不同空化诱因下低温泵内部流动数值模拟毕业论文
2020-04-15 17:31:34
摘 要
低温泵是用于输送低温流体的离心泵,广泛应用于空分、石油和化工等行业,用于提高低温流体压力,以便把流体输送到特定的工作地点。低温泵叶轮的高速转动以及低温流体的物性参数受温度影响很大使得泵内流体易于发生空化,进而引起一系列严重后果。由于引起低温泵空化的诱因有多种,所以对不同空化诱因下低温泵内部流动进行研究具有重要意义。为避免低温泵内发生空化,增加泵运转过程中的安全性、稳定性和使用寿命,本文采用CFD数值模拟方法,用Zwart空化模型和RNG k-ε湍流模型研究进口压力、出口流量两个空化诱因对低温泵内部流动的影响。本文研究的主要内容和结论如下:
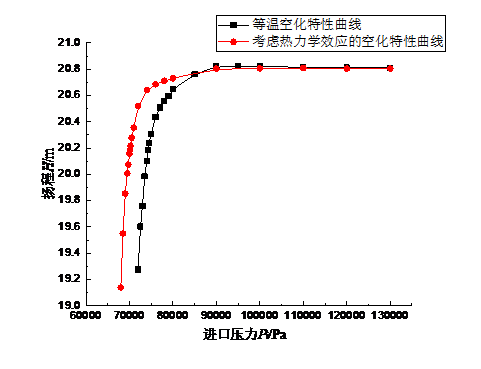
(1)研究了等温空化和考虑热力学效应空化条件下的空化特性曲线,并对两者进行了对比分析。结果表明:等温空化和考虑热力学效应空化条件下的临界空化压力分别为74250Pa和70125Pa,考虑热力学效应后的空化模型更适用实际运行工况,同时为防止液氮空化的发生,低温泵的进口总压不应过低。
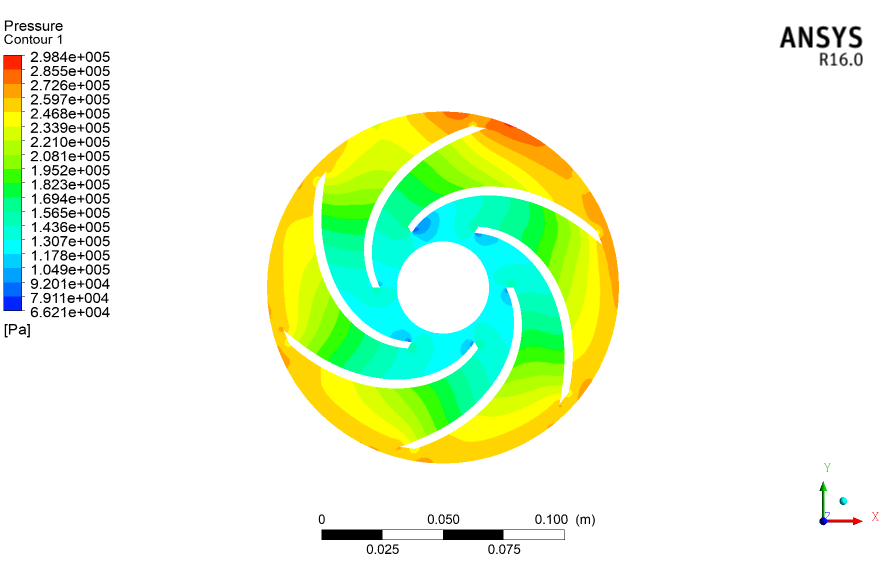
(2)对不同进口压力下低温泵内的压力分布云图、液相温度分布云图、气相体积分数分布云图进行了分析。结果表明:低温泵内低压区、低温区、空化区初现于叶轮吸力面,随着进口压力的降低,低压区、低温区、空化区沿着叶轮径向不断发展,直至出现在叶轮的压力面,最终充满整个叶轮流道。
(3)研究了扬程-流量、效率-流量特性曲线,并分析了不同工况下低温泵中间截面上的速度流线图。结果表明:在小流量工况时随流量的增大扬程缓慢减小,在大流量工况时随流量的增大扬程快速减小,随流量的增大低温泵的效率先增大后减小,效率最高点位于设计流量点附近且ηmax=88.7%,小流量工况下的旋涡和大流量工况下的水力损失以及空化的影响引起了效率的下降。
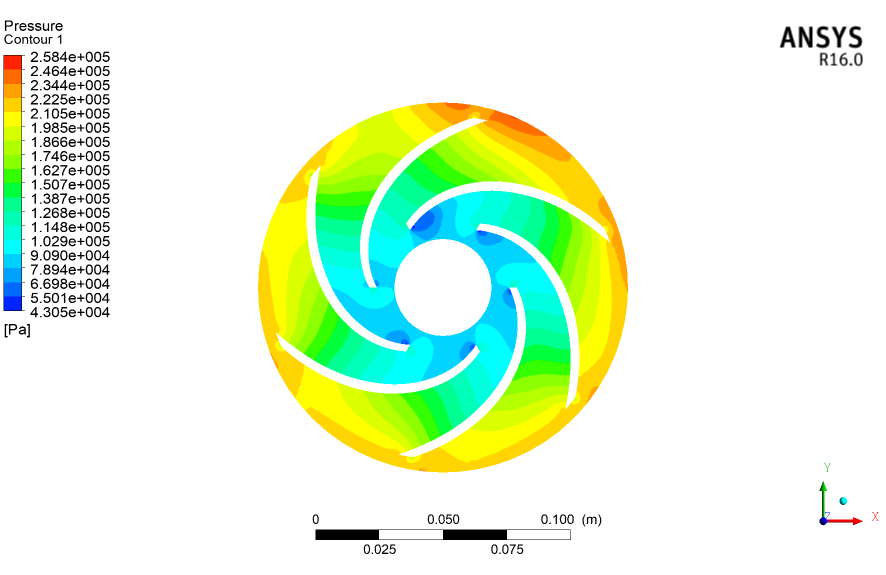
(4)对不同流量工况下低温泵内的压力分布云图、液相速度分布云图、气相体积分数分布云图进行了分析。结果表明:随着流量增大,低压区、高速区、空化区不断增多,泵内在大流量工况下发生了较为严重的空化,空化发生的位置主要靠近叶轮压力面的进口。可见,为防止空化流动的影响,低温泵不应在较大的流量工况下工作。
关键词:CFD 空化 离心泵 低温流体 数值模拟
Numerical simulation of internal flow in cryogenic pump
under different cavitation inducements
Abstract
Cryogenic pumps are centrifugal pumps used to transport cryogenic fluids. They are widely used in air separation, petroleum and chemical industries to increase cryogenic fluid pressure in order to transport fluids to specific work places. The high-speed rotation of the impellers and the physical parameters of cryogenic fluid greatly affected by temperature make the fluid in the pump prone to cavitation, and then causes a series of serious consequences. Because there are many causes of cavitation in cryogenic pump, it is important to research the flow in the cryogenic pump at different cavitation inducements. In order to avoid cavitation and increase the safety, stability and service life of the cryogenic pump during operation, CFD numerical simulation method was adopted in this dissertation, and Zwart cavitation model and RNG k-ε turbulence model were used to study the influence of two cavitation inducements-inlet pressure and flow rate. The main contents and conclusions of this dissertation are as follows:
- The characteristic curves of isothermal cavitation and thermodynamic cavitation were studied and compared. The results show that the critical cavitation pressures under isothermal cavitation and thermodynamic cavitation are 74250Pa and 70125Pa respectively. The cavitation model considering thermodynamic effect is more applicable in actual operating conditions. At the same time, in order to prevent the occurrence of liquid nitrogen cavitation, the total inlet pressure of cryogenic pump should not be too low.
