内部硫酸盐侵蚀对水泥基材料性能的影响毕业论文
2020-04-18 20:00:45
摘 要
硫酸盐侵蚀的研究是一个悠久的课题,已经有了近百年的历史。目前在理论方面对其机理解释已十分完整。一般认为,发生硫酸盐侵蚀最重要的一个原因便是钙矾石等物质的产生,导致混凝土内部出现体积增大的现象,从而发生破坏。到目前为止,对于石膏的引入导致的内部硫酸盐侵蚀的研究不尽如人意。由于石膏的硫酸根离子位于混凝土内部,因此,重点对于外部引入硫酸根离子的理论体系并不适用,而其自身的评估体系还不完善。
本文通过净浆和砂浆试件膨胀率、抗压强度和抗折强度的表征,采用XRD、SEM等微观结构分析手段,研究了不同石膏掺量、养护温度、石膏粒径三个因素,对内部硫酸盐侵蚀下水泥基材料性能变化进行了分析。得出如下结论:
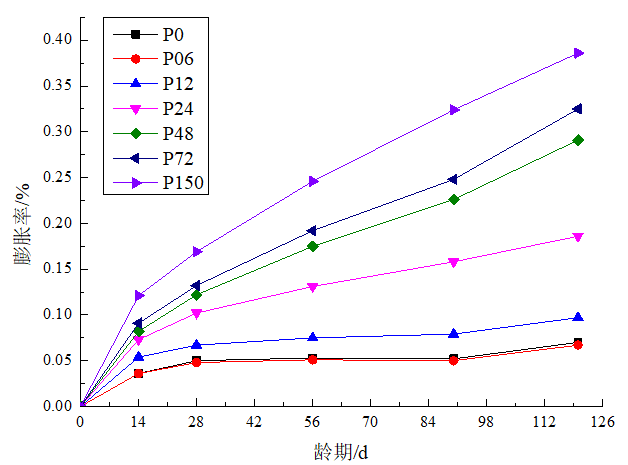
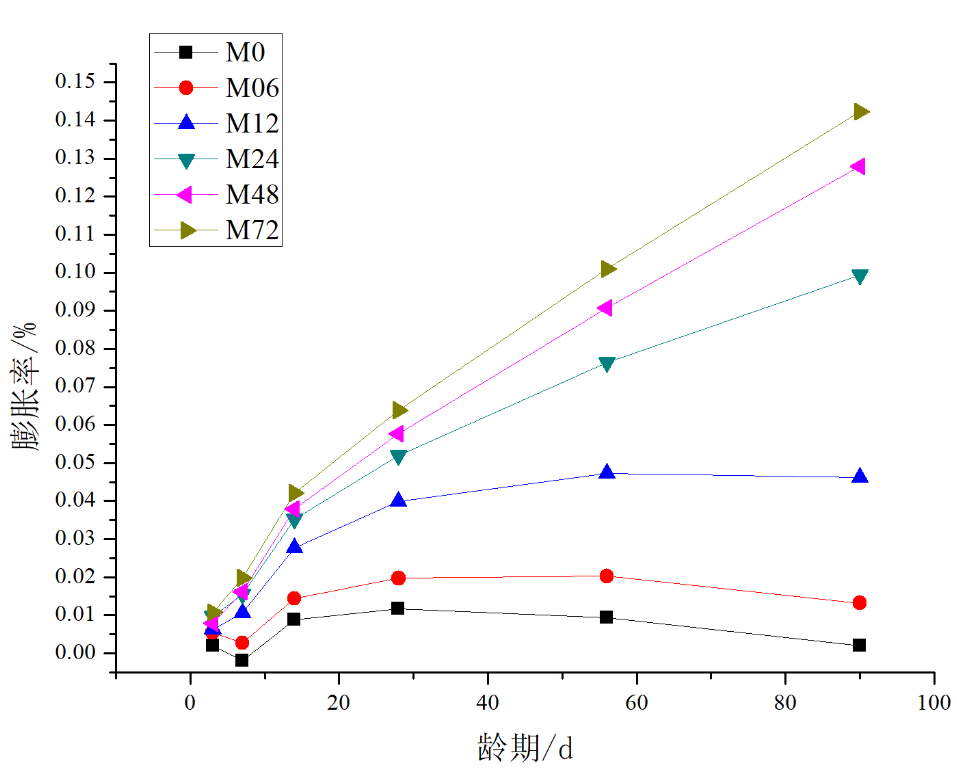
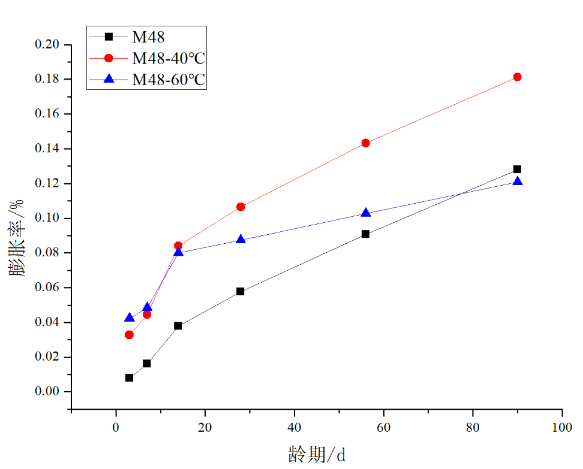
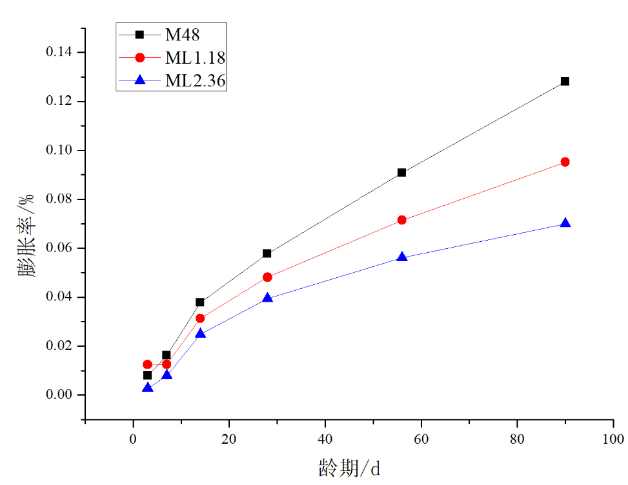
(1)净浆和砂浆试件的膨胀率可以看出,其石膏含量越多,膨胀率越大,说明其内部硫酸盐侵蚀的程度越高。
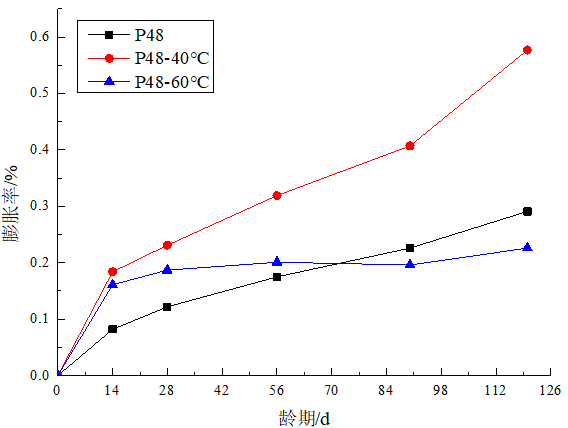
(2)养护温度达到60℃时,净浆和砂浆膨胀率都不如40℃,原因是,在60℃环境下钙矾石的稳定性较差,侵蚀产物的生成较为困难。
