基于多孔掺氮碳球的无酶传感器的构建研究毕业论文
2020-04-20 13:12:55
摘 要
抗坏血酸(AA)是一种抗氧化剂,尿酸(UA)是嘌呤代谢产物,多巴胺(DA)是神经递质,它们共存于中枢神经系统和血清中,在人体代谢过程中发挥关键作用,因此,选择一种高灵敏度并且能同时检测AA、UA、DA的方法对医学临床、生物活动方面具有重要意义。电化学传感器具有高的选择性,且操作简便、成本低,因而广泛应用于生物样品中活性物质的检测。
本实验基于介孔碳球的优异性能,首先,合成一种多孔掺氮碳球材料,并用SEM等检测方法对此材料进行表征。其次,基于该材料,构建了一种简易的无酶电化学传感器,并采用循环伏安法(CV)和差分脉冲伏安法(DPV)研究了所构建传感器的电化学性能。最后,将构建的无酶电化学传感器(NPC/GCE)用于同时检测AA,DA,UA。结果表明,该传感器(NPC/GCE)能够实现对AA,DA,UA的同时检测且不发生相互干扰,检测的这三种物质的线性范围分别为10~2000μM(AA)、1~70μM(DA)和 1~50μM(UA),检测限分别为20μM(AA)、1μM(DA)、1μM(UA) (S/N=3)。该实验为同时、准确、快速的检测实际样品中的AA,DA,UA提供了新的检测方法。

Construction of enzyme-free sensor based on porous nitrogen-doped carbon sphere
ABSTRACT
Ascorbic acid (AA) is an antioxidant, uric acid (UA) is a metabolite of sputum, and dopamine (DA) is a neurotransmitter. They coexist in the central nervous system and serum, and play a vital role in human metabolism. Therefore, choose a method with high sensitivity and simultaneous detection of AA, UA, DA is of great significance for medical clinical and biological activities. Electrochemical sensors are highly selective, easy to operate, and low in cost, and are therefore widely used for the detection of active substances in biological samples.
