基于预测控制的燃料电池空压机流量控制毕业论文
2020-04-13 11:25:27
摘 要
质子交换膜燃料电池(PEMFC) 是汽车新型动力系统的研究热点,它低温起动快、比能量和比功率高、寿命长、无电解液流出且无腐蚀[1]。
在发电期间,燃料电池阴极消耗氧气。“氧饥饿”是当氧气的分压低于临界水平时,发生在阴极空气流曲折处的任何可能位置的复杂现象。通过电池电压的快速下降可以观测到这种现象,在严重的情况下会导致短路和膜电池的表面出现过热点。因此,当PEMFC系统的需求电流突然变化时,需要快速提供充足的氧气,在避免“氧饥饿”的同时保证电池堆的使用寿命。然而,为燃料电池堆供应过多的氧气会消耗电堆更多的电量,降低燃料电池系统的发电效率。虽然这种现象在空间上是变化的,但很大程度上它可以通过调节阴极的过氧比来避免。
本文针对PEMFC系统开展系统建模,利用预测控制方法对PEMFC空压机电压优化控制从而控制空气供应端的最优过氧比,并对比分析了预测控制方法与传统PID控制方法对燃料电池性能的影响。
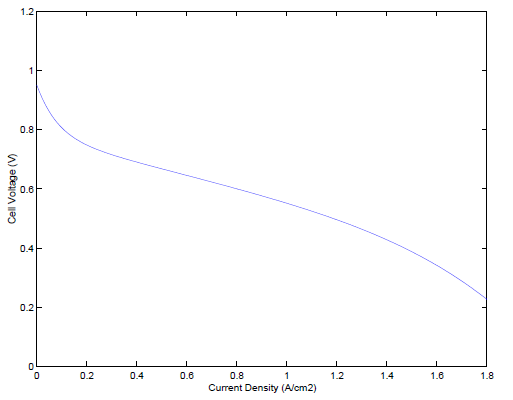
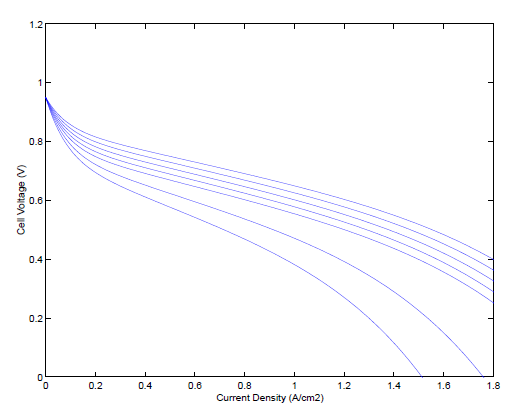
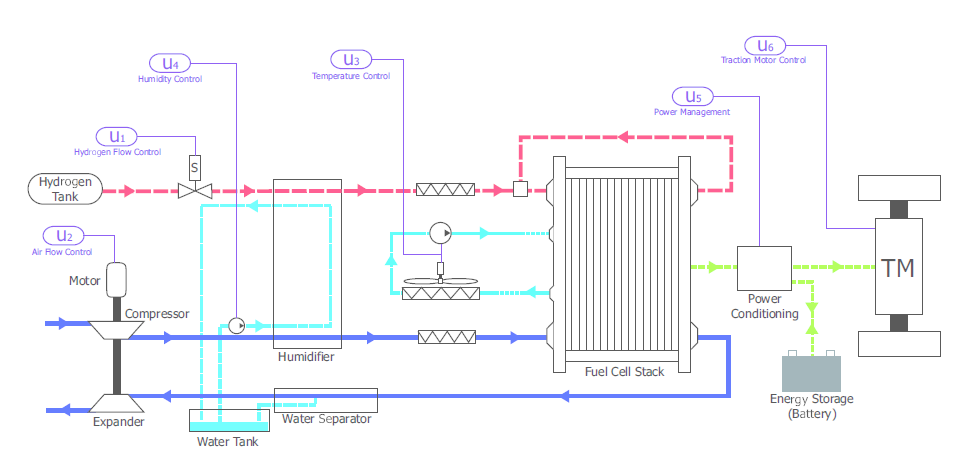
本文首先基于Pukrushpan的相关建模工作,使用Matlab/Simulink仿真工具建立PEMFC系统的动态模型,包括由阴极流道模型、阳极流道模型、电压模型、、膜水传递模型组成的燃料电池堆模型和由空压机模型、供气管路模型以及排气管路模型等组成的辅助设备模型。每部分都具有相应的动态环节。本研究通过描绘电堆输出的U-I曲线验证了该模型在多个工作点处的稳态特性,分析负载电流阶跃变化对系统输出电压以及气体流量等的影响,验证了模型的动态特性,说明所建动态模型适用于本文的过氧比的控制研究。
接着,主要针对PEMFC系统的需求电流对PEMFC系统空气供应端的最优过氧比控制,通过调节空压机的电压控制空压机流量,达到预定的最优过氧比值。常用的控制方法有前馈控制和前馈/反馈控制,其中反馈控制又有PID控制和预测控制。本文分别对上述三种控制方法在Matlab/Simulink中进行仿真验证,并将仿真结果进行分析比较,得出三种控制方法的特点:前馈控制可以快速将过氧比定位到需求电流所对应的最优过氧比值;反馈控制可以减小实际的过氧比与过氧比参考值之间的偏差,保证过氧比控制的准确性,而相比于传统的PID控制,预测控制方法在静态误差为0的同时提高了过氧比响应速度并有效减小了超调量。
关键词: 质子交换膜燃料电池,预测控制,空压机流量,过氧比控制
ABSTRACT
The proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) has the advantages of low temperature starting, high specific energy and specific power, and long service life, no electrolyte outflow and no corrosion, etc. Thus it is a new research hotspot of the new type of vehicle power system.
During power generation, the fuel cell cathode consumes oxygen. "Oxygen starvation" is a complex phenomenon that occurs at any possible location at the tortuosity of the cathode air flow when the partial pressure of oxygen is below a critical level. This phenomenon can be observed by a rapid drop in the battery voltage, which in severe cases can cause short circuits and hot spots on the surface of the membrane cell. Therefore, when the demand current of the PEMFC system suddenly changes, it is necessary to rapidly provide sufficient oxygen to ensure the life of the battery stack while avoiding "oxygen starvation". However, supplying too much oxygen to the fuel cell stack consumes more electricity in the stack and reduces the power generation efficiency of the fuel cell system. Although this phenomenon is spatially variable, it can be largely avoided by adjusting the cathode oxygen ratio.
