PEI接枝壳聚糖微球的制备及酸性染料吸附性能研究毕业论文
2020-04-15 00:17:33
摘 要
染料废水的存在长期使人类手足无措,随着环境的恶化,处理染料废水越来越急迫。
本文以低分子量壳聚糖、聚乙烯亚胺(PEI)600为原料,冰醋酸溶液为溶剂,环氧氯丙烷(ECH)为交联剂,制备PEI-g-Chitosan。通过旋转粘度测试,确定最佳原料配比,经注射器逐滴放入表面皿,烘干处理得到PEI-g-Chitosan微球。用金橙Ⅱ模拟常规染料,探索金橙Ⅱ溶液的浓度、PEI-g-Chitosan微球的用量、溶液的pH等变量对金橙Ⅱ吸附性能的影响和PEI-g-Chitosan微球对金橙Ⅱ的吸附机制。
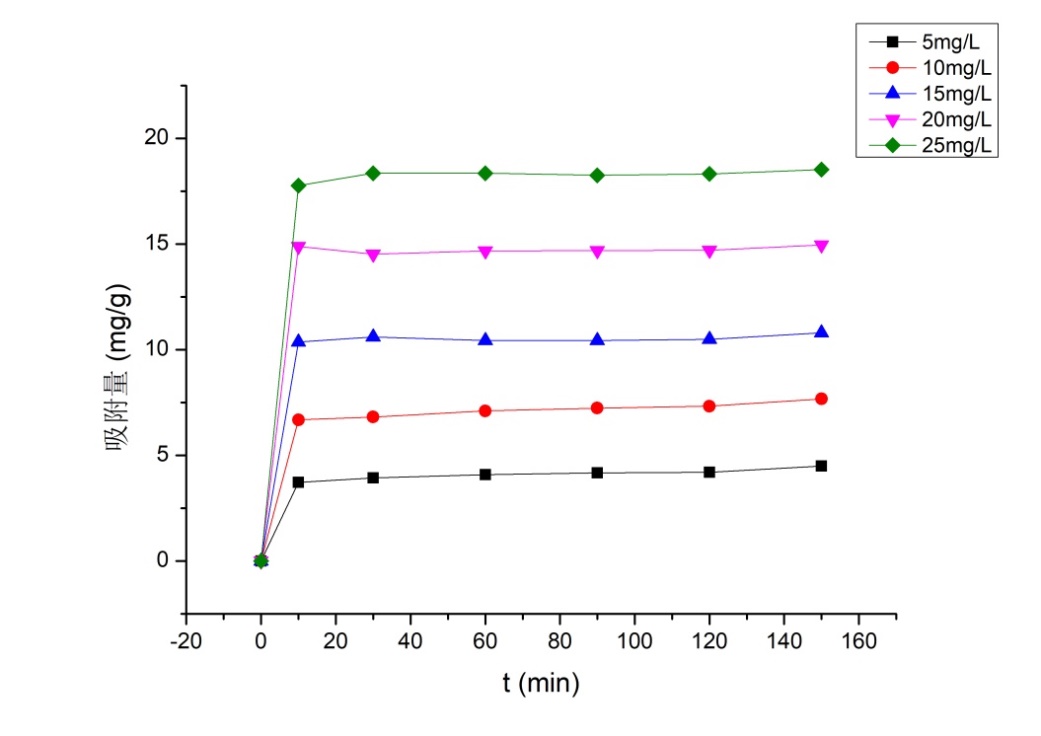
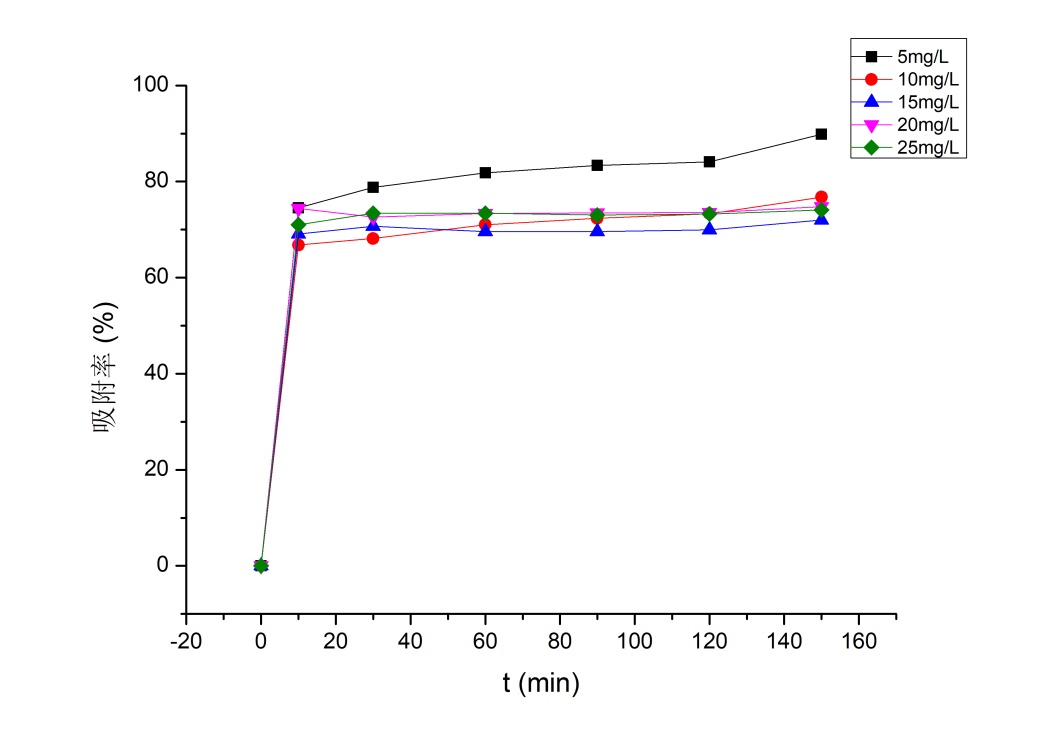
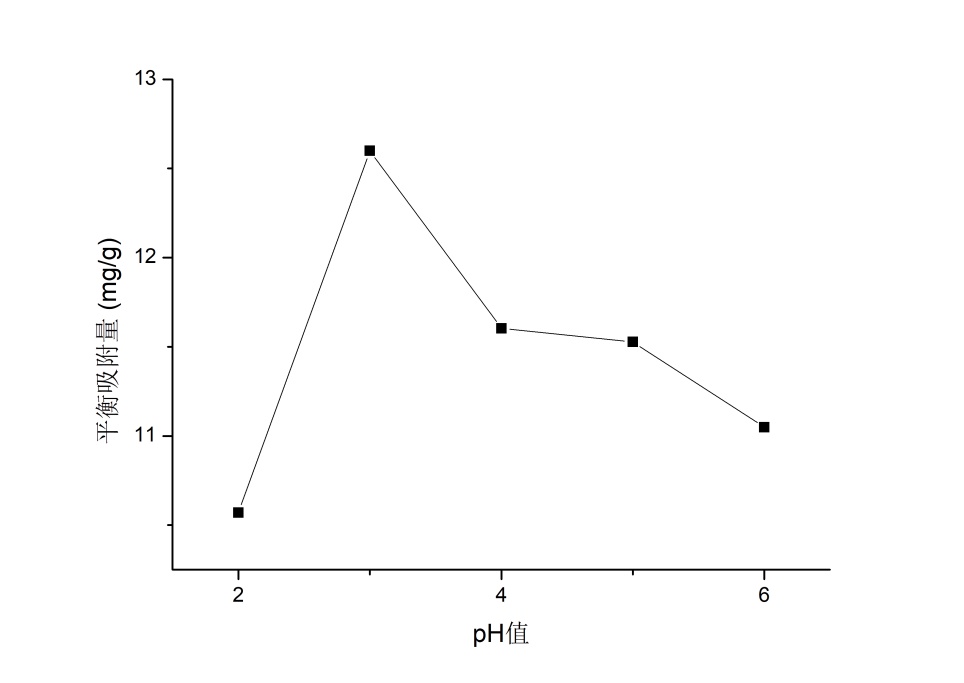
实验表明,随着金橙Ⅱ初始浓度的增加,PEI-g-Chitosan微球对金橙Ⅱ的吸附过程由剧烈到变缓直至恒定;PEI-g-Chitosan微球对金橙Ⅱ溶液的吸附程度随着吸附剂用量的增大呈现上升趋势;随着溶液pH的增大,PEI-g-Chitosan微球对金橙Ⅱ的吸附平衡量先增大后减小,最佳pH为3。PEI-g-Chitosan微球对金橙Ⅱ的吸附体系以准二级吸附动力学、弗罗因德利胥吸附等温模型为主,是吸热、自发不可逆的混乱过程,升高吸附温度有利于吸附进行。
关键词:壳聚糖 聚乙烯亚胺 改性 交联 吸附
Preparation of PEI grafted chitosan microspheres and study on adsorption properties of acid dyes
Abstract
