纤维素PVDF复合聚合物电解质的制备及其电化学性能研究毕业论文
2020-04-15 17:41:40
摘 要
现在全球能源资源日趋紧张,人类和地球上的生物的生存和发展造成威胁。油然而生的风能、太阳能、核能、地热能、生物质能源为代表的绿色可再生能源成为世界各国节能减排的首要选择。由于这些可再生能源的间歇性、时效性的缺点,人们意识到储能材料的开发成为了必然之路,所以必须加大对储能材料的研发。
但是传统的锂离子电池大多采用有机电解质(LiPF6)和易燃的PP/PE隔膜,因此在锂离子电池在使用过程中有不规范操作或电池内部发生短路导致电池过热的情况下,极易引起隔膜刺穿以及有机电解液的燃烧甚至电池爆炸。为此人们研制出了聚合物电解质。
从实用的观点来看,聚烯烃隔膜的两个最大缺点是热稳定性差和电解质润湿性,这影响了LIB的安全性能。针对聚烯烃隔膜的两大学点,本课题以天然纤维素为基础材料,在其基础上加入PVDF,这样既能够提高锂离子电池的安全性能的同时,也因为在聚合物电解质体系中有聚偏氟乙烯的存在而提高了电池的单离子导体聚合物电解质的离子电导率,加入的PVDF也可以改善隔膜的力学性能,而使用常见的天然纤维素本身就降低了电池的制作成本,同时本实验也力求能够达到与商用隔膜Celgard2400接近的物理化学性能和电化学性能。
开展工作如下:采用聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF)和木浆为原材料,先将木浆进行溶解提炼出纤维素溶液,将纤维素溶液和PVDF共混,通过相转化法制备得到复合聚合物膜,并将其与商用隔膜Celgard2400进行了性能比较。然后对膜的表面形貌观察、孔隙率计算和拉伸试验,测量制备的膜的物理化学性能。进过试验发现隔膜的吸液率与Celgard2400隔膜相差不大。由于聚合物无孔膜中大量强吸电子基团的存在,该凝胶电解质的锂离子迁移数也超过商用隔膜。虽然在小电流充放电上,聚合物电解质明显不如Celgard2400,但对于正常充放电循环与Celgard2400相差不大。
关键词:锂离子电池 复合聚合物电解质 聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF) 天然纤维素
Abstract
Now the global energy resources are increasingly tense, the survival and development of human beings and living things on the earth pose a threat.Green renewable energy, represented by wind, solar, nuclear, geothermal and biomass energy, has become the primary choice for energy conservation and emission reduction in the world.Due to the intermittency and timeliness of these renewable energy resources, people realize that the development of energy storage materials has become an inevitable way, so we must increase the research and development of energy storage materials.
However, most conventional lithium-ion batteries use organic electrolyte (LiPF6) and flammable PP/PE diaphragm. Therefore, in the case of non-standard operation or battery overheating caused by short circuit inside the battery, it is very easy to cause membrane puncture, combustion of organic electrolyte and even battery explosion.Therefore, in order to improve the safety performance of lithium ion batteries, it is urgent to develop more stable electrolytes. In this case, polymer electrolytes have been developed.
From a practical point of view, the two biggest disadvantages of polyolefin membranes are poor thermal stability and electrolyte wettability, which affect the security performance of LIB.For polyolefin at both the university of the diaphragm, this topic on the basis of natural cellulose materials, on the basis of its join in PVDF, such already can improve the lithium-ion batteries of safety property, because in polymer electrolyte system is the presence of poly vinylidene fluoride and improves the single ion conductor of the battery the ionic conductivity of polymer electrolyte, the use of common natural cellulose itself to reduce the production cost of the battery, at the same time, this experiment also can achieve and commercial diaphragm Celgard 2400 close to the physical and chemical properties and electrochemical performance.
The work is carried out as follows: using polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and wood pulp as raw materials, the wood pulp was dissolved to extract cellulose solution, cellulose solution and PVDF were blended, and the composite polymer film was prepared by phase conversion method, and its performance was compared with the commercial membrane Celgard2400.Then the surface morphology, porosity calculation and tensile test of the membrane were carried out to measure the physical and chemical properties of the prepared membrane.After the test, it was found that the suction rate of the diaphragm was not significantly different from that of the Celgard2400 diaphragm.Due to the presence of a large number of strong electron-absorbing groups in the polymer non-porous membrane, the lithium ion migration number of the gel electrolyte also exceeds that of the commercial membrane.Although the polymer electrolyte is significantly inferior to Celgard2400 for low-current charging and discharging, it is not significantly different from Celgard2400 for normal charging and discharging cycles.
