P91钢补焊焊接残余应力规律研究毕业论文
2020-04-15 17:47:39
摘 要
本课题采用弹塑性有限元方法,利用开发结构-热顺序耦合技术,实现虚拟焊接过程,采用数值模拟方法研究P91钢补焊结构的焊接残余应力分布,以寻求合理的焊接修补工艺。本文的主要研究内容及结论如下:
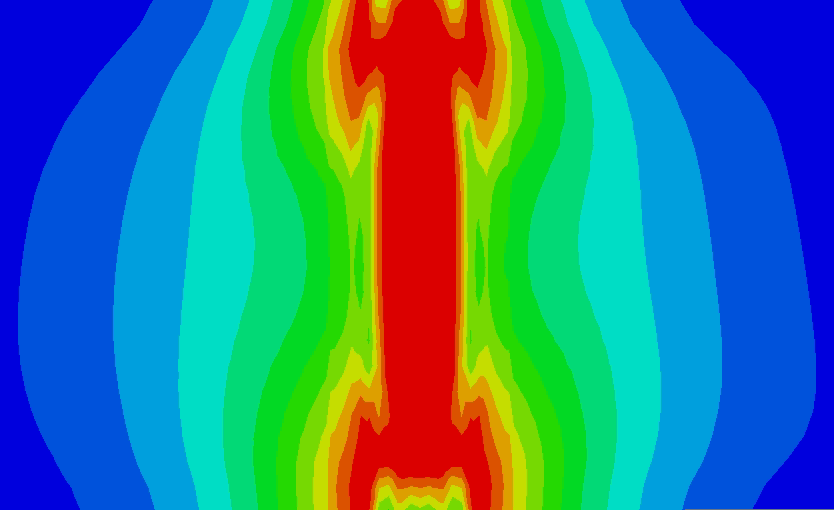
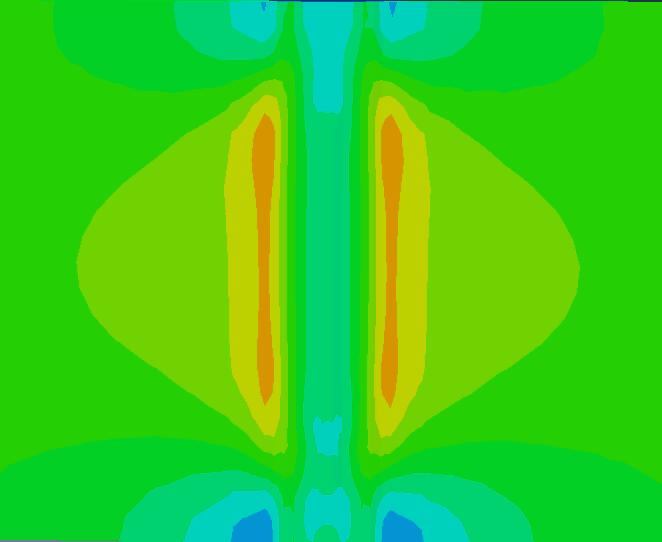
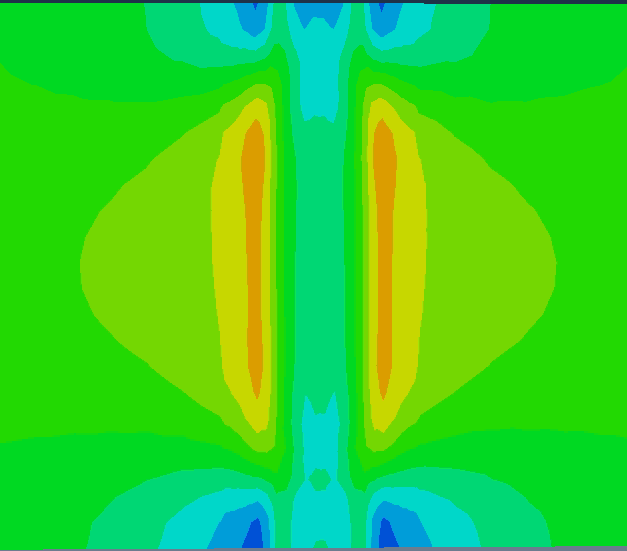
(1)对P91钢采取不同热输入进行补焊数值模拟,热输入分别取18KJ/cm、20KJ/cm、22KJ/cm,分析焊后残余应力的分布规律。结果表明,在补焊区域,随着热输入的增加 S11 应力总体上呈上升趋势,而Mises 应力、S33 应力的变化值逐渐减小。
(2)对P91钢采取不同位置进行补焊数值模拟,补焊位置分别处于焊缝、熔合区、热影响区,分析焊后残余应力的分布规律。结果表明,在补焊区域,随着距焊缝中心的距离增加Mises应力总体上呈上升趋势,而当补焊位置处于熔合区时,S11、S33应力达到最小峰值,Mises应力达到最大峰值,当补焊位置处于焊缝区时,S11、S33应力达到最大峰值,Mises应力达到最小峰值。
(3)对P91钢研究不同补焊长度、宽度、深度对焊后残余应力的影响。结果表明,在补焊区域,结果表明,随着补焊长度的增加,高应力区域也随之扩大,且Mises应力也随之减小,而 S11 残余应力逐渐增大。S33应力随补焊长度的影响无显著规律;随着补焊宽度的增加,S33应力也随之增大,Mises应力、S11应力无明显变化规律;随着补焊深度的增加,Mises应力无明显变化,S11应力峰值整体上是增大的,S33应力无明显变化规律。
关键词:ABAQUS P91钢 补焊 热输入 补焊尺寸 补焊位置
Abstract
This thesis intends to use the elastoplastic finite element method, using the development structure-thermal sequence coupling technology, realizing the virtual welding process, using numerical simulation method to study the welding residual stress distribution of P91 steel repair welding structure, so as to obtain the reasonable welding repair process. The main research contents and conclusions of this paper are as follows:
(1) For the P91 steel, different heat input is used to simulate the repair welding. The heat input is taken as 18KJ/cm, 20KJ/cm and 22KJ/cm respectively, and the distribution law of residual stress after welding is analyzed. The results show that in the repair welding area, along with increasing the heat input the S11 stress generally increases, while the value of Mises stress and S33 stress decreases.
(2) the numerical simulation of repair welding of P91 steel is carried out in different positions, which are located in weld, fusion zone and heat affected zone respectively, and the distribution of residual stress after welding is analyzed. The results show that in the repair welding area, the Mises stress increases with the increase of the distance from the weld center, but when the repair welding position is in the fusion zone, the stress of S11 and S33 reaches the minimum peak value, and the Mises stress reaches the maximum peak value. When the repair welding position is in the weld zone, the stress of S11 and S33 reaches the maximum peak value, and the Mises stress reaches the minimum peak value.
(3) the effects of different repair welding length, width and depth on the residual stress of P91 steel were studied. The results show that in the repair welding area, with the increase of the repair welding length, the high stress area also expands, and the Mises stress decreases, while the S11 residual stress increases gradually. The S33 stress has no significant effect on the repair welding length, and the S33 stress increases with the increase of the repair welding width, and the Mises stress and S11 stress have no obvious change. With the increase of repair welding depth, the Mises stress has no obvious change, the S11 stress peak value increases as a whole, and the S33 stress has no obvious change rule.