- The contours of pressure distribution, liquid temperature distribution and gas volume fraction distribution in the cryogenic pump under different inlet pressure were analyzed. The results show that the low-pressure area, low-temperature area and cavitation area in the cryogenic pump appear initially on the suction surface of the impeller. With the decrease of inlet pressure, the low-pressure area, low-temperature area and cavitation area develop continuously along the radial direction of the impeller until they appear on the pressure surface of the impeller and finally fill the whole impeller passage.
- The characteristic curves of head-flow rate and efficiency-flow rate were studied, and the velocity streamlines on the middle section of the cryogenic pump under different working conditions were analyzed. The results show that the head decreases slowly with the increase of flow rate at low flow rate, but decreases rapidly at high flow rate. The highest efficiency is located near the rated point and its value is 88.7%. The eddy at low flow rate and the hydraulic losses and cavitation effects at high flow rate lead to efficiency decreased.
- The contours of pressure, liquid velocity and gas volume fraction at different flow rates were analyzed. The results show that the low-pressure area, high-speed area and cavitation area increase continuously with the increase of flow rate. Serious cavitation only occurs in the pump under the condition of large flow rate. It can be seen that, in order to prevent the influence of cavitation flow, cryogenic pump should not work under large flow rate conditions.
Key Words: CFD; Cavitation; Centrifugal pump; Cryogenic fluid; Numerical simulation
目 录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景和意义 1
1.1.1 研究背景 1
1.1.2 研究意义 1
1.2 国内外研究现状和发展趋势 1
1.2.1 常温水空化数值模拟 2
1.2.2 低温流体空化数值模拟 3
1.2.3 现状总结与展望 5
1.3 本文主要内容 5
第二章 数值模拟方法 7
2.1 几何模型及网格划分 7
2.1.1 几何模型 7
2.1.2 网格划分 7
2.2 数学模型 8
2.2.1 控制方程 8
2.2.2 空化模型 9
2.2.3 湍流模型 10
2.3 边界条件 11
2.4 收敛判据 12
2.5 本章小结 12
第三章 进口压力对低温泵空化流动的影响 13
3.1 进口压力影响下的低温泵数值模拟过程概述 13
3.2 空化特性曲线的绘制与对比分析 14
3.2.1 临界空化压力 14
3.2.2 等温空化特性曲线 14
3.2.3考虑热力学效应的空化特性曲线 15
3.2.4 不同空化特性曲线的对比分析 18
3.3 低温泵空化流动下流场参数的分析 19
3.3.1 低温泵空化流动下压力的分析 19
3.3.2 低温泵空化流动下温度的分析 21
3.3.3 低温泵空化流动下气相体积分数的分析 22
3.4 本章小结 24
第四章 出口流量对低温泵空化流动的影响 26
4.1 出口流量影响下的低温泵数值模拟过程概述 26
4.2 不同工况下低温泵空化流动的外特性分析 27
4.2.1 不同工况下低温泵扬程的分析 27
4.2.2 不同工况下低温泵效率的分析 28
4.3 不同工况下低温泵内的流场参数分析 30
4.3.1 不同工况下叶轮上压力的分析 30
4.3.2 不同工况下中间截面上液相速度的分析 33
4.3.3 不同工况下叶轮上气相体积分数的分析 34
4.4 本章小结 36
第五章 结论与展望 38
5.1 结论 38
5.2 展望 39
参考文献 40
致谢 44
第一章 绪论
1.1 研究背景和意义
1.1.1 研究背景
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示:



课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



