碳点修饰的石墨型氮化碳复合材料的制备及其光催化性能研究毕业论文
2020-04-15 16:54:07
摘 要
越来越少的不可再生能源和越来越糟糕的生存环境正逐步威胁人类的生存与发展。因此,大力发展以太阳能为主的绿色可再生能源是解决上述问题的当务之急。在已经研究出来并加以应用的太阳能利用方式当中,光催化技术是它们当中比较绿色、比较高效的一种方式。光催化技术就是一种以有机或是无机半导体材料为载体,在光照的条件下,进行降解有机物或是分解H2O的技术。此外,最吸引人的一点是光催化技术可以实现自清洁,并且成本极低,在商业领域非常容易受到追捧。但是目前所使用的光催化材料不可避免地会存在着一些不能够令人满意的地方,这也限制了光催化技术进一步推广应用到实际当中去的进程。因此,如何解决这些问题从而开发出高效新型的光催化材料,进而使光催化技术更容易地推广开来成为了目前光催化领域研究的核心问题。
石墨型氮化碳(g-C3N4)在强酸强碱中比较稳定、在高温环境材料的结构不容易被破坏、性能容易被改变等优点,在现在以及未来都可能会拥有巨大的利用价值。g-C3N4的禁带宽度相对来说较窄,约为2.7eV,并且具有合适的价带与导带,适合收集紫外-可见光用来对水体或是空气中的一些污染物进行降解,同时还能拥有产氢的功效。然而,其还没达到十全十美的地步,存在着诸多不足。因此,为解决这些问题从而开发出在可见光下催化效率更高的g-C3N4光催化材料,科研人员采取了一系列的措施包括:离子掺杂、孔结构的制造、选择禁带位置不同的半导体进行复合等。
近些年以来,碳点(CDs)的出现为开发这种高效的g-C3N4光催化材料提供了契机。
CDs作为众多碳材料(如石墨烯、石墨烯量子点、碳纳米管等)中的一员,它具有很多的优点,其中就包括容易通过实验制得、容易调节它的结构以及对其表面进行修饰、并且安全无毒。在光催化的过程中,CDs通过减缓光生载流子的复合速度同时将吸光范围进一步扩大,因此可以将光催化材料的光催化性能进一步地提升。值得注意的是,N掺杂的碳点(NCDs)可以进一步地促进光生载流子的转移以及扩大可见光吸收区域。
因此本论文将采用碳点来对g-C3N4光催化材料进行修饰来提高其光催化性能。实验内容主要包括:(1)通过水热法合成N掺杂碳点(NCDs)。(2)通过简单的对前驱体进行加热的方法制备出g-C3N4。(3)采用简单的水热法合成出NCDs/g-C3N4。然后对实验制得的碳点修饰的石墨型氮化碳复合材料进行XRD、SEM以及FTIR,初次确定样品材料是否拥有继续深入研究的价值;之后,开展研究材料光催化性能的工作,包括对材料进行吸光度的测试以及RhB的降解。最后结合详细的物化性能以及光催化性能表征,研究出碳点对光催化性能具有显著的提升。
关键词:光催化技术;石墨型氮化碳;碳点;半导体材料;水热法
Abstract
Non-renewable energy is becoming less and less, and the living environment is getting worse and worse, which gradually threatens the survival and development of human beings. Therefore, it is urgent to develop green renewable energy mainly based on solar energy to solve the above problems. Photocatalytic technology can play a important role in using solar energy. This technology can develop and utilize solar energy cleanly and efficiently, such as hydrogen production from water, non-catalytic self-cleaning, low cost, etc. This is a promising clean energy production technology. However, the existing photocatalysts based on titanium dioxide semiconductor materials have some shortcomings such as low solar energy utilization, poor stability and low quantum efficiency, which also limit the further application of photocatalytic technology in practice. Therefore, how to solve these problems, develop new high-efficiency photocatalytic materials, and make photocatalytic technology easier to promote, has become the core issue in the field of photocatalysis.
