氢氧燃料电池膜电极的制备及性能研究毕业论文
2020-04-15 16:50:13
摘 要
能源是人类社会生存的重要组成部分,目前全世界能源矛盾问题突出。新型能源在日常生活中的地位越来越重要。燃料电池作为一种高效、绿色环保的能源转换装置,可以有效解决能源问题。质子交换膜燃料电池作为燃料电池的一种,其具有能量密度高、操作简便等优点。质子交换膜燃料电池以氢气作为燃料,氧气作为氧化剂同时也是氢氧燃料电池,其能量转换率较高、产物无污染。但由于质子交换膜燃料电池的核心——膜电极(Membrane Electrode Assembly,MEA)中铂成本的高昂和膜电极性能的低下,限制了此类电池的发展。本文着重以膜电极为对象进行研究,研究膜电极各组成部分:质子交换膜、催化层、气体扩散层的制备方法以及膜电极的性能情况,以期望可以提高膜电极的性价比。
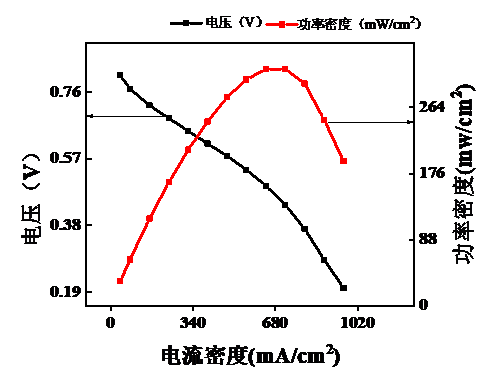
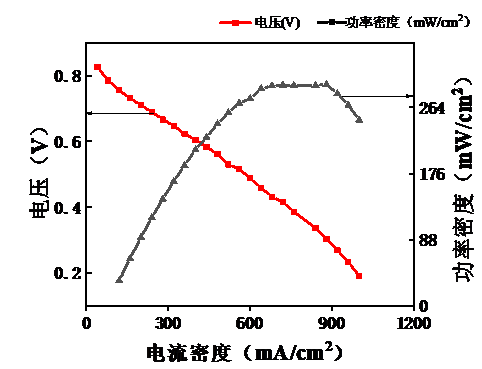
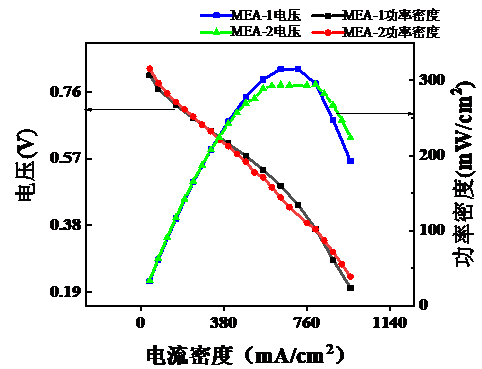
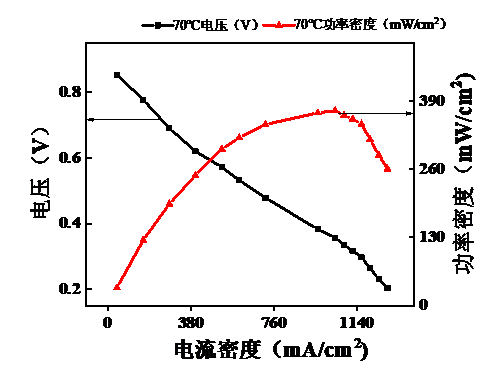
气体扩散层的制备采用碳纸作为支撑层,炭黑加PTFE溶液喷涂在碳纸上作为微孔层。质子交换膜采用购买的Nafion®115膜。对于催化层在之前的实验研究中发现采用CCM (catalyst-coated membrane)制备可以改变多种参数来研究膜电极性能。在传统的CCM制备方法:保持催化层每层Nafion浓度不变的基础上,本文提出了一种新型制备思路:催化层中Nafion浓度按照梯度分布,贴近质子交换膜那侧浓度最高,之后逐层递减。将传统制法得到的膜电极称为MEA-1,新型制法得到的称为MEA-2。采用极化曲线法(电流密度-电压、电流密度-功率密度),保持其他实验条件一致,采用电流-电压法对MEA-1和MEA-2进行表征,采用极化曲线法进行分析。最后得出结论,温度设定在30℃下,MEA-1的最大功率密度约为315 mW/cm2,而MEA-2的最大功率密度约306 mW/cm2,由此可见Nafion浓度逐层梯度分布制备有利于膜电极性能的优化。由于Nafion浓度的梯度分布,催化层上每层质子传输通道大小改变,最底层建立传输通道有利于质子通过,最外层通道小有利于阻碍电子通过。此外本文探究了在不同温度,不同气体流速下燃料电池MEA的性能情况。研究气体流速对膜电极性能的影响,由理论计算表明:氢气的流速需大于1.1 L/min,而为了安全起见通入含氧气量为21%的高纯空气的流速需大于1.8 L/mi。在使用用高性能电池测试系统测试过程中:发现当气体流速未达到要求的流速时,加大气体流速,电池的开路电压明显增大,表面电池的性能提高。研究电池在不同温度下的电压随反应温度的变化,使用MEA-1进行研究,反应温度控制在30、50和70℃,气体流速不变。结果用极化曲线法分析发现,50℃下电池的功率密度约350 mW/cm2 ,是30℃下功率密度的1.11倍,而70℃下电池的功率密度约为370 mW/cm2,是30℃下功率密度的1.17倍。因此得出结论:温度对燃料电池膜电极的性能有所影响且温度越高,膜电极的性能越好。温度升高,有利于增强催化剂活性,促进电化学反应,从而提高电池性能。
此次实验研究提出一种新型的膜电极制备方法,结果表明这种方法可以相对提高膜电极的性能。同时本文还讨论了其他条件:温度、气体流速对膜电极性能的影响。结果发现反应温度越高、气体流速越大,膜电极的性能越优。
关键词:氢氧燃料电池 膜电极 浓度梯度分布 逐层
Preparation and properties of hydrogen and oxygen fuel cell membrane electrode
Abstract
Energy is important to the survival of human society. At present, the problem of energy contradiction is prominent all over the world. New energy is very important in daily life. Fuel cell is a kind of energy conversion device with high efficiency,and it is green and environmental protection, can effectively solve the energy problem. Proton exchange membrane fuel cell is a one of the fuel cell. When hydrogen is used as fuel and oxygen is used as oxidant ,it is also called oxygen-hydrogen fuel cell. However,because the cost of platinum is high and the performance of membrane electrodes is low in membrane electrode assembly (MEA), the development of such cells is limited. This paper studies the preparation and performance of MEA mainly.