(3)从强度来看,强度和石膏掺量是反比关系,石膏掺量越高,试件强度越低,并且养护温度越高,强度越大。
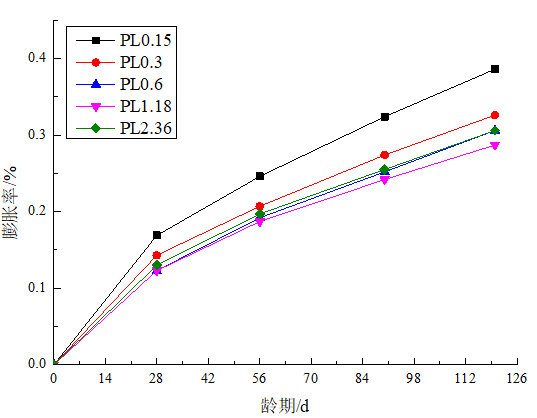
(4)随着石膏粒径的增大,试件的膨胀率逐渐降低。
关键词:内部硫酸盐 侵蚀 钙矾石 石膏
ABSTRACT
At present, the mechanism is very complete in theory. It is generally believed that the main cause of sulfate attack is that sulfate produces erosive products such as ettringite in concrete, resulting in expansion cracking. So far, research on internal sulfate attack caused by the introduction of gypsum has not been satisfactory. Since the sulfate ion of gypsum is located inside the concrete, the emphasis is not applicable to the theoretical system of external introduction of sulfate ion, and its own evaluation system is not perfect.