In this experiment, based on the excellent properties of mesoporous carbon spheres, firstly, a porous nitrogen-doped carbon sphere material was synthesized and characterized by SEM and other methods. Secondly, the enzyme-free electrochemical sensor was constructed with this material as the carrier, and the electrochemical performance of the constructed sensor was studied by means of cyclic voltammetry (CV) and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). Finally, the enzyme-free electrochemical sensor was constructed for simultaneous detection of AA,DA and UA. The results show that the sensor (NPC/GCE) can achieve simultaneous detection of AA, DA, UA without mutual interference. The linear range of the three substances is 10~2000μm (AA), 1~70μm (DA) and 1~50μm (UA), respectively. The detection limits were 20μM (AA), 1μM (DA), 1μM (UA) (S /N=3). This experiment provided an efficient and rapid detection method for co-existing AA,DA and UA in actual samples.
Key Words: porous carbon material; nitrogen doping; electrochemical sensor; ascorbic acid; dopamine; uric acid
目录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 文献综述 1
1.1 研究背景 1
1.2 多孔碳材料概述 2
1.3 多孔碳材料的制备 2
1.3.1 模板法 2
1.3.2 直接碳化法 3
1.3.3 活化法 3
1.4多孔碳材料的功能化 4
1.4.1 氮掺杂 4
1.4.2 硼掺杂 5
1.4.3 磷掺杂 5
1.4.4 硫掺杂 6
1.5 多孔碳材料的应用 6
1.5.1 能源材料 6
1.5.2 催化材料 7
1.5.3 吸附材料 7
1.6 研究意义 7
第二章 碳花材料的合成 9
2.1 引言 9
2.2 实验材料 9
