磷石膏-镍渣基胶凝材料的固化和改良盐渍土的性能评价毕业论文
2020-04-17 15:08:37
摘 要
目前,我国滨海地区是很多工程项目的聚集地,而滨海地区的土层含大量的盐渍淤泥土,其含盐率及含水率都比较高,并且容易发生溶陷,翻浆,盐涨等病害,若直接置于工程用土使用会有极大的危害。而在我国工业生产中,如高镁镍渣、磷石膏这些固体废弃物已经对我们的生存环境造成了很大的威胁,这些固废的年产量巨大,但利用率很低,对于环保造成了很大的压力。本课题结合磷石膏,镍渣及滨海地区盐渍土的物理及化学特性,利用磷石膏-镍渣基胶凝材料对滨海地区盐渍土进行固化与改良,提高盐渍土的力学性能及理化性能。同时又解决了磷石膏、镍渣的回收处理,减轻环保负担。
本文以高镁镍渣和磷石膏等工业固体废弃物为主要胶凝材料,针对盐渍土的处理难点,采用固化和改良同时进行的方式来处理盐渍淤泥。为了获得-磷石膏-镍渣基复合胶凝材料的最优配比,评价了各种掺量配比下浆体的无侧限抗压强度,另外,评价了磷石膏-镍渣基胶凝材料固化盐渍土的路用性能,以及磷石膏-镍渣基胶凝材料改良盐渍土后的理化性能,并对固化作用机制进行了分析;最后通过种植试验验证磷石膏-镍渣基胶凝材料固化改良盐渍土的可行性。
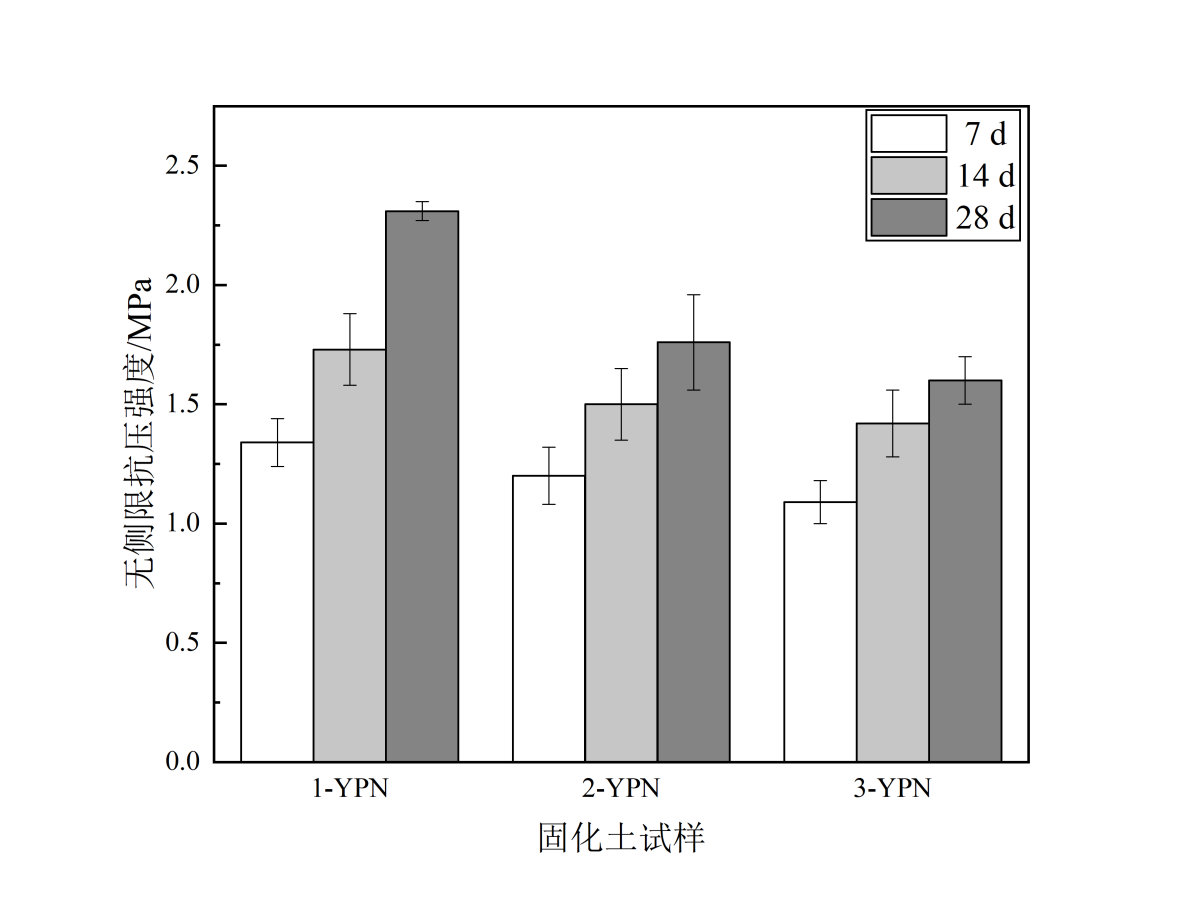
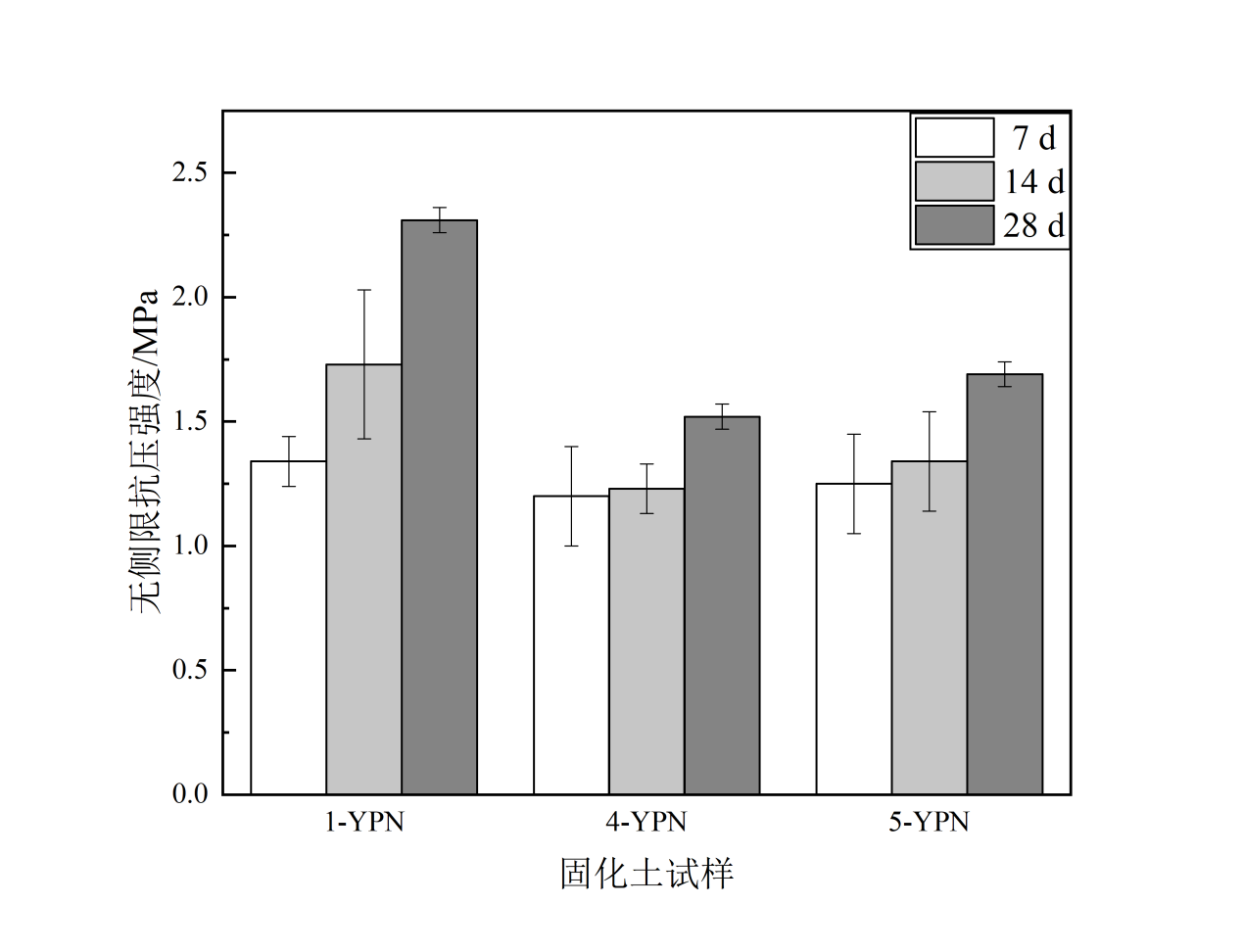
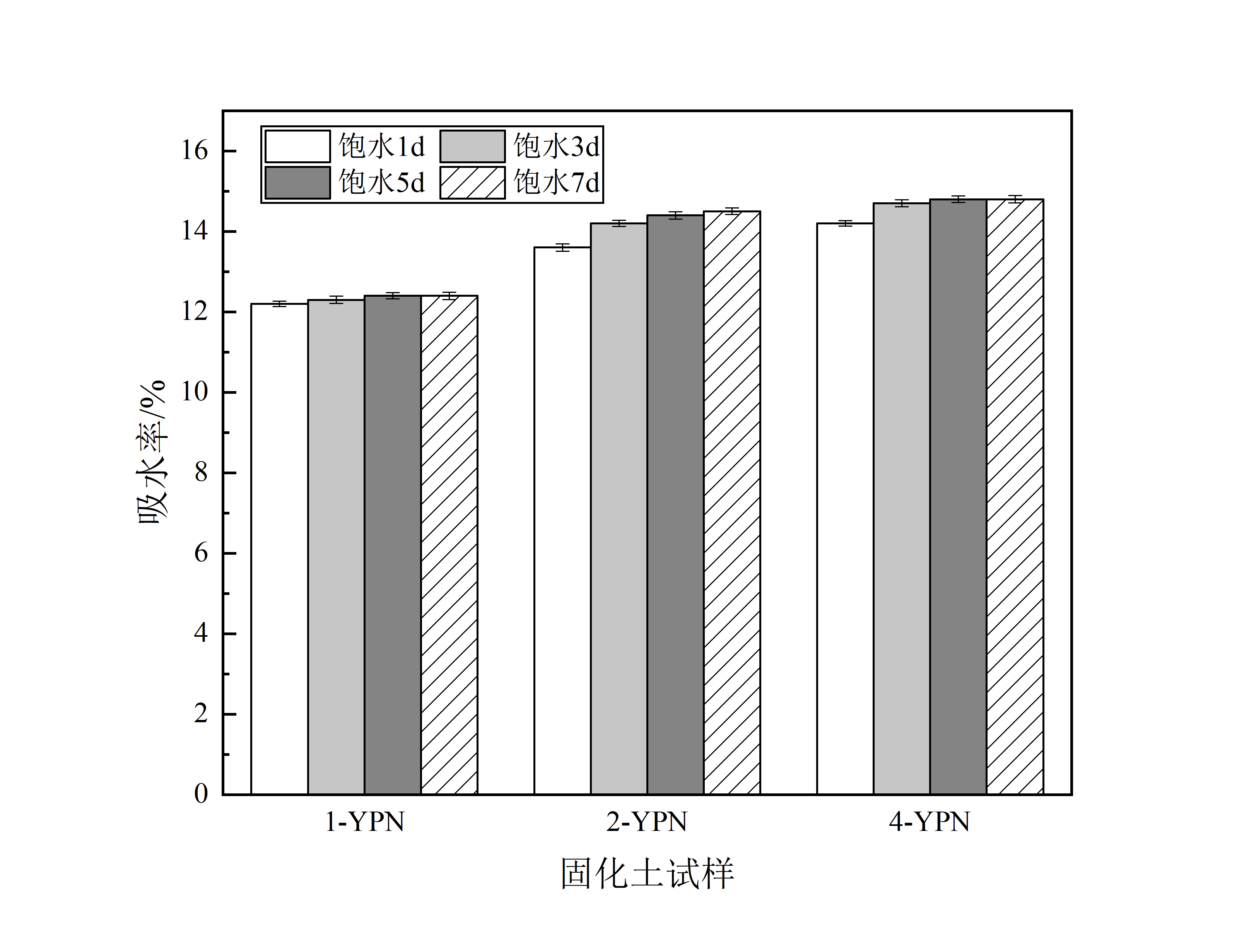
在掺量为20%的磷石膏-镍渣基胶凝材料固化土中,高镁镍渣镍渣与磷石膏掺量配比为3/2时,可以使固化土试样有最优的无侧限抗压强度性能。在养护7d时,1-YPN固化土试样强度达到了1.4Mpa。随着养护时间增加,在养护至28d时其强度可以达到2.6Mpa。