The existence of dye wastewater has long left humans at a loss, and as the environment deteriorates, it is becoming more and more urgent to treat dye wastewater. In this paper, PEI-g-Chitosan was prepared by using low molecular weight chitosan, polyethyleneimine (PEI) 600 as raw materials, glacial acetic acid solution as solvent and epichlorohydrin (ECH) as crosslinking agent. Through the rotary viscosity test, the optimum ratio of raw materials was determined, and the PEI-g-Chitosan microspheres were obtained by dropping into a watch glass by a syringe and drying. The conventional dyes were simulated by Orange II, the effects of the concentration of Orange II solution, the amount of PEI-g-Chitosan microspheres, the pH of the solution on the adsorption performance of Orange II and the adsorption mechanism of PEI-g-Chitosan microspheres on Orange II were explored.
The experimental results show that with the increase of the initial concentration of Orange II, the adsorption process of PEI-g-Chitosan microspheres on Orange II from intense to slow to constant; as the amount of PEI-g-Chitosan microspheres increases, the degree of adsorption increases; as the pH of the solution increases, the adsorption equilibrium of PEI-g-Chitosan microspheres on Orange II increases first and then decreases, and the optimum pH is 3. The adsorption system of PEI-g-Chitosan microspheres on Orange II is mainly quasi-secondary adsorption kinetics and Freundlich adsorption isotherm model. It is an endothermic and spontaneous irreversible chaotic process. Increasing the adsorption temperature is conducive to adsorption.
Key words: chitosan; polyethyleneimine; modification; cross-linking; adsorption