This paper mainly focuses on the system modeling of PEMFC system and uses the predictive control method to optimize the voltage control of the air compressor of the PEMFC to control the optimal oxygen ratio of the air supply. Besides, the effects of predictive control methods and traditional PID control methods on fuel cell performance were compared and analyzed.
Firstly, based on the related modeling work of Pukrushpan, the Matlab/Simulink simulation tool is used to establish a dynamic model of the PEMFC system, including four parts of a fuel cell stack model, an air compressor model, a gas supply pipeline model, and an exhaust gas pipeline model. With the corresponding dynamic link. This study demonstrates the steady-state characteristics of the model at multiple working points by depicting the UI curve of the stack output, analyzes the effect of load current step changes on the system output voltage and gas flow, and validates the dynamic characteristics of the model. The built dynamic model is suitable for the control study of the peroxide ratio in this paper.
Then, mainly for the PEMFC system demand current on the PEMFC system air supply end of the optimal control of the peroxide ratio, by adjusting the air compressor voltage control air compressor flow, to achieve the desired optimal peroxide ratio. The commonly used control methods are feedforward control and feedforward/feedback control, where the feedback control has PID control and predictive control. This article separately carries on the simulation verification to the above-mentioned three kinds of control methods in Matlab/Simulink, and analyzes and compares the simulation result, obtains the characteristic of three kinds of control methods: Through the feedforward control, may quickly position the peroxide ratio to this demand current The corresponding optimal peroxide ratio; through feedback control, the error between the actual peroxide ratio and the optimal peroxide ratio can be reduced, ensuring the accuracy of the peroxide ratio control, compared to the traditional PID control, the prediction The control method improves the peroxide response speed and effectively reduces the overshoot while the static error is zero.
In the follow-up work, we can further optimize the modeling work, and consider the simultaneous control of the air compressor and back pressure valve actuators, so that the content of this article is more realistic.
Key Words: Proton exchange membrane fuel cell, predictive control, air compressor flow, excess oxygen ratio control
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示:

课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