Keywords:ABAQUS; P91 steel repair; welding heat input;repair welding size;repair welding position
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 课题研究的背景及意义 1
1.2 焊接残余应力的产生 1
1.3 焊接残余应力数值模拟现状 2
1.4 补焊残余应力数值模拟研究现状 3
1.5 论文主要研究内容 4
第二章 P91钢焊接接头补焊数值模拟 6
2.1焊接温度场 6
2.2焊接应力应变场 7
2.3焊接接头补焊有限元模型的建立 8
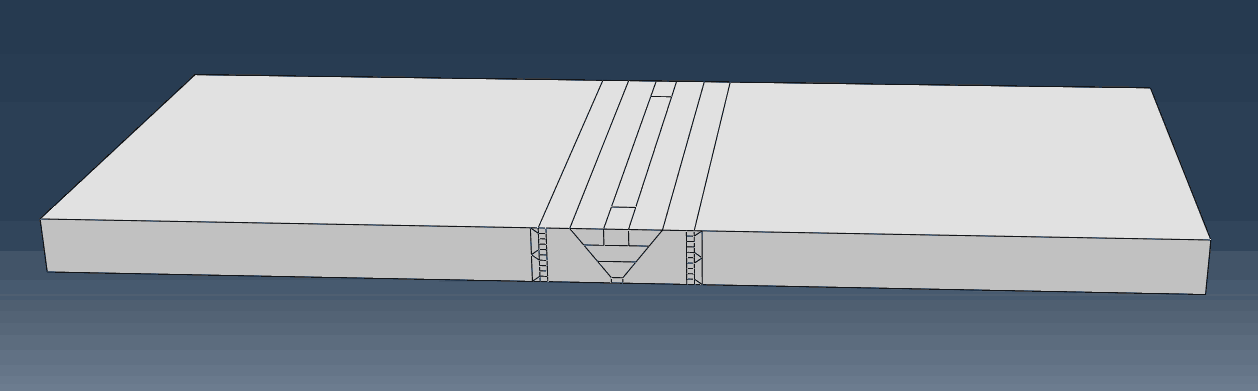
2.3.1焊接补焊模拟建模方案 8
2.3.2 材料性能参数 8
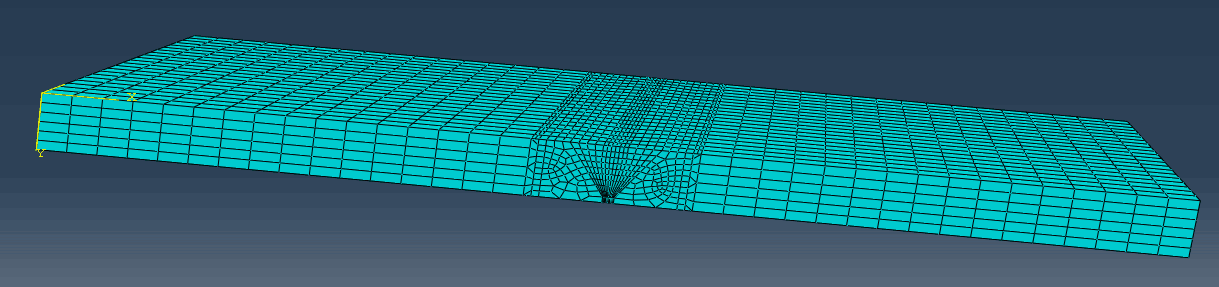
2.3.3 网格划分 9
2.3.4 热源模型 10
2.3.5 初始条件和边界条件 10
2.3.6 焊接数值模拟关键技术和步骤 10
2.3.7 补焊过程模拟步骤 11
第三章 P91钢不同热输入和焊接位置对残余应力的影响 12
3.1 不同热输入补焊残余应力研究 12
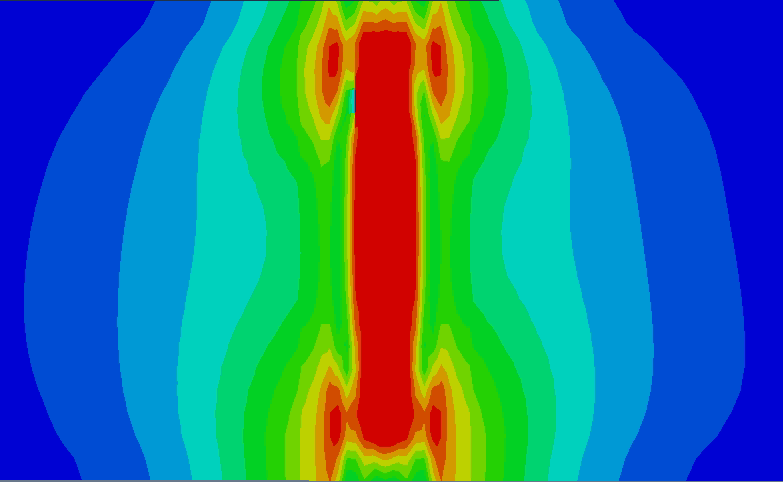
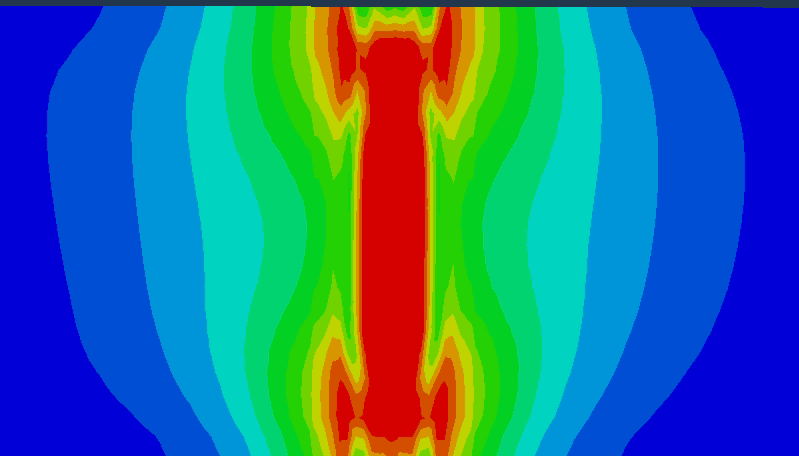
3.1.1 不同热输入补焊数值模拟 12
3.1.2 小结 17
3.2 P91钢不同补焊位置对残余应力的影响 17
3.2.1不同补焊位置应力研究 17
3.2.2 不同补焊位置数值模拟 17
3.2.3 小结 23
第四章 P91钢不同补焊尺寸对残余应力的影响 24
4.1不同补焊尺寸数值模拟 24