目 录
摘要 I
Abstract II
目 录 III
第一章 前言 1
1.1 选题背景及意义 1
1.2 壳聚糖的改性研究 2
1.3 壳聚糖微球的制备 3
1.4 酸性染料处理现状 3
1.5本文思路 5
第二章 实验部分 6
2.1实验药品与仪器 6
2.1.1 药品 6
2.1.2 仪器 6
2.2实验过程 6
2.2.1 PEI-g-Chitosan的合成 6
2.2.2 PEI-g-Chitosan旋转粘度测试 7
2.2.3 PEI-g-Chitosan微球的制备 8
2.2.4 金橙Ⅱ标准曲线的测定 8
2.2.5 PEI-g-Chitosan微球对金橙Ⅱ吸附性能的测试方法 8
2.2.6 金橙Ⅱ溶液吸附效果的单因素实验 8
2.2.7 吸附等温模型研究 9
2.2.8 吸附动力学研究 9
2.2.9 吸附热力学研究 9
第三章 结果与讨论 11
3.1 PEI-g-Chitosan 微球的最佳制备工艺 11
3.2 金橙Ⅱ溶液的标准曲线 11
3.3 金橙Ⅱ溶液吸附效果的单因素实验 11
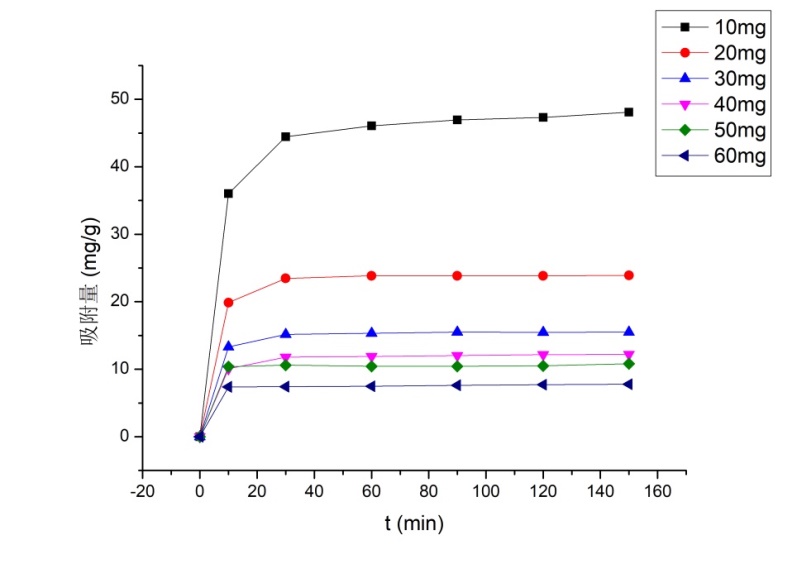
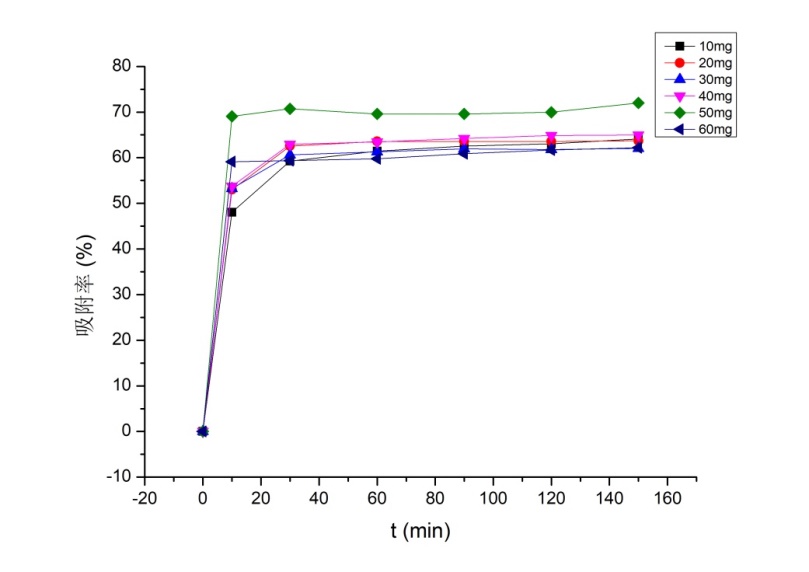
3.3.1 金橙Ⅱ初始浓度对吸附性能的影响 11
3.3.2 PEI-g-Chitosan微球用量对吸附性能的影响 13
3.3.3 溶液pH值对吸附性能的影响 14
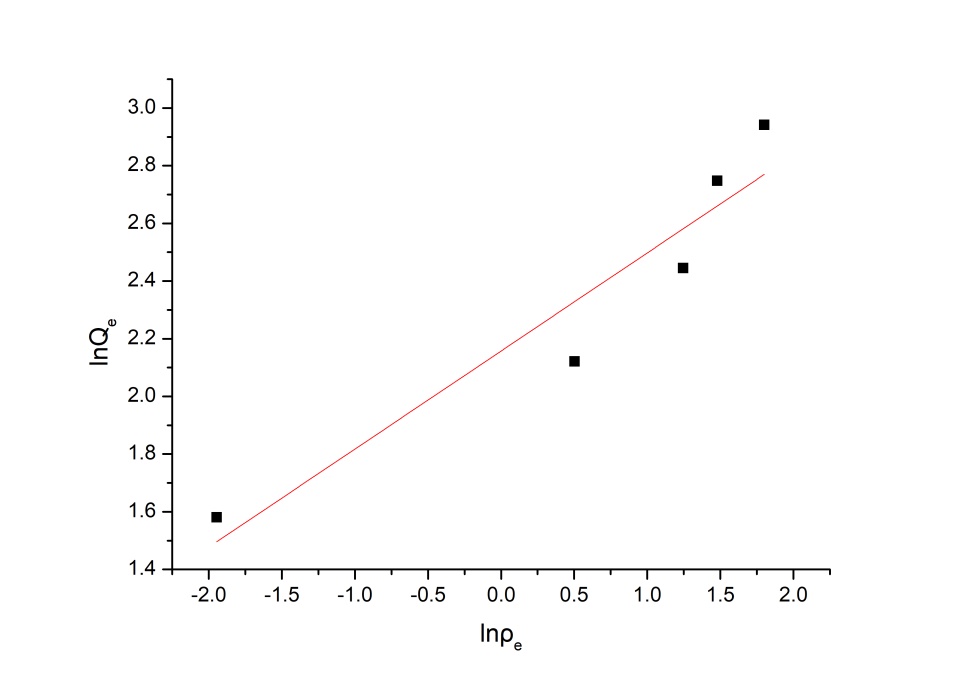
3.4 吸附等温线模型分析 14
3.5 吸附动力学模型分析 16
3.6 吸附热力学分析 18
第四章 结论与展望 19
4.1 结论 19
4.2 创新与展望 19
参考文献 20
致谢 23
第一章 前言
1.1 选题背景及意义
