混凝土侵蚀抑制剂性能评价及作用机制毕业论文
2020-04-20 13:52:37
摘 要
混凝土材料是当今建筑工程的主要材料,因此混凝土的腐蚀问题引起了大家广泛的关注,混凝土在使用期间,造成耐久性差,大量工程过早劣化以致退役,实际上,混凝土遭到破环的主要原因是由于侵蚀性介质通过各种传输通道(孔、界面和裂纹等)进行入到混凝土内部生产腐蚀产物造成结构破坏,在海洋干湿交变区氯离子的侵蚀尤为严重,因此,研究氯离子在混凝土中的传输规律有极其重要的意义。
通过对比掺入侵蚀抑制剂前后混凝土内部氯离子传输的深度以及其浓度,评价侵蚀抑制剂在混凝土结构中的作用机理以及作用效果。针对氯盐环境下钢筋腐蚀的特点,制备适用于氯盐环境条件下的侵蚀抑制剂材料,模拟干湿交替环境下混凝土结构的氯离子侵蚀,构建了氯离子的一维扩散传输模型,用3.5%的NaCl溶液浸泡混凝土,通过控制水位让混凝土试块长期处于全浸泡和半浸泡条件下,研究C35、C50两种强度等级混凝土在掺入侵蚀抑制剂后各项性能指标的变化以及氯离子的传输机理,分别测试不同龄期在半浸泡和全浸泡条件下氯离子传输深度以及相应深度氯离子浓度。实验表明:在掺入侵蚀抑制后,混凝土的各项性能指标均有小幅度的波动,但都在正常范围内,且完全不影响混凝土的正常使用;测试不同龄期(10d、20d)氯离子在混凝土中传输的深度以及氯离子的含量,实验数据显示:在加入侵蚀抑制剂后能明显降低氯离子的含量其传入深度,而这种作用效果对半浸泡的混凝土更加明显,通过实验直观的展现了侵蚀抑制剂的作用效果。
关键词:耐久性,氯离子侵蚀,抑制剂,干湿交变。
Evaluation of concrete erosion inhibitors and study of their action mechanism
ABSTRACT
Concrete material is current the main material of construction projects, so the corrosion problem of concrete has attracted widely attention, during the life of the concrete, causing poor durability, a large number of engineering premature deterioration that retired, in fact, is the main reason of the concrete were broken due to the corrosive media through a variety of transport channel (hole, interface and crack, etc.) into the concrete internal structure damage caused by corrosion products, the production area in ocean alternating wet and dry seasons of chloride ion erosion is particularly serious, therefore, the research on the rules of transport of chloride ions in concrete has extremely vital significance.
By comparing the depth and concentration of chloride ion transfer in concrete before and after adding corrosion inhibitor, the mechanism and effect of corrosion inhibitor on concrete structure were evaluated.According to the characteristics of the steel corrosion of chlorine salt environment, chlorine preparation is suitable for the conditions of corrosion inhibitor materials, simulation of concrete structure under dry-wet alternate environment of chloride ion erosion, building a transmission model of one dimensional diffusion of chloride ions, soaking in 3.5% NaCl solution, concrete by controlling the water level to concrete test piece in full immersion and long-term half soaking conditions, two research C35 and C50 concrete strength grade after adding corrosion inhibitor changes in various performance indicators and the transmission mechanism of chloride ions,The chloride ion transfer depth and chloride ion concentration at corresponding depths were measured at different ages under semi-immersion and full-immersion conditions.The results show that the performance indexes of concrete have a small range of fluctuation after erosion inhibition, but all of them are in the normal range, and do not affect the normal use of concrete at all.Test different age (10, 20 d d) the depth of the transmission of chloride ions in concrete as well as the content of chloride ion, the experimental data showed that after adding corrosion inhibitors can significantly reduce the chloride ion content in the incoming depth, and the effect of half-and-half of concrete more apparent, intuitive by experiments show the effect of corrosion inhibitors.
Keywords: durability, chloride ion erosion, inhibitor, dry-wet alternation.