In this paper, through the characterization of the expansion rate and mortar specimens, the three factors of different gypsum content, curing temperature and gypsum particle size were studied by XRD, SEM and other microstructural analysis methods. The performance changes of cement-based materials under sulfate attack were analyzed. The following conclusions are drawn:
(1) The expansion ratio of the pulp and mortar specimens can be seen that the more the gypsum content, the greater the expansion ratio, indicating the higher the degree of internal sulfate attack.
(2) When the curing temperature reaches 60 °C, the expansion ratio of the paste and mortar is not as good as 40 °C. The reason is that the stability of ettringite is poor in the environment of 60 °C, and the formation of erosion products is difficult.
(3) In terms of strength, the strength and gypsum content are inversely proportional. The higher the gypsum content, the lower the strength of the test piece, and the higher the curing temperature, the greater the strength.
(4) As the particle size of the gypsum increases, the expansion ratio of the test piece gradually decreases.
Key Words: internal sulfate attack; ettringite; gypsum
目录
摘要
ABSTRACT I
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景 1
1.2 机理 2
1.2.1 化学侵蚀 2
1.2.2 物理侵蚀 3
1.3 影响内部侵蚀的要素 3
1.3.1 矿物掺合料和胶凝材料的影响 3
1.3.2抗渗性 3
1.4研究现状 4
1.5 评价方法和评价指标 4
1.6 研究内容 5
第二章 原材料及实验方法 6
2.1 原材料 6
2.1.1 硅酸盐水泥 6
2.1.2 石膏 6
2.2 试件制备方法 7
2.2.1净浆 7
2.2.2 砂浆 7
2.2.3 养护条件 8
2.3 试验方法 8
2.3.1 变形性能 8
2.3.2 强度 9
2.3.3 矿物相组成 10
2.4 实验仪器 10
第三章 内部硫酸盐侵蚀过程 11
3.1 膨胀率 11
3.2 强度 13
3.2.1 抗压强度 13
3.2.2 抗折强度 15
3.3 微观结构 16
第四章 结论和展望 20
4.1 结论 20
4.2 展望和不足 20
参考文献 21
致谢 23
第一章 绪论
1.1 研究背景
虽然诞生了千年之久,但目前人们用的最多的施工材料还是水泥,这一点毋庸置疑,每年的水泥使用量都创新高。然而,使用水泥的时候,有一个很严重的问题,那就是硫酸盐侵蚀。近年来,许多工程并没有达到预期的使用寿命,便出现了大量提前损坏的现象,人们一开始归咎于施工单位的懈怠和贪腐,然而,最新的研究发现这种损坏与人为因素关系不大,更多的是由于硫酸盐侵蚀造成的。水泥受到破坏、使用寿命缩短的一个重要缘故就是硫酸盐侵蚀[1]。混凝土与含硫酸基离子丰富的土壤、地下水或海水等媒介长期接触,使得硫酸基离子和混凝土中的水化物发生化学反应[2]。而产生的这些反应造成了水泥混凝土体积的增加,致使其破坏。
按硫酸盐来源可分为外部硫酸盐侵蚀和内部硫酸盐侵蚀,一般来说,硫酸盐侵蚀指的是,混凝土的空隙被外界环境中的硫酸盐填充,与某些成分反应而导致的膨胀从而产生破环[3]。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示:

课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