4.2补焊长度对残余应力的影响 24
4.3 补焊宽度对焊接残余应力的影响 29
4.4 补焊深度对焊接残余应力的影响 34
4.5 本章小结 39
第五章 结论与展望 40
5.1 结论 40
5.2展望 40
参考文献 42
第一章 绪论
1.1 课题研究的背景及意义
由于焊接结构本身的特点,一些焊接结构在制造和安装过程中不可避免地产生了焊接缺陷,并且,这些部件往往在恶劣环境下运行,在原有缺陷发展的同时,又可能产生新的缺陷,缺陷越多,返修率也越高,对于十分严重的缺陷立即进行现场挖补修复[1]。局部补焊时,焊接残余应力的问题将是较为突出的,而焊接残余应力的存在又往往是接头产生裂纹的重要原因,它将严重降低结构的强度、疲劳寿命,并加速裂纹的扩展破坏[2]。
1.2 焊接残余应力的产生
焊接时发生应力和变形的原因是焊件受到不均匀加热,并且,因加热所引起的热变形和组织变形受到焊件本身刚度的约束,在焊接过程中所发生的应力和变形被称为暂态或瞬态的应力变形,而在焊接完毕和构件冷却后残留的应力和变形,称之为残余或剩余的应力变形,某种程度上,会影响焊接结构的承载能力和服役寿命,因此对此问题的研究不仅具有理论意义,而且也有重要的实际工程价值[3]。
引起焊接应力和变形的机理为,自然界中的物体都有热胀冷缩的现象,而焊接过程又是一个不均匀的局部加热过程,从熔池中心至熔合线再到热影响区再到母材,温度梯度非常高,电弧加热阶段,电弧下方的金属膨胀,但是远端母材温度低,刚性大阻碍其膨胀变形,而在冷却阶段熔池金属收缩,收缩同样受到周围冷端的抑制,这样最终产生塑性变形[3]。如图1.1。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示:
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