染料被广泛应用于纺织染整、造纸、皮革、塑料、橡胶等工业领域,这导致我国每年有大量染料废水产生,若得不到有效的治理,这些废水将会严重影响环境,污染水资源,甚至影响人类健康。所以,处理染料废水越来越紧急。目前,染料废水的常用处理方法有吸附法、膜分离法、电化学法、好氧法等[1]。其中,从制备成本和效率方面考虑,吸附法在众多处理方法中是最合适的。但是一般的吸附材料存在显而易见的缺点,如吸附容量低、吸附速度慢、无法再生和重复使用等。因此,对吸附材料进行改性,使之具有高效、廉价、可再生等优点对处理染料废水极其重要。
壳聚糖在自然界中含量丰富,原料易得,大分子链上存在大量羟基和氢键,具有良好的吸附性、保湿性、成膜性等性能[2],其化学结构如图1-1所示。由于壳聚糖的氨基在酸性介质中质子化,可以作为天然电解质[2]。相比于其他吸附剂,壳聚糖成本低、吸附量大、不会造成二次污染,是极具发展潜力的环保型吸附材料[4]。
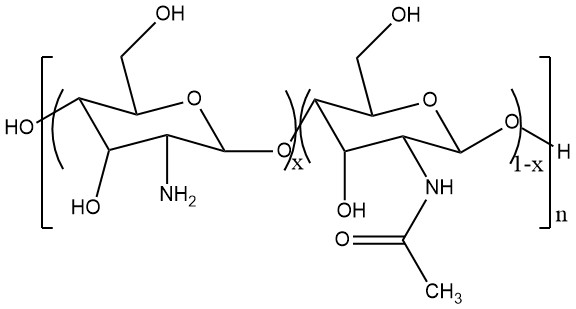
图1-1 壳聚糖的结构式
但壳聚糖不耐酸,在酸性溶液中不稳定,容易发生溶解并形成胶体[5],需要对壳聚糖进行交联改性,大多数基于壳聚糖的生物吸附剂,对改性后的特定金属离子或染料显示出优异的吸附能力[5][7]。利用壳聚糖结构中的活性氨基和羟基,通过物理改性和化学交联改性可以制备系列壳聚糖吸附剂[8],并将其应用于染料废水的吸附处理中。
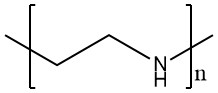
聚乙烯亚胺,又称聚氮杂环丙烷,具有支链结构的阳离子聚电解质,是目前发现的电荷密度最高的阳离子高聚物[9], 其分子链上具有大量氨基,反应活性较高,对金属离子有较强的螯合能力[9],结构式见图1-2。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示:

课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