在路用性能方面,掺量为20%的磷石膏-镍渣基胶凝材料固化土在高镁镍渣镍渣与磷石膏掺量配比为3/2时,饱水1d、3d、5d、7d后的水稳定系数分别为: 0.84、0.82、0.81、0.79,,相较于其他配比之下的固化土试样,其水稳定性最好。在经过冻融循环5次之后4-YPN固化土无侧限强度损失率低至6.6%。在土壤改良方面,磷石膏-镍渣基胶凝材料改良盐渍土后,盐渍土pH值降低,电导率提高,理化性能得到改善。并且在种植试验中,通过比对经改良前后的南通盐渍土的青菜种植情况得知,经改良后,青菜成活率从13.3%提高到73.3%,平均株高从2.4cm提高到4.4cm。改良后成活率大大提高,长势良好。可见磷石膏-镍渣基胶凝材料作为改良材料大大改善了植物生产环境。
关键词:磷石膏 镍渣 固化 改良 盐渍土
ABSTRACT
At present, China's coastal areas are the gathering place of many engineering projects, while the soil layer in the coastal area contains a large amount of saline silt, its salt content and water content are relatively high, and it is prone to segregation, tumbling, salt rise and other diseases. If it is directly placed in the engineering soil, it will be extremely harmful. In China's industrial production, solid waste such as high-magnesium-nickel slag and