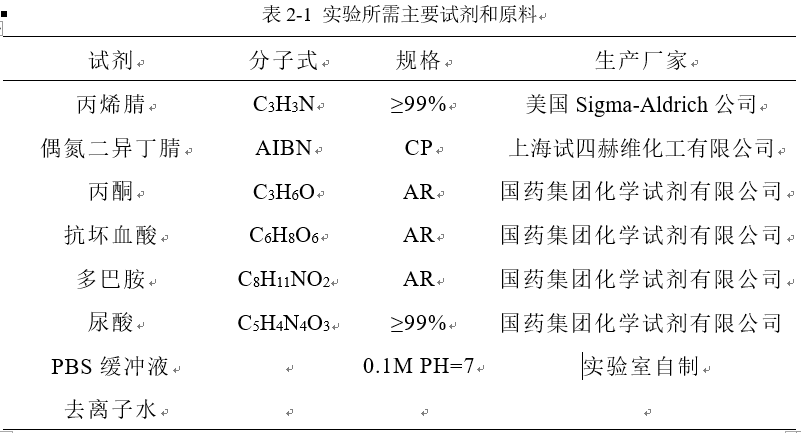
2.2.1 实验试剂 9
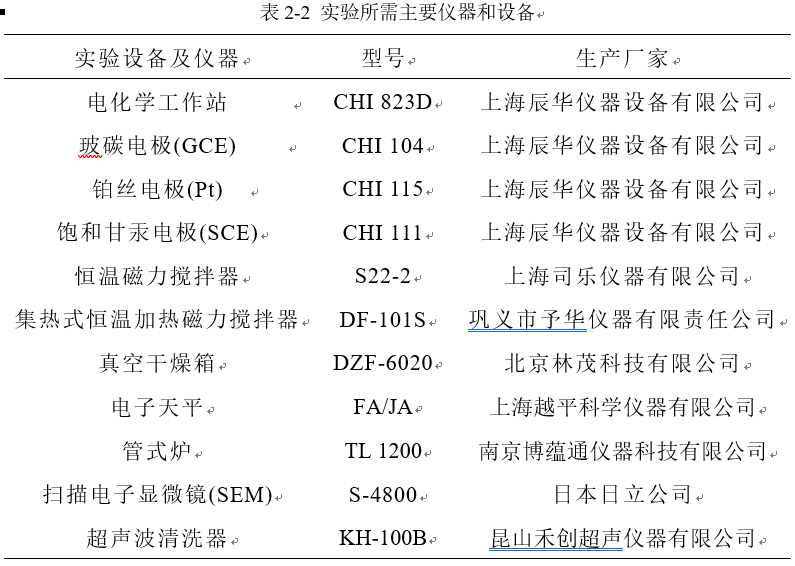
2.2.2 实验设备及仪器 10
2.3 碳花材料(PACN-F-900C)合成实验步骤 10
2.3.1 PACN花状结构(PACN-F)合成过程 10
2.3.2 碳上层结构(PACN-F-900C)合成过程 11
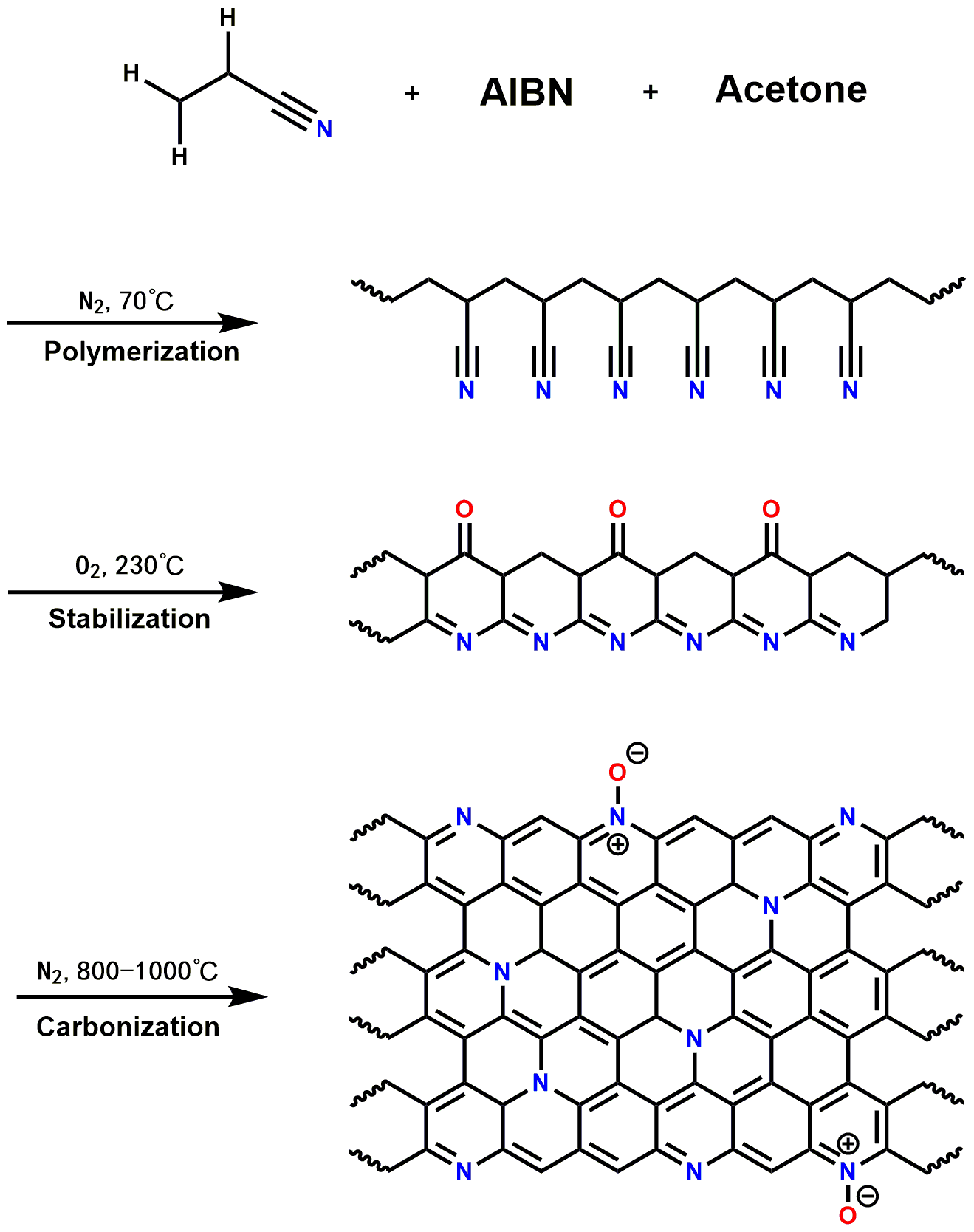
2.4 实验合成路线 11
2.5 结果与讨论 12
2.5.1 现象 12
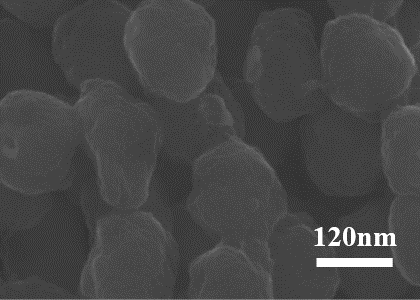
2.5.2 SEM表征 12
2.5.3 结果与讨论 13
2.6 本章小结 13
第三章 构建的多孔掺氮碳球材料电化学传感器(NPC/GCE)对AA,DA,UA的检测研究 15
3.1 引言 15
3.2 实验部分 16
3.2.1 材料的选择 16
3.2.2 电化学传感器的构建 16
3.3 结果与讨论 17
3.3.1 电催化氧化 17
3.3.2 NPC/GCE检测 AA、DA、UA 的选择性 17
3.4 本章小结 19
第四章 结论及展望 20
4.1 结论 20
4.2 展望 20
参考文献 22
致谢 28
第一章 文献综述
1.1 研究背景
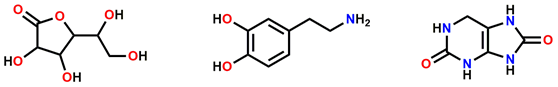
抗坏血酸(AA)是人体必需的营养物质,它既可作为抗氧化剂,也可用于治疗癌症、普通感冒、精神疾病和艾滋病[1][2]。多巴胺(DA)是一种重要的神经递质,广泛分布于哺乳动物中枢神经系统(脑、肾、激素、心血管系统等)中[3],DA水平异常可能导致许多疾病,如帕金森病、精神分裂症等[4][5]。此外,尿酸(UA)主要是嘌呤代谢产物的最终产物,其浓度异常在人体内可表现为高尿酸血症、白血病、肺炎等多种疾病症状[6]。许多研究表明尿酸(UA)的抗氧化能力比较强,且具有神经保护作用。痛风、高尿酸血症或乐氏-尼汉综合征、关节炎、糖尿病、高胆固醇、肾脏、神经系统、心血管、肾脏疾病等多种疾病可通过测量尿酸异常水平来诊断。因此,检测人体生理体液中的抗坏血酸(AA)、多巴胺(DA)、尿酸(UA)水平是预防、诊断疾病的关键[7]。此外,众所周知的是,抗坏血酸(AA)、多巴胺(DA)和尿酸(UA)共存于中枢神经系统和血清中[8]。但是由于裸电极的氧化峰电位重叠,表面积不足,同时进行测定的选择性和灵敏度不高,因此许多研究也集中在分离它们的峰值电位,特别是碳基纳米材料已广泛应用于同时检测抗坏血酸(AA)、多巴胺(DA)、尿酸(UA)[9][10][11]。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示:


课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



