热处理对α β锻Ti-Al-Fe-B合金组织和力学性能的影响毕业论文
2020-04-21 17:06:12
摘 要
由于钛及钛合金具有良好的性能因而广泛应用高科技领域,但其较高的成本限制了其在其他领域的广泛应用。本文通过采用添加廉价的合金化元素来制备获得新型的Ti-Al-Fe-B低成本钛合金,本实验以Ti-3Al-2Fe-0.1B合金为研究对象,借助仪器及软件观察和分析不同热处理工艺对α β锻Ti-Al-Fe-B微观组织和力学性能的影响,通过实验得到了以下结论:
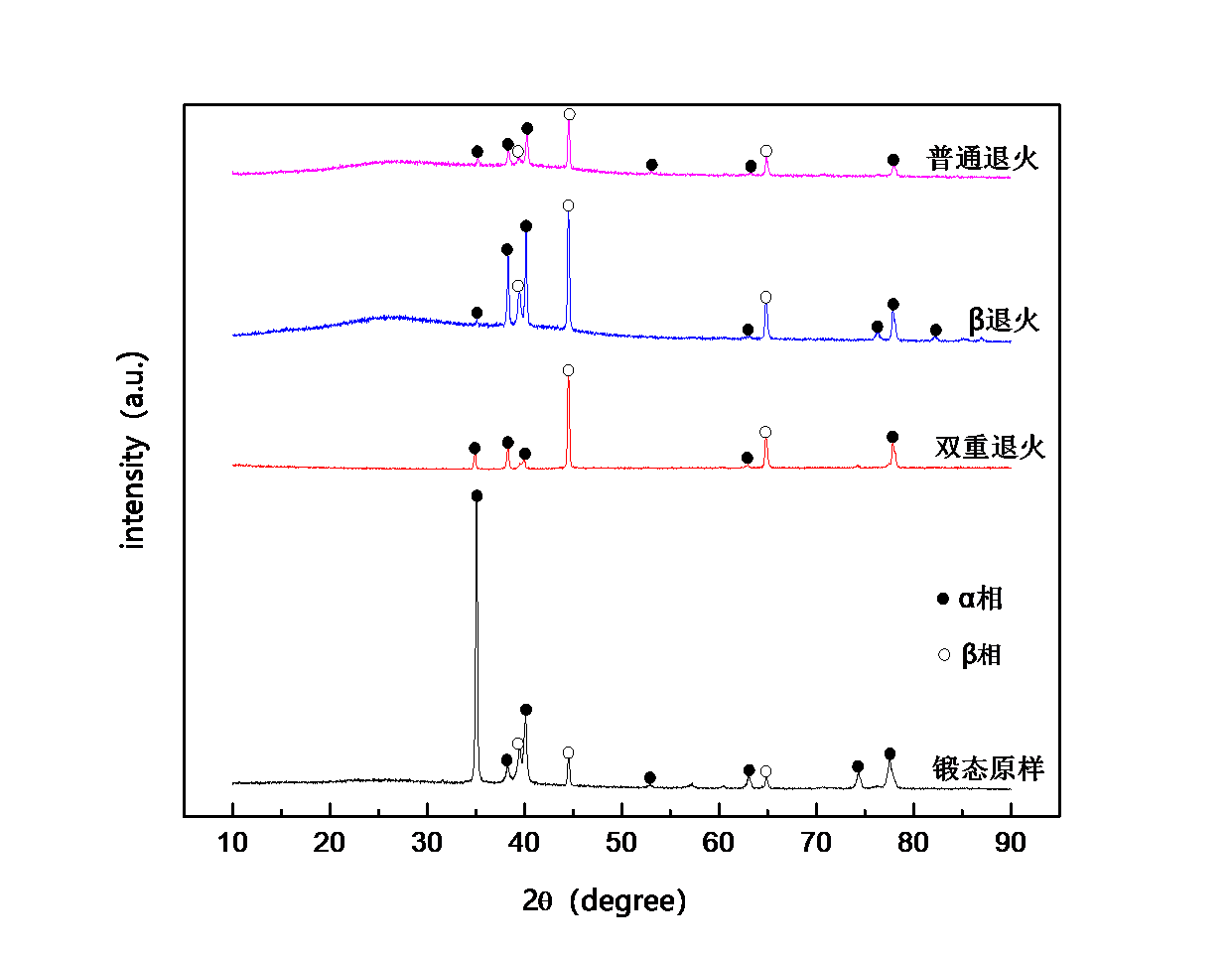
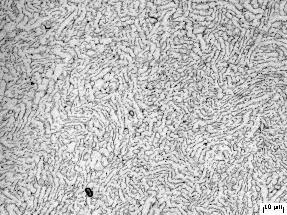
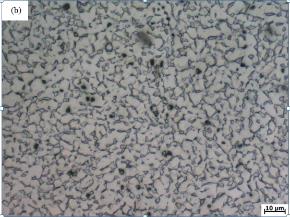
(1)锻态及热处理态Ti-3Al-2Fe-0.1B合金均由α相和β相组成,但两相含量不相同。锻态合金中初生α相呈现长条状,普通退火后Ti-3Al-2Fe-0.1B合金中部分长条状的初生α相等轴化,合金中α相由等轴α相和长条状的初生α相共同组成,双重退火之后合金由等轴α相和β相组成,可以明显观察到等轴状的α相占了50%以上,因而为等轴组织,β热处理后合金组织为魏氏体组织,由α集束、晶界α相和β相构成。
(2)锻态合金的强度在650MPa左右,强度属于中等级别,塑性良好,硬度在290HV左右。普通退火后合金强度在800MPa左右,塑性方面比锻态合金优异,合金的伸长率在20%左右。双重退火后合金组织为等轴组织,塑性较好,强度在790MPa左右,此时合金硬度有明显提高,与锻态合金相比提高了约44HV。β退火后的合金强度和塑性均大幅提高,此时强度达到810MPa,合金的伸长率达到24%。综合分析后发现,β退火后合金综合性能最优。
关键词:钛合金 热处理 微观组织 力学性能
Effect of Heat Treatment Process on Microstructure and
Mechanical Properties of α β Forged Ti-Al-Fe-B Alloy
Abstract
Due to its good performance, titanium and titanium alloys are used in aerospace and navigation far and wide, but their high cost limits their wide application in other fields. In this paper, a new kind of low-cost Ti-Al-Fe-B titanium alloy was made by adding inexpensive alloying elements. In this experiment, Ti-3Al-2Fe-0.1B alloy was used as the research object. The effects of different heat treatment processes on the microstructure and mechanical properties of α β forged Ti-Al-Fe-B alloy were observed and analyzed by instrument and software. The following conclusions were obtained through experiments:
