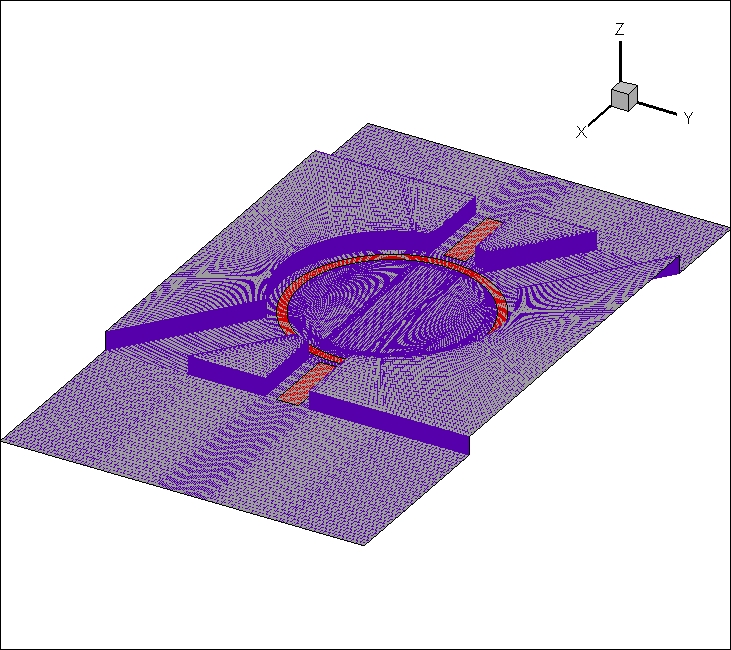
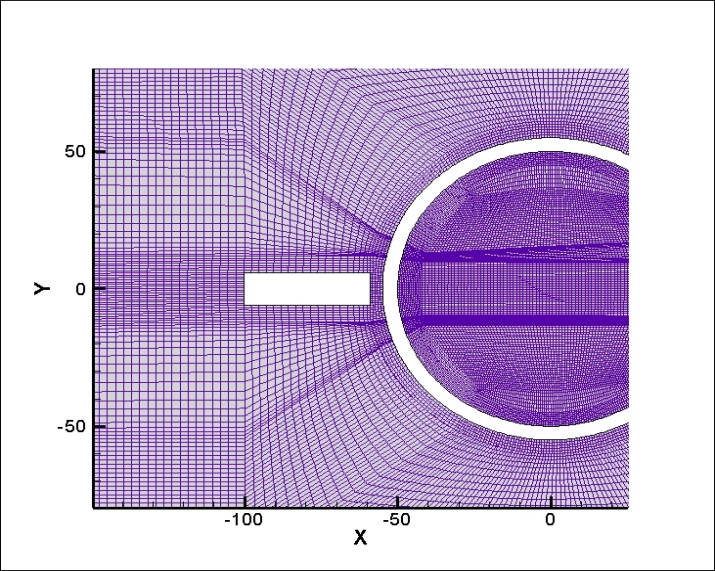
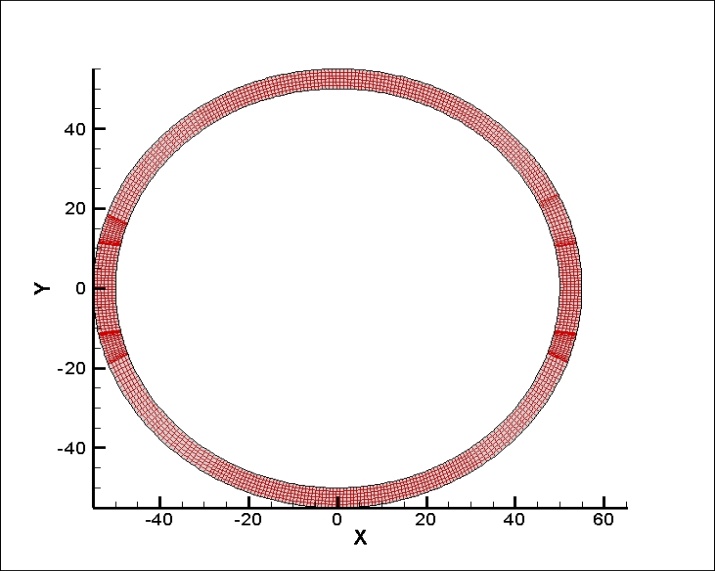
相关图片展示:


课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