phosphogypsum has already caused great threat to our living environment. The annual output of these solid waste is huge, but the utilization rate is very low, which has caused environmental protection. a lot of pressure. Combining the physical and chemical properties of phosphogypsum, nickel slag and saline soil in coastal area, this paper uses phosphogypsum-nickel slag-based cementing material to solidify and improve saline soil in coastal area, improve the mechanical properties and physical and chemical properties of saline soil. performance. At the same time, it solves the recycling treatment of phosphogypsum and nickel slag and reduces the environmental burden.
In this paper, industrial solid waste such as high-magnesium nickel slag and phosphogypsum is used as the main cementing material[1]. For the treatment of saline soil, the salted sludge is treated by solidification and improvement. In order to obtain the optimum ratio of the phospho-gypsum-nickel slag-based composite cementitious material, the unconfined compressive strength of the slurry under various blending ratios was evaluated, and in addition, the phosphogypsum-nickel slag-based gelation was evaluated. The road performance of the material solidified saline soil, and the physicochemical properties of the phosphogypsum-nickel slag-based cementitious material after the improvement of the saline soil, and the mechanism of the solidification mechanism was analyzed. Finally, the phosphogypsum-nickel slag based rubber was verified by field test. The feasibility of curing the cement material to improve the saline soil.