Key words: Lithium ion battery;Composite polymer electrolyte;Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF);Natural cellulose
目录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1引言 1
1.2 锂离子电池简介 2
1.2.1锂离子电池的发展史 2
1.2.2锂离子电池的工作原理 3
1.2.3正极材料 3
1.2.4负极材料 4
1.2.5电解质 4
1.3聚合物电解质简介 5
1.3.1聚合物电解质发展史 5
1.3.2制备方法 6
1.4本论文的研究目的和主要内容 6
1.4.1研究目的 6
1.4.2研究内容 7
第二章 实验材料与研究方法 8
2.1实验试剂 8
2.2实验仪器 8
2.3材料物理性能表征 10
2.3.1形貌表征[26] 10
2.3.2吸液率与孔隙率表征[27] 10
2.3.3力学性能表征 11
2.4电化学性能测试 11
2.4.1离子电导率测试[29] 11
2.4.2线性扫描伏安测试[31] 12
2.4.3锂离子迁移数测试[32] 12
2.4.4恒流充放电测试[34] 12
第三章 纤维素/PVDF复合聚合物电解质 13
3.1 引言 13
3.2纤维素/PVDF复合聚合物电解质的制备 14
3.3纤维素/PVDF复合聚合物电解质的物理性能 15
3.3.1表面形貌 15
3.3.2吸液率和孔隙率 15
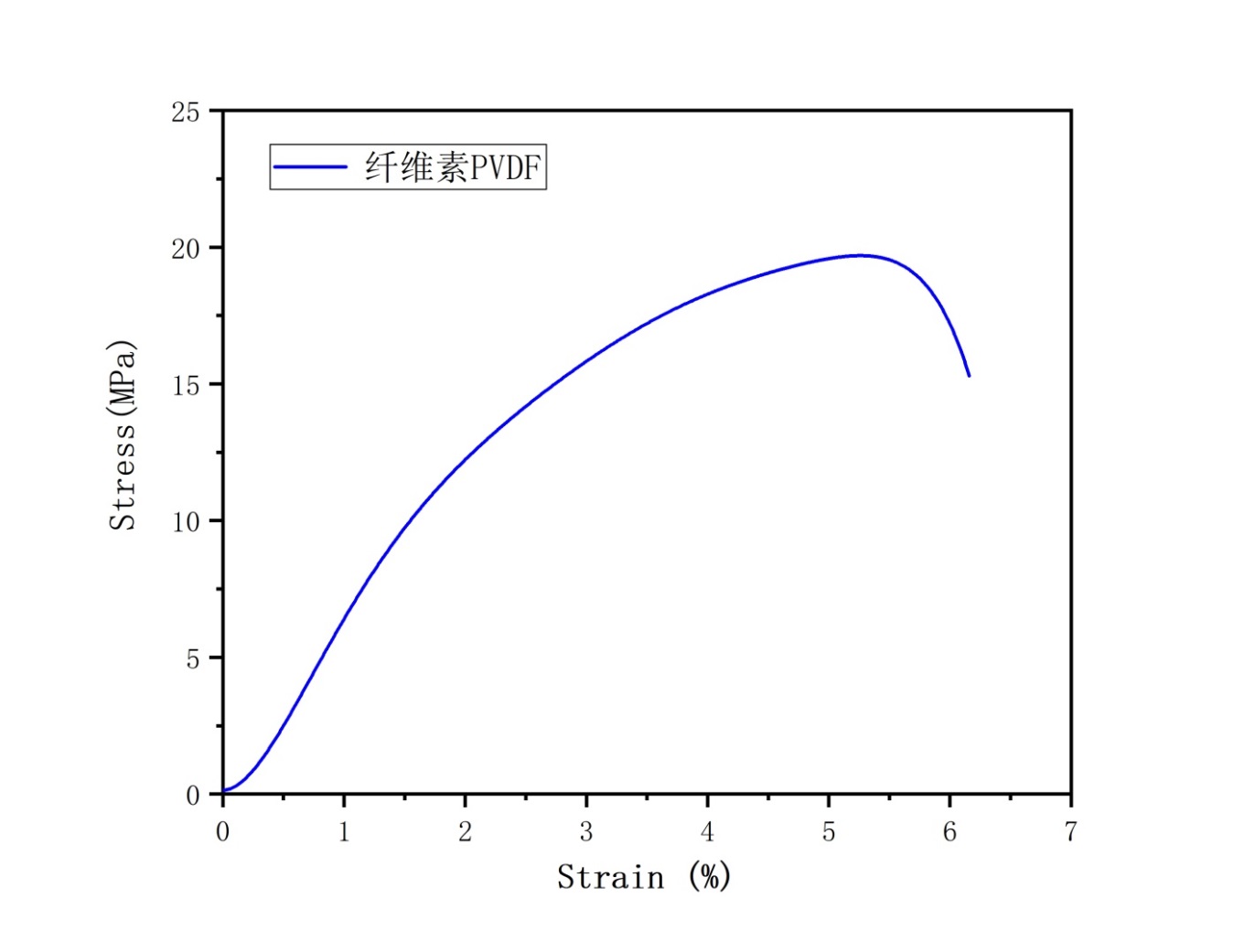
3.3.3力学性能 16
3.4 纤维素/PVDF复合聚合物电解质的电化学性能 16
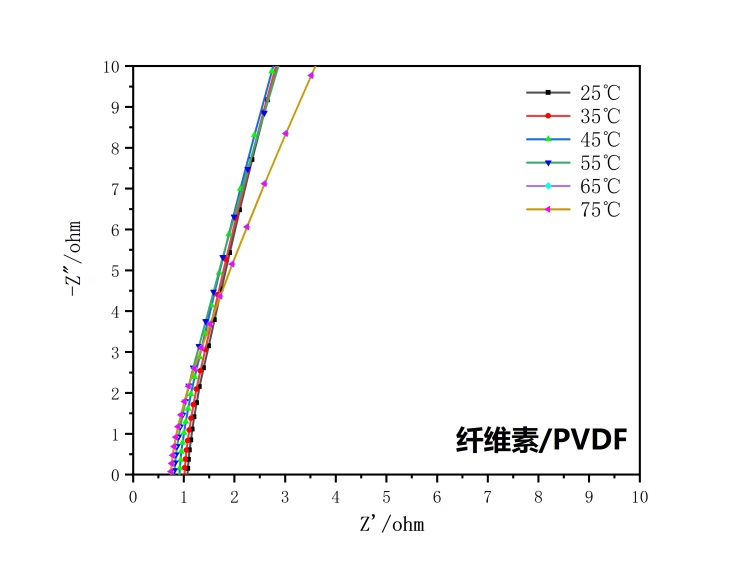
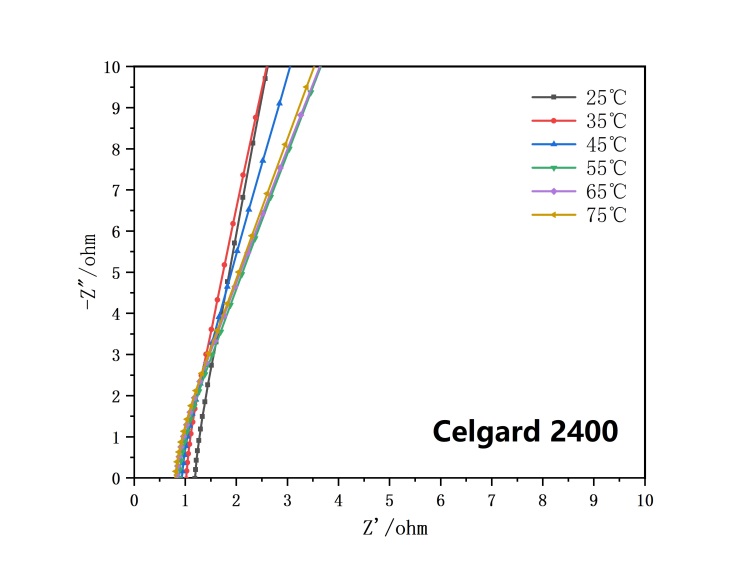
3.4.1 离子电导率 16
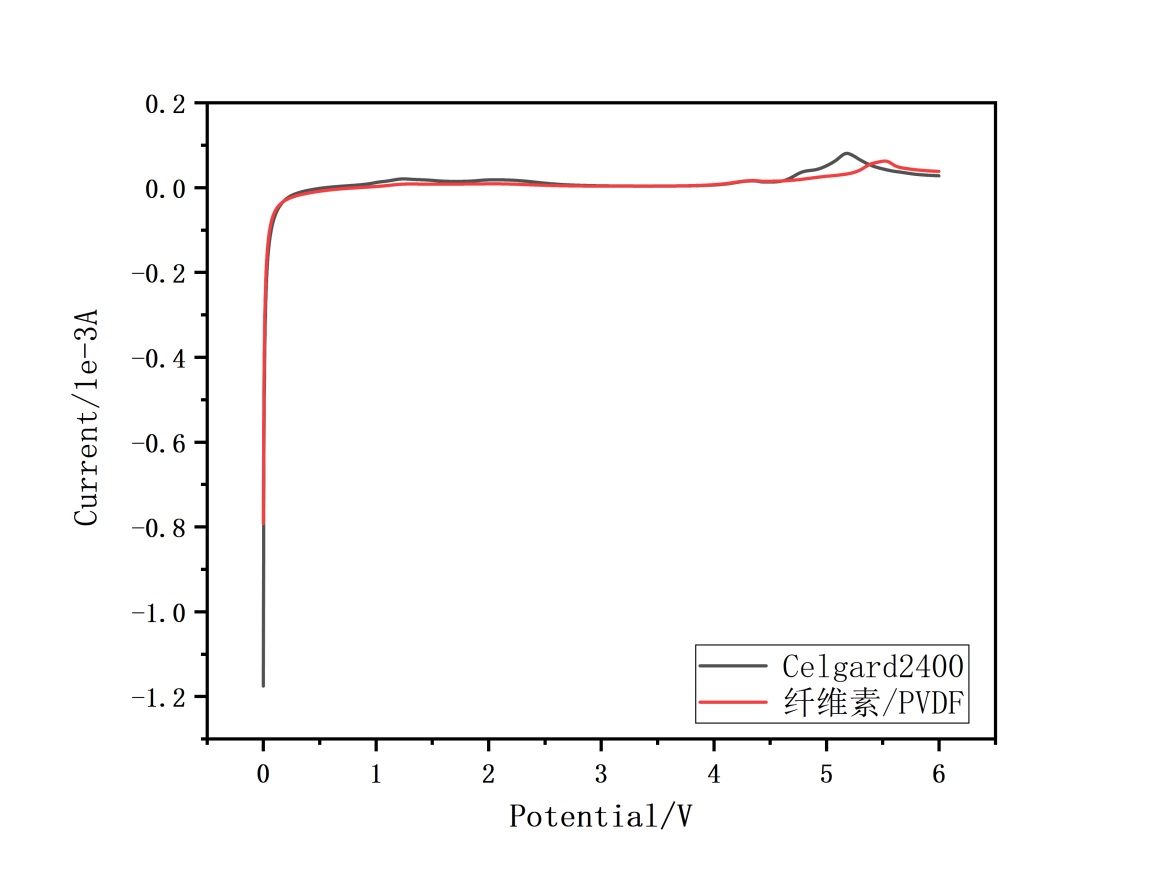
3.4.2 电化学窗口 17
3.4.3 离子迁移数 18
3.4.4 循环性能和倍率性能 19
3.5 本章小结 20
第四章 结论与展望 22
4.1 结论 22
4.2 展望 22
参考文献 23
致谢 27
第一章 绪论
1.1引言
随着人们对能源的不断需求与开发,据统计目前化石燃料使用以占全球能源消耗的70%以上[1]。但是我们应该意识到化石燃料是不可再生的,化石燃料的使用方便了我们的生活的同时带来了严重的环境污染和全球变暖等不利影响。随着经济的发展科技的创新,人们对于能源的需求量越来越多,对于清洁能源的要求越来越高,因此人们开始寻找代替化石燃料的绿色能源,以此来渡过眼前的能源危机。