MEA includes proton exchange membrane, catalytic layer and gas diffusion layer. Carbon paper was used as supporting layer in the preparation of gas diffusion layer, and carbon black and PTFE solution were sprayed on carbon paper. Proton exchange membranes use the purchased Nafion®115 membranes. Previous experimental studies have found that using CCM (catalyst-coated membrane) can change parameters to study MEA performance. The traditional preparation method of MEA is to use CCM to keep the Nafion concentration in each layer of catalytic layer same. A new method is proposed: Nafion in the catalytic layer distributes according to concentration gradient, when Nafion is close to the side of proton exchange membrane with the highest concentration, and then the concentration decreases layer by layer. The membrane electrode obtained by traditional method is called MEA-1, and the new is called MEA-2. Using same experimental conditions to test and study MEA-1 and MEA-2. Finally came to the conclusion that at 30℃,the maximum power density of the new membrane electrode is about 315 mW/cm2 and that of MEA-2 is about 306 mW/cm2 . The results show that this method can improve the performance of membrane electrodes relatively. Because of the gradient distribution of Nafion concentration, the size of each proton transport channel in the catalytic layer changes. The innermost layer is favorable for proton passage and the outermost layer is favorable for limiting electron passage.
In addition, this paper explores the performance changes of MEA in fuel cells at different temperatures and gas velocities. The effect of gas flow rate on the performance of membrane electrodes is studied. The theoretical calculation shows that the flow rate of hydrogen should be greater than 1.1 L/min, while the flow rate of high purity air with 21% oxygen content should be greater than 1.8 L/min for safety. Finally when the gas flow rate increased, the open circuit voltage of the battery increased and the performance of the battery improved. The voltage of the battery varies with the current density at different temperatures, and the reaction temperature is controlled at 30, 50 and 70℃. The results show that the power density of the battery is about 350 mW/cm2 at 50℃, which is 1.11 times higher than that at 30℃, while the power density of the battery at 70℃ is about 370 mW/cm2, which is 1.17 times higher than that at 30℃. Therefore, the higher the temperature, the better the performance of membrane electrodes.