In the 20% phosphoric gypsum-nickel slag-based cementitious material solidified soil, when the ratio of high magnesium nickel slag nickel slag to phosphogypsum is 3/2, the solidified soil sample can be optimally free. Confined compressive strength properties. At 7 days of curing, the strength of the 1-YPN solidified soil sample reached[2] 1.4 MPa. As the curing time increases, the strength can reach[3] 2.6Mpa when it is cured to 28d.In terms of road performance, the phosphorus-gypsum-nickel slag-based cementitious material solidified soil with a content of 20% is saturated with water for 1d, 3d, 5d when the ratio of high-magnesium nickel slag nickel slag to phosphogypsum is 3/2. The water stability coefficients after 7d are: 0.84, 0.82, 0.81, 0.79, which is the best water stability compared with the solidified soil samples under other ratios. The unconfined strength loss rate of the solidified soil after the freeze-thaw cycle was 5 times as low as 6.6%.In terms of soil improvement, after the phosphogypsum-nickel slag-based cementitious material improves the saline soil, the pH value of the saline soil decreases, the electrical conductivity increases, and the physical and chemical properties are improved. And in the planting test, by comparing the south before and after the improvement.[4]The cultivation of green vegetables in saline soil showed that after improvement, the survival rate of green vegetables increased from 13.3% to 73.3%, and the average plant height increased from 2.4cm to 4.4cm. After the improvement, the survival rate is greatly improved and the growth is good[5]. It can be seen that the phosphogypsum-nickel slag-based cementitious material as a modified material greatly improves the plant production environment.