Graphite-type carbon nitride (g-C3N4) is relatively stable in strong acid and alkali environment, with high thermal stability, good biocompatibility and easy modification. As an organic semiconductor material, the bandgap of g-C3N4 is relatively narrow, about 2.7eV, with suitable valence band and conduction band. It is suitable for collecting ultraviolet and visible light to degrade organic pollutants, and also allows water to be illuminated to produce hydrogen. However, the photocatalytic activity of photocatalysts is severely limited due to the shortcomings of fast recombination rate, low utilization of visible light, low photocurrent response and small specific surface area. Therefore, it is very essential for us to study and develope some more useful material. Researchers have taken a series of measures, including ion doping, pore structure preparation and selection of semiconductor materials with different bandgap positions. In recent years, the emergence of carbon quantum dots has provided opportunities for the development of this efficient g-C3N4 photocatalytic material.
Cadmium sulfide not only has the advantages of simple preparation, easy surface modification, adjustable chemical composition and structure, non-toxicity, but also has its own structural characteristics, which determines its unique optical absorbance. Banes. Option properties. Carbon adsorption and charge transfer are excellent. In the process of photocatalysis, CdS can further improve the photocatalytic performance of photocatalysts by slowing down the recombination speed of photogenic carriers and expanding the absorption range. It can improve the photocatalytic activity of semiconductor materials. In addition, the conjugate structure of CdS can also enhance the interaction between CdS and semiconductor, thus forming stable composite materials. It is noteworthy that N-doped carbon quantum dots (NCDs) can further promote the transfer of photogenerated carriers and expand the visible absorption region.
So,we did a lot of jobs to improve the photocatalytic performance of g-C3N4 photocatalyst by carbon spots. As follows: (1) N-doped carbon quantum dots were synthesized by hydrothermal method. (2) g-C3N4 was prepared by simple heating precursor. (3)NCDs/g-C3N4 was synthesized by simple hydrothermal method. Then X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and infrared spectroscopy were carried out to determine whether the sample material has the value of further research. Then, the photocatalytic properties of the material were studied, including adsorption test and RhB degradation. Finally, combined with detailed physical and chemical properties and photocatalytic performance characterization, it was found that carbon quantum dots significantly improved the photocatalytic performance.
Key words: photocatalytic technology; graphite carbon nitride; carbondots;
semiconductor materials; hydrothermal method
目录
摘要 I
Abstract III
第一章 绪论 1
1.1引言 1
1.2 光催化简介 2
1.2.1 光催化商业化进程及应用 2
1.2.2 光催化材料 2
1.2.3 光催化机理 3
1.2.4 光催化研究方向 4
1.2.5 光催化性能影响因素 5
1.2.6 提高光催化材料性能的途径 6
1.3 石墨型氮化碳简介 7
1.3.1 g-C3N4历史 7
1.3.2 g-C3N4物化性质及结构 7
1.3.3 g-C3N4优缺点 8
1.3.4 碳点简介 8
1.4 研究目的和主要内容 8
1.4.1 研究目的 8
1.4.2 研究内容 9