目录
摘 要 I
ABSTRACT II
目录 IV
第一章 前 言 1
1.1研究背景与意义 1
1.2国内外研究现状 2
1.2.1 氯离子引起钢筋锈蚀机理 2
1.2.2 氯离子传输理论的研究 3
1.2.3 混凝土微观结构对离子传输的影响 4
1.3主要存在的问题 4
1.4本文研究目标及内容 4
第二章 原材料及实验方法 6
2.1原材料 6
2.2配合比设计 7
2.3主要实验仪器 7
2.4实验方法 9
2.4.1 混凝土拌合物性能的测试方法 9
2.4.2 混凝土抗压强度的测定 9
2.4.3 混凝土氯离子渗透系数 9
2.4.4 混凝土收缩率的测定 10
2.4.5 粉体中氯离子含量测试方法 10
2.4.6 水化产物XRD测试方法 11
2.4.7 水化产物XRF测试方法 12
2.4.8 水化产物烧失量测试方法 12
第三章 混凝土侵蚀抑制剂性能评价 13
3.1混凝土侵蚀抑制剂自身性能测试 13
3.2混凝土拌合物性能 13
3.2.1 坍落度与含气量 13
3.2.2 凝结时间与泌水率 14
3.3力学性能与耐久性性能 15
3.3.1 抗压强度 15
3.3.2 氯离子渗透系数 16
3.4水化产物 16
3.4.1 XRF 16
3.4.2 烧失量结果 16
3.4.3 XRD 17
3.5小结 18
第四章 混凝土侵蚀抑制作用机制研究 20
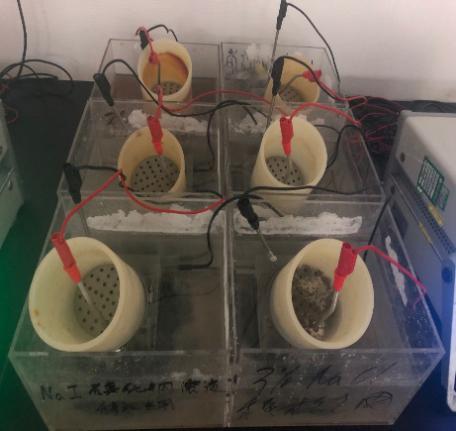
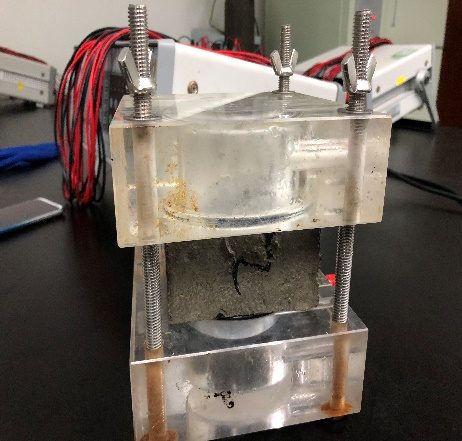
4.1混凝土全浸泡及干湿交变试验装置及试块处理过程 20
4.1.1 混凝土全浸泡及干湿交变试验装置 20
4.1.2 钢筋处理过程与混凝土成型 20
4.1.3 混凝土表面处理过程 21
4.2钢筋锈蚀指标 22
4.2.1 腐蚀电压与腐蚀电流密度 22
4.2.2 直观对比 22
4.3浸泡及半浸泡条件下氯离子传输过程研究 23
4.3.1 逐层磨粉过程 23
4.3.2 粉体酸溶过程 23
4.3.3 氯离子浓度测试 23
4.3.4 全浸泡条件下氯离子侵蚀过程 24
4.3.5 干湿循环条件下氯离子侵蚀过程 24
4.4小结 25
第五章 结论与展望 26
参考文献 27
第一章 前 言
1.1研究背景与意义
自改革开放以来,中国经济高速发展,其中大量建筑工程在祖国各地遍地开花,以水泥为胶凝材料的混凝土成为应用最普遍、最广泛的建筑材料[1]。而钢筋混凝土由混凝土包裹在钢筋的外部构成,结合了钢筋和混凝土共同的优点,使钢筋混凝土在拥有高强度抗压性能的同时具备长期稳定的抗拉性能;促使其广泛应用在国防工程、铁路工程、公路工程、坝体工程以及民用建设中[2]。由于钢筋表面覆盖了一层混凝土保护层使钢筋混凝土具有优良的耐久性能,但是在一些特殊的环境中(海洋、盐湖、盐渍土、冻融、撒除冰盐等环境),钢筋混凝土往往出现过早的失效,带来巨大的经济损失。
根据调查显示,我国沿海城市地区的海工混凝土结构在使用10至15年之后便会出现严重的侵蚀破坏,氯盐引起钢筋锈蚀是导致混凝土结构遭到破坏的主要原因。报道显示[3]每年腐蚀造成的经济损失占各国GDP总值的份额较大,美国约占GDP的4.9%,英国占GDP的3.5%,而波兰更占GDP的6-10%;在美国,仅仅1975年,就会造成700亿美元的损失,其中有40%左右是由于混凝土中钢筋的锈蚀引起,十年后,更是增加到1680亿美元[4];2018年,我国的GDP总量超过90万亿元,依照以上比例计算,我国因钢筋锈蚀问题而造成的经济损失约为1080亿元[5]。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示:




课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