人们首先意识到将一些常见却易被忽略的能源转化成易使用的能源,如将太阳能、风能、潮汐能、水能等绿色能源由动能转化为电能或热能。包括传统的在江河上游建造大坝以存储水能,并通过水力发电机将水能转化为电能;在沿海或高原等风能聚集地建造大量的风力发电机使风能传输出的机械能转化为电能;在阳光聚集地或住宅区建造太阳能收集站使太阳能转化成电能和热能,但是这些绿色能源会受到时间、地理位置等自然条件的限制,有供电量低、受益范围小、随机性、成本高、间歇性等缺点,无法达到大规模的使用[2]。因此,人们将目光放到了储能体系中,试图找到高比容量的储能体系,将这些间歇性的能源储存起来,便于使用。因此电化学储能体系成为了当前研究的首要选择。
伴随着科技的进步,电子产品变得更加的普及,同时人们对于电子产品的电池储存容量,形状大小,重量和安全也有了更高的要求。由于锂离子电池具有比能量密度高的优点,并其它对外的输出功率相对来说较大,自身的放电又比较低,电池本身并不如同铅酸电池那般具有记忆效应这一缺陷,因而已经大规模的在手机这种便携式处理装置中得到应用,在航天军事中也有锂离子电池的身影[3, 4]。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示:
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