(1)Both forged and heat-treated Ti-3Al-2Fe-0.1B alloys are composed of α phase and β phase, but the contents of them are different. The primary α phase in the forged alloy exhibits a long strip shape. After the ordinary annealing, some elongated strips of primary α in the Ti-3Al-2Fe-0.1B alloy are equiaxed. The α phase of the alloy consists of an equiaxed α phase and a long strip of primary α phase. After double annealing, the alloy consists of an equiaxed α phase and a β phase. It can be clearly observed that the equiaxed α phase accounts for more than 50%. Therefore, it is an equiaxed structure. The alloy structure after the β heat treatment named Weiss structure, which is composed of an α bundle, a grain boundary α phase, and a β phase.
(2)The strength of the forged alloy is about 650 MPa, which the strength of it is moderate in the same time with the good plasticity, and the hardness is about 290 HV. After normal wear, the strength of an alloy is about 800 MPa, and the plasticity is superior to the alloy of forged alloys. The elongation of the alloy is about 20%. After double annealing, the alloy structure is equiaxed, and the plasticity is good. The strength is about 790 MPa. At this time, the rigidity of the alloy was clearly improved, which is about 44 HV higher than the forged alloy. The strength and stiffness of the alloys after the steel has been greatly improved. At this time, the power reached 810 MPa, and alloy elongation reached 24%. After comprehensive analysis, it was found that alloys have the best overall performance after steel.
