乳液模板法制备多孔地聚物材料及性能研究毕业论文
2020-04-20 13:14:20
摘 要
地质聚合物是硅铝化合物在碱性环境下被激发经解聚—缩聚反应形成的一种具有三维网状结构的胶凝材料。由于其三维网状结构,地质聚合物在吸附重金属离子领域表现了优良的性能,成为了这几年来金属吸附领域的研究热点。
在地质聚合物中,孔隙率和孔结构对地质聚合物的性能产生了很大的影响。本文以油作模板剂制备地质聚合物入手,研究模板剂种类和用量、表面活性剂种类等因素对多孔地聚物孔隙率、孔结构特征的影响,主要探究了以下内容:
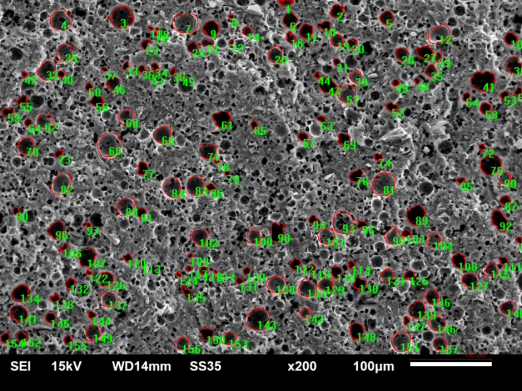
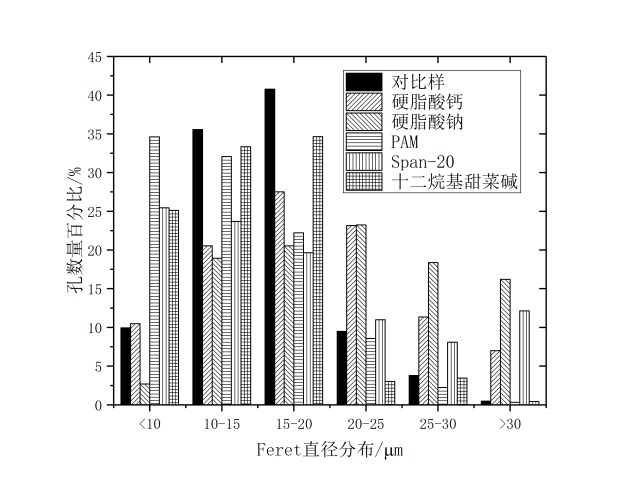
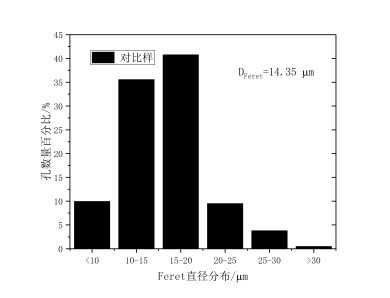
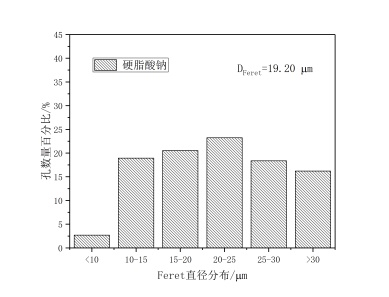
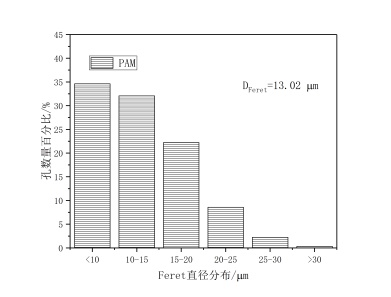
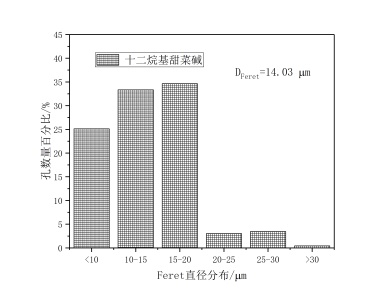
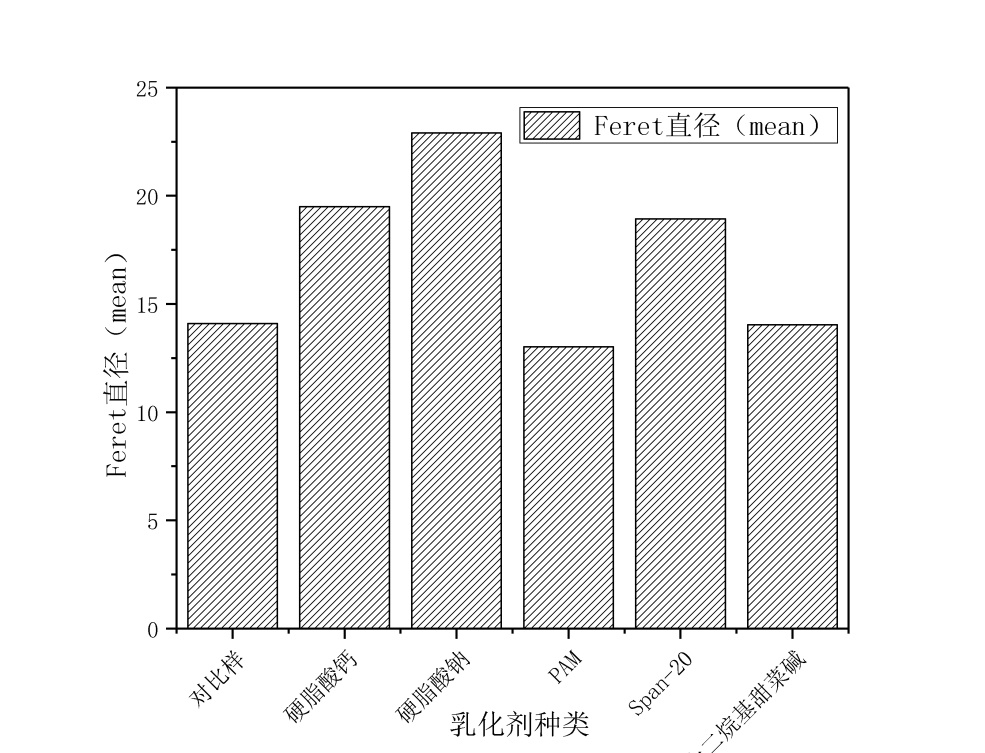
(1)以橄榄油和玉米油作模板剂,PAM、Span-20、硬脂酸钙、硬脂酸钠、十二烷基甜菜碱作乳化剂分别制备地质聚合物,观察孔分布情况,利用IPP软件得出Feret直径的分布,发现硬脂酸钙和硬脂酸钠作乳化剂制得的地质聚合物孔径分布呈正态分布,且平均Feret直径也较大。
(2)对比橄榄油和玉米油作模板剂,硬脂酸钙和硬脂酸钠作乳化剂制得的地质聚合物的孔径分布情况,发现通过玉米油制得的地聚物大孔径占比较多,平均Feret直径也更大。
关键词:多孔地聚物 模板剂 乳化剂 孔径分布
Preparation and properties of porous Geopolymer Materials by emulsion template method
Abstract
Geopolymer is a kind of cementitious material with three-dimensional network structure, which is stimulated by depolymerization-condensation reaction of silica-aluminium compounds in alkaline environment. Because of its three-dimensional network structure, geopolymer has shown excellent performance in the field of heavy metal ions adsorption. Compared with traditional adsorption materials, the adsorption process is green and pollution-free, which has become a research hotspot in the field of metal adsorption in recent years.