第二章 实验材料与研究方法 10
2.1实验试剂与仪器 10
2.2实验过程 11
2.2.1 g-C3N4制备 11
2.2.2 NCDs制备 11
2.2.3 NCDs/g-C3N4制备 11
2.3.4 光催化降解罗丹明B 12
第三章 结果与讨论 13
3.1 g-C3N4表征 13
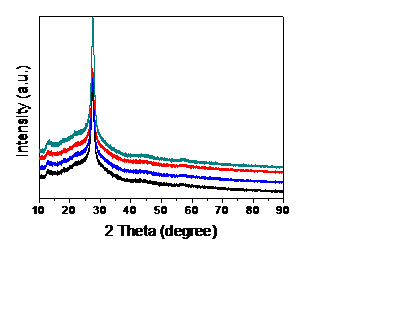
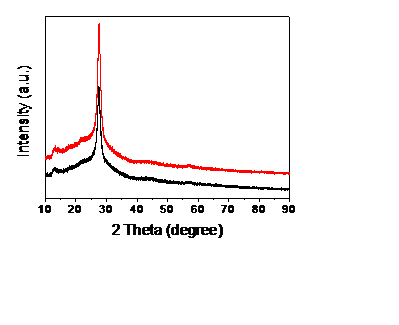
3.1.1 XRD表征 13
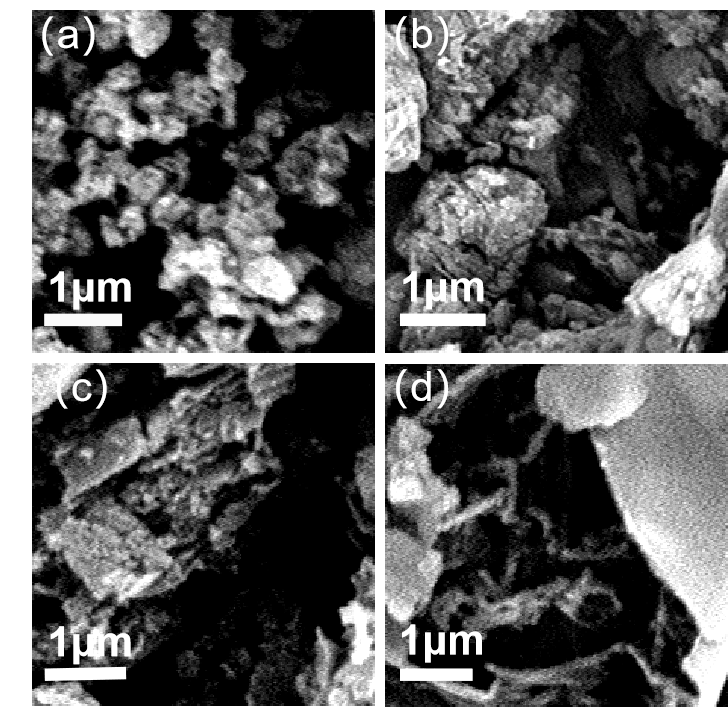
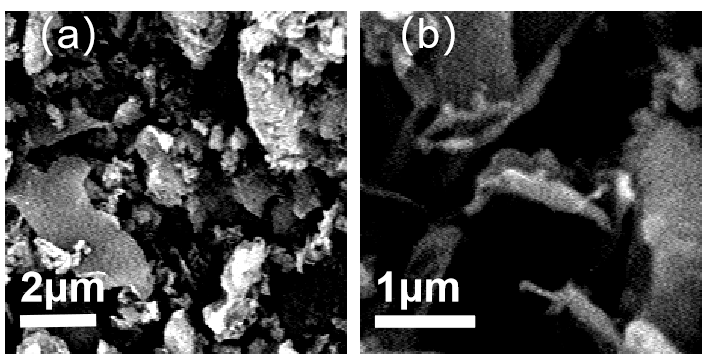
3.1.2 SEM表征 13
3.2 NCDs/g-C3N4表征 14
3.2.1 XRD表征 14
3.2.2 SEM表征 15
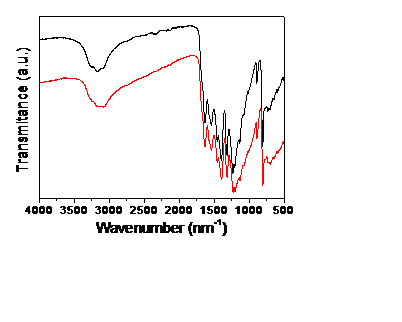
3.2.3 傅里叶变换红外光谱 15
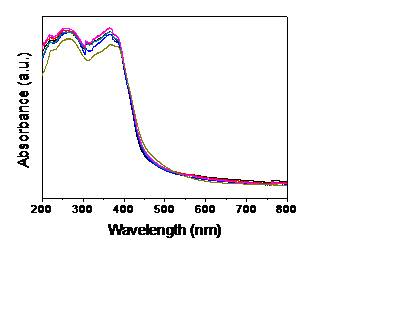
3.2.4 紫外-可见漫反射吸收光谱 16
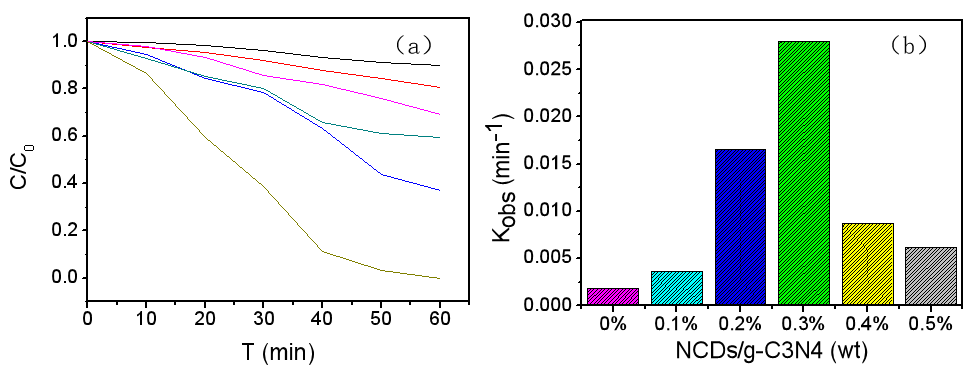
3.2.5 RhB降解 17
第四章 结论与展望 18
4.1 结论 18
4.2 展望 18
参考文献 19
致谢 22
第一章 绪论
1.1引言
能源和环境问题与我们人类的生存与发展是密切相关的。伴随着人类文明的不断进步,更加得依赖能源资源成为了一种大趋势,于是便导致了便于开采的化石能源的日益减少,留给我们子孙后代的能源资源已少之又少。因此,人类想要持续稳定地在这个星球上生存发展下去,能源问题是个不可避免的重大问题。同样,煤炭、石油等能源资源的燃烧势必会带来很多的污染物,从而会对我们的环境造成很大的破坏。地球上的先进分子早已经明白了一点,只有尽快找到一种可以取代化石能源又不影响效率的新型能源,才能实现本国的经济、社会的持续进步,从而在国际地位上能持续地领先他国,站在时代前沿。一直以来,我们人类连几岁的小孩子都知道太阳光是持续不断的,无论发生什么,它都一直在那里,哪怕人类将来在地球上继续生存个几千万年、几亿年,都会依然能感受到阳光的照射。而且,对太阳能的利用是非常方便的,它是可以洒落在地球上每一个角落的,只要有设备就可以对它进行利用。在太阳能众多优点当中,最为宝贵的一点就是其是一种清洁能源,在开发利用的过程中并不会对环境造成破坏,因此可以直接对其进行利用,不需要考虑污染或是其他问题[1]。但是开发利用太阳能来代替其他能源地行为并没有我们想象中的那么广泛。人类对其的应用仍处于一个低效和低利用率的阶段。所以如何更有效更大效率地利用太阳能就成为了全球科学家们面临的一个难题。
1972年,A.Fujishima与Honda发现,TiO2受到一束强光照射时,可以将与材料接触的水分解,形成H2和O2[2],于是在惊喜之余,他们课题组开始了对这个项目的研究,并在科研界引起了不小的轰动。因为光催化技术的应用受到来自周边环境的影响微乎其微,在室温条件下就可以进行太阳能的转化,并且对太阳能的利用率也挺可观,最重要的一点是其无污染,并不会对环境造成任何破坏。因此40多年来,光催化技术在科学家们不断地努力下实现逐步发展,正慢慢变成一个涉及到多种科目的研究项目,在净化空气、净化水体、武器装备行业、汽车制造行业、家居纺织行业等非常多的行业中有较高的利用价值,这也引起了许多国家的重视[3]。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示:
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