Key words: phosphogypsum, nickel slag, solidification, improved saline soil
目录
摘 要 I
ABSTRACT III
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 引言 1
1.2 盐渍土的固化及改良难点 2
1.3 镍渣的研究现状 3
1.4 磷石膏的研究现状 4
1.5本论文研究方案与内容 5
第二章 试验原料及试验方法 7
2.1实验原料 7
2.1.1 盐渍土 7
2.1.2镍渣 7
2.1.3 活性材料AK 7
2.2 实验设备 8
2.3试验方法 9
2.3.1 胶凝材料的制备与养护 9
2.3.2 盐渍土标准试样的制备和养护 9
2.3.3 无侧限抗压强度性能的测定 10
2.3.4磷石膏-镍渣基胶凝材料固化土水稳性试验 10
2.3.5磷石膏-镍渣基胶凝材料固化体冻融循环试验 11
2.3.6改良土壤的pH及电导率测定 11
2.3.7土壤改良后种植性能试验 11
2.3.8 微观表征 11
第三章 实验结果与讨论 12
3.1磷石膏-镍渣基胶凝材料试验 12
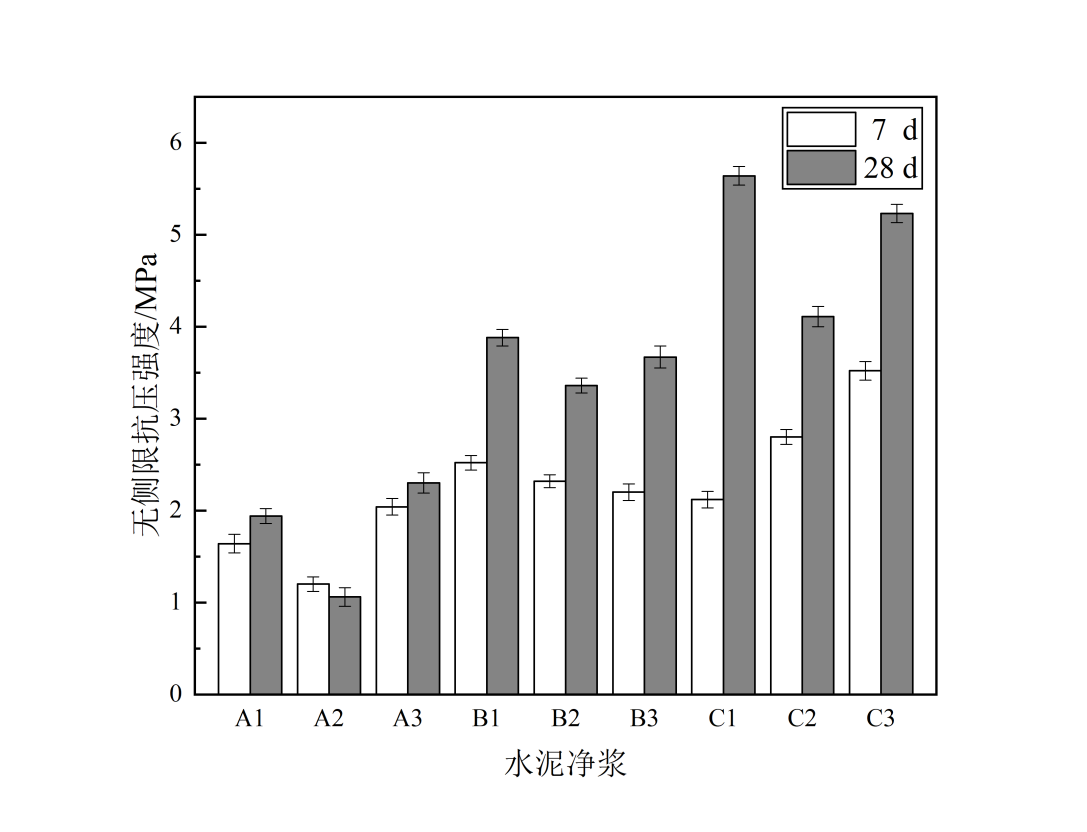
3.1.1磷石膏-镍渣基胶凝材料净浆性能测定 12
3.1.2探究不同镍渣掺量对磷石膏-镍渣基固化土性能的影响 12
3.1.3探究不同磷石膏掺量磷石膏-镍渣基固化土性能的影响 14
3.2磷石膏-镍渣基胶凝材料固化土的路用性能评价 15
3.2.1磷石膏-镍渣基胶凝材料固化土水稳定性试验 15
3.2.2磷石膏-镍渣基固化土的冻融循环 17
3.3 微观分析 18
3.4 磷石膏-镍渣基胶凝材料的改良性能测试 19
3.4.1土壤改良后的电导率及pH 19
3.4.2土壤改良后的种植试验 21
第四章 结论 23
参考文献 25
致 谢 28
第一章 绪论
1.1 引言
盐渍土是盐土和碱土以及各种盐化、碱化土壤的总称。主要分布在我国滨海地区以及内陆干旱地区。目前国内很多经济发展项目都聚集在滨海地区,然而滨海地区的地下土层大部分土层为盐渍土,其工程性能较差。盐渍土的弊端是其含盐率及含水率都比较高,并且容易发生溶陷,翻滚,盐胀等病害。如若直接用于工程土使用会有极大的危险,因此,我们对盐渍土进行固化与改良,提高其强度及其他工程性能,则对于滨海地区的工程则是一个良好的改进。
国际上很多研究过对盐渍土进行固化改良的学者都完成过提高盐渍土的工程性能[6-8]。并有大量的文献表明以加入水泥为固化剂的盐渍土在早期强度都表现得比较良好。但是在后期因为盐渍土中的盐分含量较高,盐分会侵蚀加入的水泥固化剂,使水泥对盐渍土的固化效果大大降低[9],从而导致固化土的耐久性下降。另外,还要考虑到水泥的成本问题对于土壤固化的经济效益影响。因此,目前仍需一种新型的固化材料来解决上述性能问题。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示:



课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