Key words: Titanium alloy;Heat treatment;Microstructure;Mechanical properties
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1钛合金的概述 1
1.2钛合金的分类 2
1.3合金的热加工工艺 2
1.4轧制 2
1.5钛合金热处理工艺 3
1.6 选题目的及研究内容 4
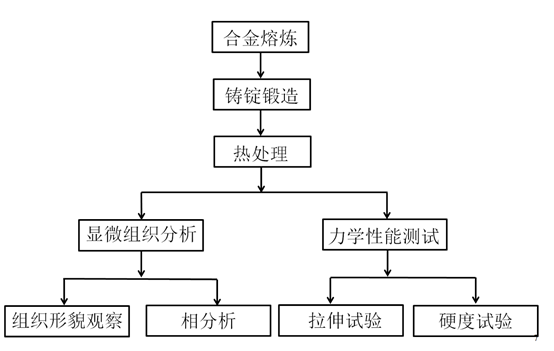
第二章 实验材料和方法 5
2.1 实验材料 5
2.2 实验方案 6
2.3 实验方法 7
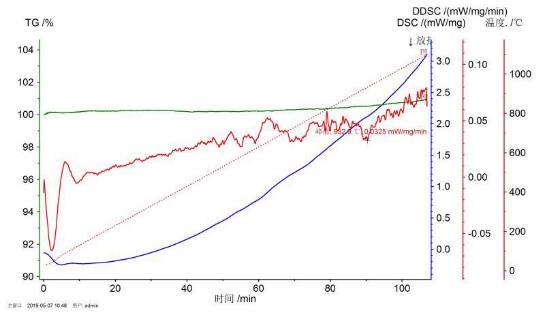
2.3.1 DSC分析 7
2.3.2金相组织观察 8
2.3.3 X射线衍射分析(XRD) 8
2.3.4拉伸实验 9
2.3.4显微硬度试验 9
第三章 热处理工艺对α β锻Ti-Al-Fe-B合金组织和力学性能的影响 11
3.1 不同热处理之后Ti-Al-Fe-B合金物相分析 11
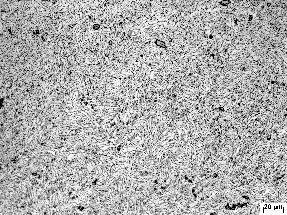
3.2 Ti-Al-Fe-B合金热处理前后微观组织形貌 12
3.3 不同热处理工艺对Ti-Al-Fe-B合金组织的影响 14
3.3 1普通退火对组织的影响 14
3.3.2双重退火对组织的影响 14
3.3.3 β退火对组织的影响 15
3.4 力学性能测试 15
3.4.1 合金室温拉伸性能测试 15
3.4.2 拉伸断口形貌分析 17
3.4.3 硬度测试 18
3.5 本章小结 18
第四章 结论和展望 20
4.1结论 20
4.2展望 20
参考文献 21
致谢 23
第一章 绪论
1.1钛合金的概述
钛和钛合金和其他金属相比具有许多优点,如比强度高,弹性模量低,无磁性,低导热性,良好的低温韧性,耐腐蚀性和对环境无污染性,使得它们能广泛使用在航空航天,化工以及汽车工业等领域。尤其将钛合金作为一种轻质结构材料应用于汽车时可以减轻车辆重量,降低油耗,提高工作效率,改善环境,降低噪音,延长车辆寿命并提高车辆安全性和舒适度[1],是实现轻型车辆的理想金属材料之一。
由于钛合金具有种种优势,因而对于钛合金的研究也在逐步深入,新型钛合金的研究工作也在不断展开。对于新型钛合金的研究与开发,主要目的是获得具有优良性能的合金,而钛合金的性能则是由合金的元素组成、制备方法以及后续的加工以及热处理综合决定的,其中最基本的影响因素就是合金中的元素。添加合适的合金化元素不仅能够提高钛合金的性能,同时也可以降低合金的成本,一举两得。其中最常用的合金化元素有Al、Fe、Mo、V,添加少量的稀土元素或者B元素可以通过细化合金晶粒大小来提高合金性能。
Al在钛合金中主要起固溶强化的作用,同时也可以显著提高再结晶温度[2]。Fe元素在合金中可以增强合金的淬透性,在高强高韧的钛合金中往往需要添加铁元素来改善合金的性能。B元素的添加可大幅细化合金晶粒,大幅提高了合金强度,并起到固溶强化的作用,增加合金的淬透性,此外,还可以提高含Fe的合金的热稳定性。Mo元素加在钛合金中可以提高合金强度并且可以细化合金组织[3]。V元素在钛合金中主要起保持合金塑性的作用,并且也可以提高合金的强度[4]。
相关图片展示:

课题毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、外文翻译、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。