In this experiment, a new preparation method of membrane electrodes was proposed. The results show that this method can improve the performance of membrane electrodes . The effects of temperature and gas flow rate on the performance of membrane electrodes were also discussed. The results show that the higher the reaction temperature and the gas flow rate, the better the performance of the membrane electrode.
Key Words: Hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell;membrane electrode assembly; Concentration gradient distribution ;Layer by layer
目 录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT III
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 引言 1
1.2 燃料电池的定义及分类 1
1.3 PEMFC介绍 1
1.3.1 PEMFC发展 2
1.3.2 PEMFC组成及作用 2
第二章 研究背景及意义 4
2.1 MEA的基本结构与作用特征 4
2.2 MEA研究现状 4
2.3 研究目的 5
第三章 制备 7
3.1 实验材料与器材 7
3.2 实验步骤 8
3.2.2 Nafion膜预处理 8
3.2.2 扩散层制备 8
3.2.3 CCM制备 9
3.3 MEA热压 11
第四章 单电池组装与性能测试 13
4.1 单电池结构 13
4.2 性能测试 14
4.2.1 性能测试设备 14
4.2.2 测试方法 14
第五章 测试结果分析 15
5.1 结果分析 15
5.1.1 气体流速对MEA性能的影响 15
5.1.2 MEA外层Nafion浓度对其性能的影响 15
5.1.3 测试温度对MEA性能的影响 17
5.2 实验结果小结 18
第六章 总结与展望 19
6.1 总结 19
6.2 展望 19
参考文献 20
致谢 24
第一章 绪论
1.1 引言
能源是生存与发展的不可或缺的一部分。传统能源的缺乏以及对世界环境的影响,造成了全球性的能源危机。所以世界上所有国家不管普遍使用哪种资源都面临着严重能源短缺的问题亟待解决。为了人类社会的可持续发展,全世界人民在寻求更加环保绿色的可替代能源,新能源在我们的日常生活中占据越来越重要的地位。
燃料电池特点是:启动快、能量转化效率高、无废气排放,被认为是解决能源危机和生态问题的最具应用前景的方案之一[1]。氢气、氧气、甲烷都可以作为新型化学电池—燃料电池的原材料。其中氢氧燃料电池便是将氢气作为燃料的电池的原材料,能量转换率相对更高,超过80%。氢氧燃料电池成为解决能源问题的一大保障。
1.2 燃料电池的定义及分类
燃料电池实际上是一种电化学装置[4,31]。燃料电池按电解质分类见表1。
表1. 燃料电池分类简介
Table 1. Classification of fuel cells
类型 | 碱性燃料电池 | 磷酸燃料电池 | 熔融碳酸盐燃料电池 | 固体氧化物燃料电池 | 质子交换膜燃料电池 |
电解质 | KOH | 磷酸 | Li2CO2-K2CO2 | YSZ | 含氟质子膜 |
电解质形态 | 液体 | 液体 | 液体 | 固体 | 固体 |
阳极 | Pt/Ni | Pt/C | Ni/Al、Ni/Cr | Ni/YSZ | Pt/C |
阴极 | Pt/Ag | Pt/C | Li/NiO | Sr/LaMnO3 | Pt/C |
启动时间 | 几分钟 | 几分钟 | 大于10分钟 | 大于10分钟 | 小于5秒哦 |
应用 | 航天、机动车 | 洁净电站、轻便电源 | 洁净电站 | 洁净电站、联合循环发电 | 机动车、分布式电站、潜艇、电动汽车等 |
1.3 PEMFC介绍
1.3.1 PEMFC发展
美国通用电气公司在20世纪60年代研制出PEMFC,并应用于美国双子星座航天飞机[35],但是受限于质子交换膜的寿命,并未在航天领域得到进一步推广应用[2]。1970年左右,美国杜邦公司研制出Nafion全氟磺酸膜,促进了质子交换膜的发展。同时,随着石墨双极板加工技术、气体流道的优化以及系统集成等技术的进步,使得PEMFC的性能进一步提高。国内外对PEMFC的深入研究,使得PEMFC在性能、寿命及成本等方面得到了长足的发展,并且在交通、分布式发电等领域得到了广泛的应用,推进了PEMFC的商业化。
1.3.2 PEMFC组成及作用
PEMFC由膜电极(MEA)、双极板及密封元件等组成[2]。
MEA是PEMFC的“心脏”,承担多相物质传输和电化学反应的责任。燃料电池性能的好坏直影响MEA性能[6,8]。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示:

课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