Porosity and pore structure have a great influence on the properties of geopolymer. Starting with the preparation of geopolymer with oil as foaming agent, this paper studies the effects of template type and dosage, surfactant type and other factors on the porosity and pore structure characteristics of porous geopolymer, and mainly explores the following contents:
(1) Geopolymers were prepared with olive oil and corn oil as templates, PAM, Span-20, calcium stearate, sodium stearate and dodecyl betaine as emulsifiers respectively. Pore distribution was observed. The distribution of Feret diameter was obtained by IPP software. It was found that the pore size distribution of Geopolymers prepared with calcium stearate and sodium stearate as emulsifiers was normal distribution, and the average Feret diameter was also higher. Big.
(2) Compared with olive oil and corn oil as templates, calcium stearate and sodium stearate as emulsifiers, the pore size distribution of geopolymer prepared by corn oil is larger, and the average Feret diameter is larger.
Key words: porous geopolymer template emulsifier pore size distribution
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景 1
1.2 研究现状 1
1.3 研究意义 1
第二章 地质聚合物概述 3
2.1 地质聚合物定义 3
2.2 地质聚合物的分类 3
2.3 地质聚合物的反应机理 3
2.3.1高钙体系的碱激发机理 3
2.3.2 低钙体系的碱激发机理 4
2.4 多孔地聚物 4
2.4.1 物理发泡法 4
2.4.2化学发泡法 5
2.4.3模板法 7
2.4.4 利用动植物性蛋白为添加剂 8
2.5 地质聚合物的特点 8
2.6 地质聚合物的应用 9
2.6.1 用于建筑和快速修补 10
2.6.2 用于NaA型分子筛合成 10
2.6.3 用作轻质、防火和耐高温材料 10
2.6.4 用作混凝土路面材料 10
2.6.5 用作灌浆料 10
2.6.6 用作工业有毒废渣和核废料固封材料 11
第三章 原材料与测试方法 12
3.1 实验原料 12
3.1.1 偏高岭土 12
3.1.2 模板剂 12
3.1.3 水玻璃 12
3.1.4 乳化剂 13
3.2 实验仪器 14
3.3 实验步骤 14
3.4表征方法 15
第四章 结果与讨论 17
4.1 乳化剂种类对多孔地聚物孔结构参数的影响 17
4.2 模板剂种类对多孔地聚物孔结构参数的影响 21
第五章 结论与展望 24
5.1 结论 24
5.2 展望 24
参考文献 25
致谢 28
第一章 绪论
1.1 研究背景
如今,我国在大力发展重工业的同时,产生了严重的重金属污染,冶金、采矿、机械制造等行业产生的金属废水越来越多,其中含有的重金属离子对人的生活、身体健康等产生了极大的危害,加上其难以处理性,已经成为人们的关注重点。地质聚合物是一种具有三维网络结构的胶凝材料,能够很好的吸附金属离子,同时又因其价格低廉,稳定性好,良好的抗压抗折强度,耐火耐高温,耐温耐腐蚀、使用寿命长被广泛应用于防火、建筑、保温、核废料固封等领域,成为新型建材和金属固化领域的研究热点。
1.2 研究现状
地质聚合物在过去几十年中经历了一个飞速发展过程,1972 年法国的Joseph Davidovits[1]教授成功对高岭土进行碱激活,申请了地聚物制备建筑的专利。之后继续研究地质聚合物的内部结构,在后来的一段时间里申请了大量专利。1978年Joseph Davidovits第一个提出并确认使用Geopolymer (地质聚合物) 这个词[1]。同时美国壳牌石油公司对Davidovits研发的地聚物很感兴趣,之后几年开始与Davidovits合作,并共同研发出PARAMENT复合水泥。
1980年开始,地质聚合物方面取得了较大的研究成果。Barbosa V F. F.等[1]通过碱激发MK并置于环境温度为65 ℃的环境下干燥1h成功制备出抗压强度高的多孔地聚物。1990年之后,Van J aarsveld等[2-3]专注于工业固废制备地质聚合物,包括固化有毒金属及化合物等。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示:
课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



